
Interpretation:
The structure of products of each of the given reactions is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electrophiles are electron deficient species that have positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles that accept electron pair.
Nucleophiles are electron rich species that have negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles that donate electron pair.
Free radical is an atom, molecule, or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a
Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
Aniline is a primary
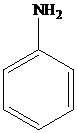
Aniline and substituted aniline reacts with nitrous acid at low temperature to form benzene diazonium salts.
The reduction of nitro group results in the formation of primary amine.
When an ethyl amine reacts with benzoyl chloride, it results in the formation of N-ethylbenzamide as the major product.
When methyl amine reacts with acetic anhydride, it results in the formation of N-methylethanamide as the major product.
Bromination reaction of para- Toluidine leads to the formation of 2,6-dibromo-4-methyl Toluidine.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Benzene can be hydroxylated by treating it with hydrogen peroxide and a strong acid such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TfOH). Propose amechanism for this reactionarrow_forwardPropose a structural formula for each lettered compound. OH CrO3 →A (CH18O2) EtO Na+ B (CH160) pyridine ELOH (racemic)arrow_forward17. A (A)-aq NaOH (B)- K₂Cr₂O, H [0] → Propanone. i) Identify the compounds (A) and (B). ii) Starting from compound (A), how would you obtain 2,3-dimethylbutane? Convert compound (B) into propene. ✓ Predict (iv) Predict the product, when compound (A) is heated with sodium methoxide. [2+1+1+1]arrow_forward
- Name and draw the products of each reaction. 1-propanol + hydrobromic acid → (a) (b) 1-pentanol H-SO A (c) N-propylmethanamide + water (d) 3-methyl oct-2-ene + hydrochloric acid -arrow_forwardThe reaction of N−bromosuccinimide with 4−methyl−3−nitroanisole has been reported in the chemical literature. This reaction yields a single product in 95% yield. Identify the product formed from this starting material.arrow_forwardOne frequently used method for preparing methyl esters is by reaction of carboxylic acids with diazomethane, CH2N2. The reaction occurs in two steps: (l) protonation of diazomethane by the carboxylic acid to yield methyldiazonium ion, CH3N2+, plus a carboxylate ion; and (2) reaction of the carboxylate ion with CH3N2+. (a) Draw two resonance structures of diazomethane, and account for step 1. (b) What kind of reaction occurs in step 2?arrow_forward
- 18-48 4-Aminobenzoic acid is prepared from benzoic acid by the following two steps. Show reagents and experimental conditions to bring about each step.arrow_forwardClaisen condensation between diethyl phthalate and ethyl acetate followed by saponification, acidification, and decarboxylation forms a diketone, C9H6O2. Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and the diketone.arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? (a) (b) 37 HO HO (c) HO NaOH EtOH ? (d) HOarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for the principal product formed when benzoyl chloride is treated with reagentarrow_forwardCH₂-CH₂-CH₂-C-OH butanoic acid CH₂ HO–C–CH,CHCH,—CHO 3-methylpentanoic acid Name each carboxylic acid. (a) HO CH₂ CH₂ 99 - 0 B) CHICHICIO CH, Draw a condensed structural diagram for each carboxylic acid (a) Hexanoic acid (b) 3-propyloctanoic acid Iarrow_forwardA dialkyl-substituted benzene, C14H22, is treated with basic potassium permanganate, followed by acid workup. The same dialkyl-substituted benzene was recovered afterward from the reaction mixture. Draw the structure of the compound.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning




