
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,
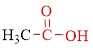
Nomenclature of
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the
alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups.
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,

Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid. If two or more carboxylic functional groups are present in the same compound then its number should be taken in to consideration and the prefix di, tri, tetra.. must be used.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
E-Z designators are used as like cis-trans terminology for non-similar groups attached
In E-Z designations, the groups attached to vinylic positions are checked by their priority on the basis of higher molecular weight. If the higher priority groups are on the same sides, then the configuration is designated as Z. If the higher priority groups are on the opposite sides, then the configuration is designated as E.
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the compound has to be given and its configuration should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl attached to a hydroxyl group as shown below,

Nomenclature of carboxylic acid:
- Find the Parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Carboxyl carbon must be numbered first.
- Replace the –e in the alkane name with –oic acid.
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- A stockroom assistant prepares three bottles, each containing one of the following compounds: However, the bottles are left unlabeled. Instead of discarding the samples, another assistant runs tests on the contents, using Tollens and Benedicts reagents. Match the compound to the bottle, based on these results. Tollens Reagent Benedicts Reagent Bottle A A dark precipitate forms A red-orange precipitate forms Bottle B No reaction No reaction Bottle C A dark precipitate and slight mirror form No reactionarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name for the attached picture? a) 5-carboxydecane b) 5-pentylhexanoic acid c) 2-pentylhexanoix acid d) 2-butylheptanoic acid. Pls explain your answerarrow_forwardShow how to convert (R)-2-phenylpropanoic acid to compoundarrow_forward
- Write the equations to show how isobutyric acid could be converted to each of the following using needed reagentsa. magnesium isobutyrateb. isobutyryl chloridec. isobutyl alcohold. ethyl isobutyratee. isobutyramidearrow_forwardShow how to convert trans-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid (cinnamic acid) to these compoundsarrow_forwardIndicate which compound in each of the following pairs has the higher value of the specified property, or if the two compounds in a pair have nearly the same value for the property. Supply the compound name or same. A: I. methyl propanoate or II. pentanal: boiling pointB: I. methyl butanoate or II. hexanal: solubility in waterC: I. methyl propanoate or II. 1-pentanol: boiling pointD: I. methyl pentanoate or II. hexanoic acid: solubility in waterE: I. butanoic acid or II. methyl propanoate: boiling pointarrow_forward
- Write TRUE if the statement is correct. Otherwise, change the underlined word/phrase to make it correct. Do not use abbreviations. 1. Tertiary alcohols reacts quickly than primary alcohols in terms of dehydration to form alkenes. 2. Zaitsev rule is applied when an alcohol has two or three beta (b) carbons. 3. Anhydrides can be used to make acid chlorides.arrow_forwardShow how to prepare pentanoic acid from each component. (a) 1-Pentanol (b) Pentanal (c) 1-Pentene (d) 1-Butanol (e) 1-Bromopropane (f) 1-Hexenearrow_forwardDescribe a laboratory procedure that would allow you to form 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone from 2-pentyne. Show a synthesis pathway in your description, including the full structural diagrams for all reactants, products, and intermediatesarrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is INCORRECT concerning the two acids below? Options: Acetic acid has higher water solubility than benzoic acid. Acetic acid has a higher melting point than benzoic acid. Benzoic acid has a larger conjugated system. Benzoic acid is the stronger acid. Acetic acid has an electron donating group in it's structure.arrow_forwardDraw the organic products formed when attached allylic alcohol A is treated with following reagent. HCrO4−–Amberlyst A-26 resinarrow_forward1. Construct a chain of 7 carbon atoms that contains an alcohol and an alkyl as a functional group. Name by IUPAC Nomenclature 2. Construct a 9-point cycle that has a carboxylic acid and an ene as functional group. Name by IUPAC Nomenclature 3. construct a carbon chain containing one esters. Name by IUPAC Nomenclature 4. build a chain of 12 carbon atoms that contains as functional group an aldehyde, an aromatic and a cycle. Name by IUPAC Nomenclaturearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
