
(a)
To identify: Whether the object is moving in positive or negative direction for segment A to B.
(a)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is moving in the negative direction.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
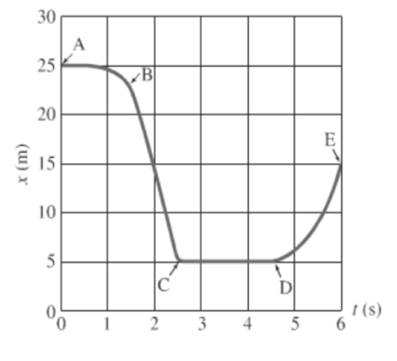
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
In the graph segment A-B, the object is moving in a negative direction as the slope of the line segment is decreasing over time.
Conclusion:
The object would be moving in the negative direction.
(b)
To identify: Whether the object is speeding up or slowing down in graph for segment A to B.
(b)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is speeding up.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
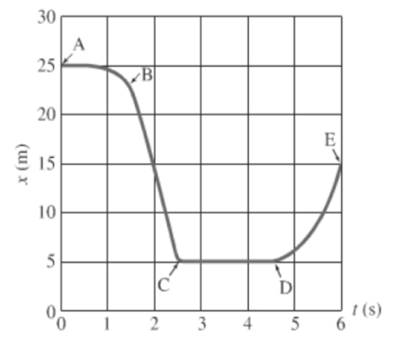
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
In the segment A to B, the object is moving from a less steep position to steeper one, this suggests that the object is speeding up.
Conclusion:
The object is speeding up.
(c)
To identify: Whether the acceleration of an object is positive or negative for segment A to B.
(c)
Answer to Problem 56P
The acceleration of the object is negative.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
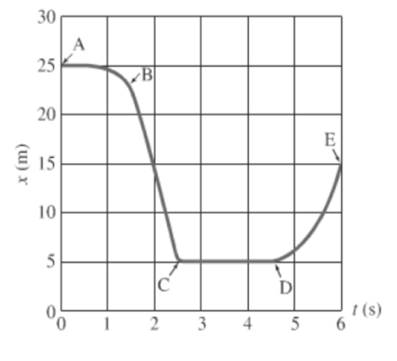
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
During the interval of A to B, the graph is going concave downward i.e. slope is going more negative. Thus, the acceleration is negative.
Conclusion:
The acceleration of the object is negative.
(d)
To identify: Whether the object is moving in positive or negative direction for segment D to E.
(d)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object would be moving in a positive direction.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
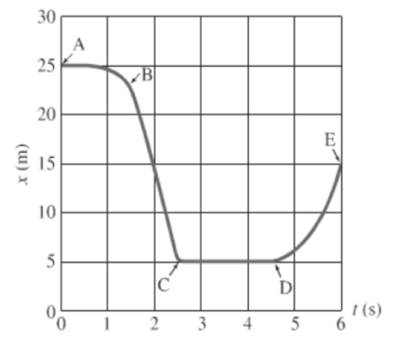
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
For the segment D to E, object’s distance increases with time then the objects moves faster.
In the graph segment D-E, the object is moving in a positive direction as the slope of the line segment is increasing.
Conclusion:
The object would be moving in a positive direction.
(e)
To identify: Whether the object is speeding up or slowing down for segment D to E.
(e)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is speeding up.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
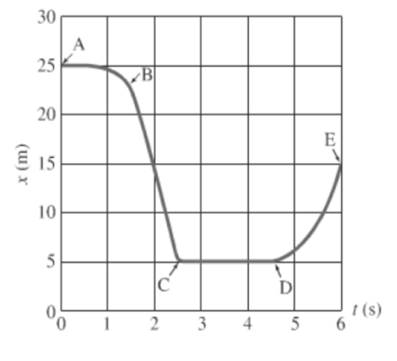
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
For the segment D to E, object’s distance increases with time then the objects moves faster.
The object is moving on the graph from a less steep position to steeper that is slope is increasing with time.This suggests that the object is speeding up.
Conclusion:
The object is speeding up.
(f)
To identify: Whether the acceleration of an object is positive or negative in the graph segment D to E.
(f)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object will accelerate.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
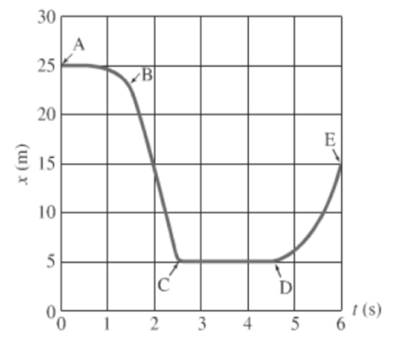
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.For the segment D to E, object’s distance increases with time then the objects moves faster.
During the interval D to E, the graph is going concave upward i.e. slope is going more positive. Thus, the acceleration is positive.
Conclusion:
The object will accelerate.
(g)
To identify: Whether the object moving in the positive or negative direction in the graph segment C to D.
(g)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is not moving in either direction. The object is at rest.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
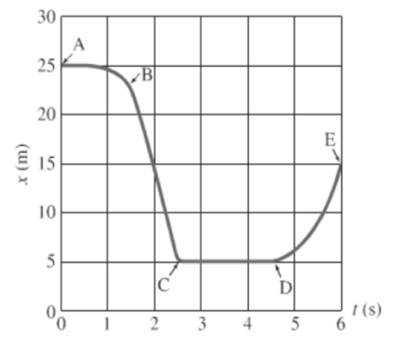
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
For the segment C to D, the object’s distance is constant with time then object remains stationary.
After reading the graph segment C-D, the object is not moving in either direction. Thus, the distance graph is linearly constant.
Conclusion:
The distance between duration of graph segment C-D is constant. Thus, the object will remain at rest.
(h)
To identify: Whether the object speeding up or slowing down in graph segment C to D.
(h)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is not moving in either direction. The object is at rest.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
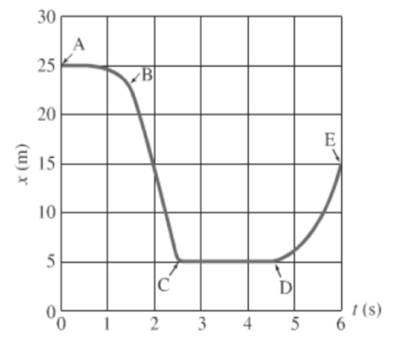
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.
For the segment C to D, the object’s distance is constant with time then object remains stationary.
After reading the graph segment C-D, the object is not moving in either direction. Thus, the velocity of the object is zero.
Conclusion:
The velocity of the object is zero that is the object is at rest.
(i)
To identify: Whether the acceleration of the object positive or negative in the graph segment C to D.
(i)
Answer to Problem 56P
The object is not moving in either direction. So, the acceleration is zero.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider the given graph as shown below.
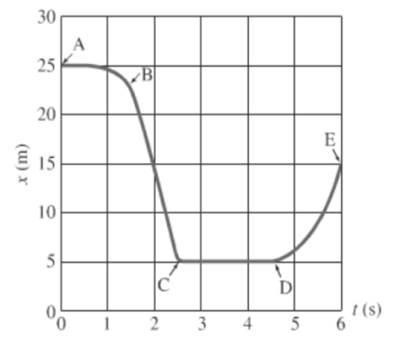
For the segment A to B, object is moving constantly and then distance decreases rapidly with time.For the segment C to D, the object’s distance is constant with time then object remains stationary.
After reading the graph segment C-D, the object is not moving in either direction. Thus, the acceleration is zero.
Conclusion:
The object is not moving in either direction. So, the acceleration is zero.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Physics: Principles with Applications
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Conceptual Integrated Science
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Introduction to Electrodynamics
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





