
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of a compound with the given formula upon oxidation by potassium dichromate in aqueous sulphuric acid gives
Concept-Introduction:
Oxidation:
Loss of electrons from an atom ion or molecule during a
Example:

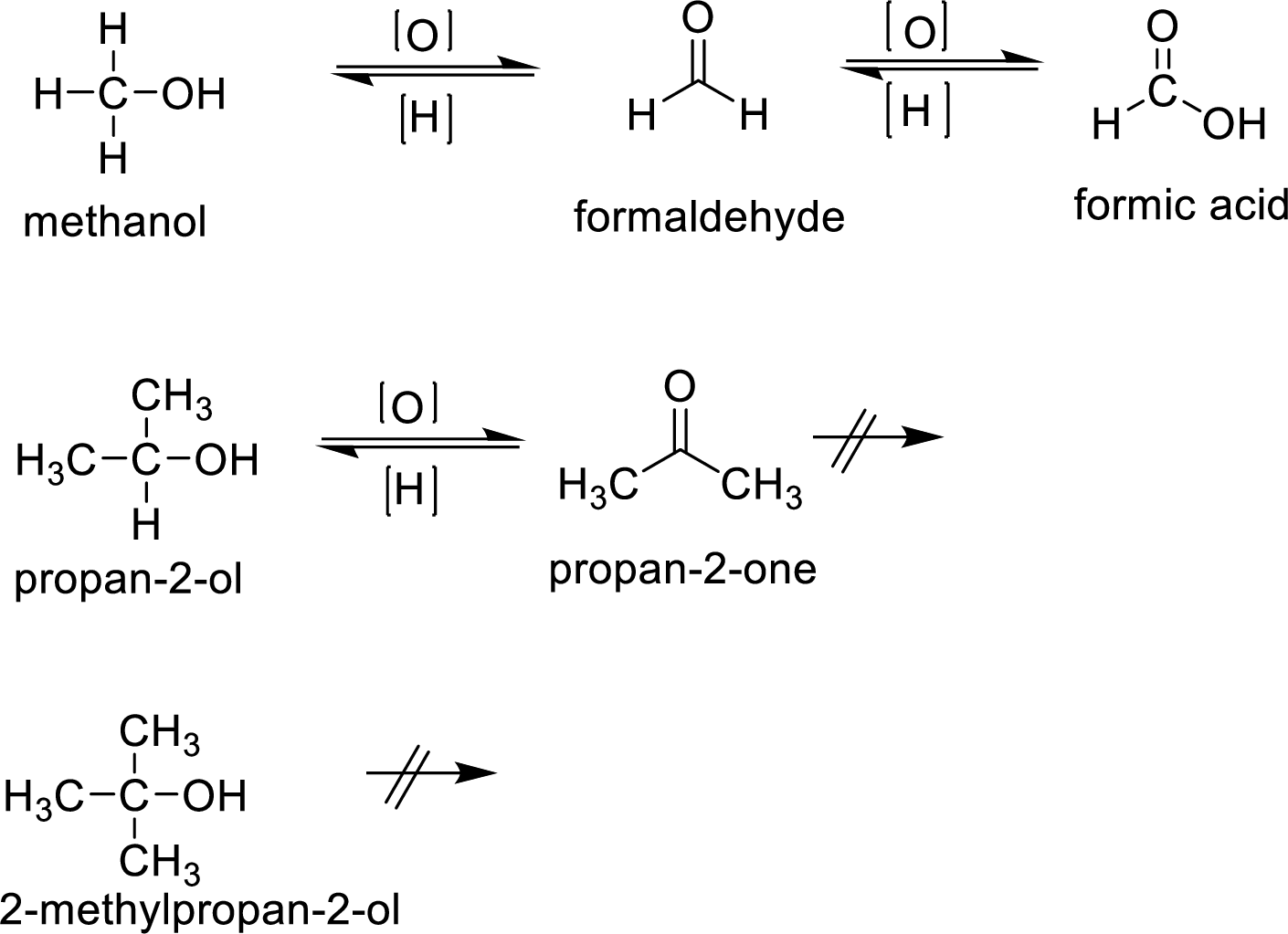
Here
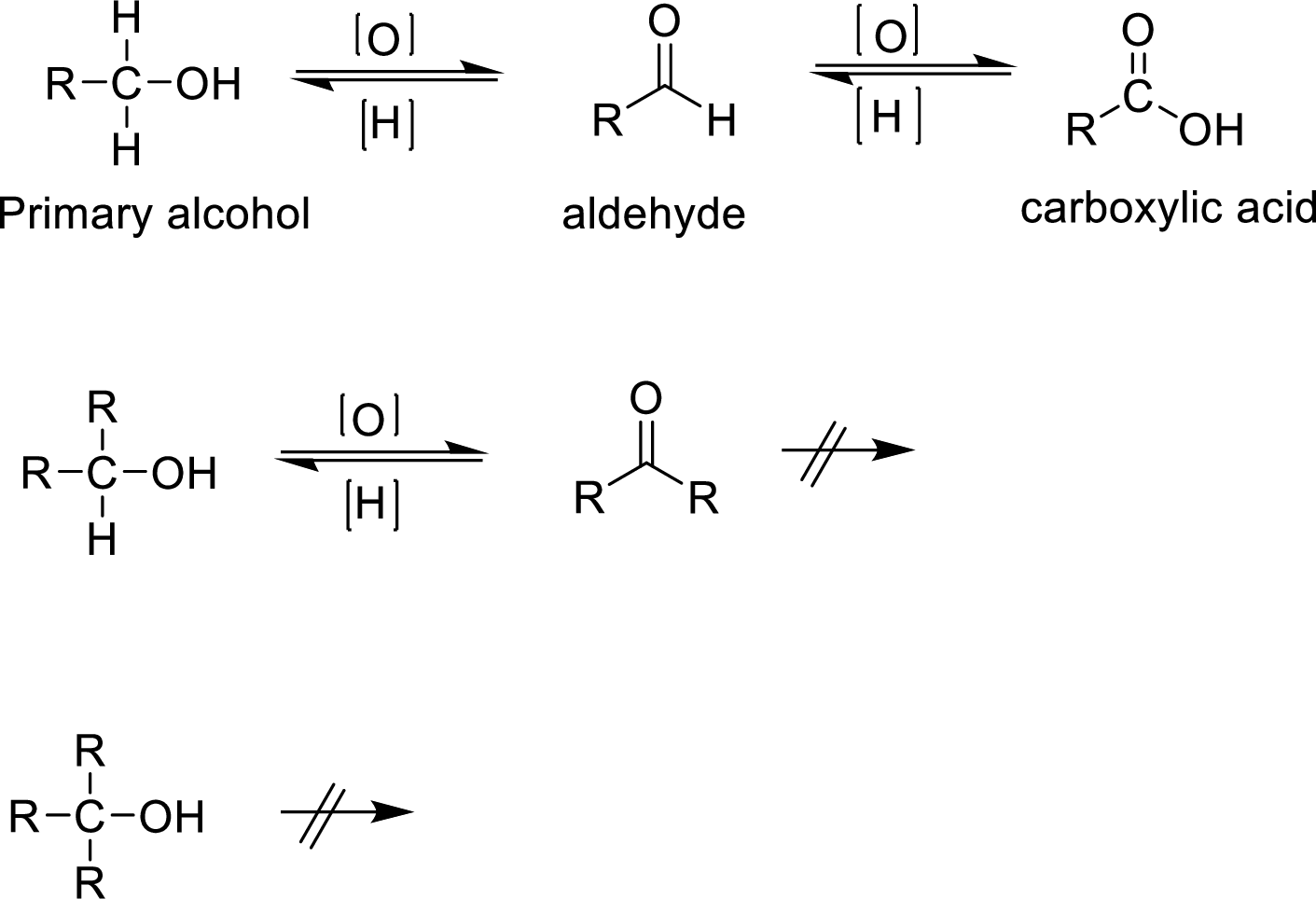
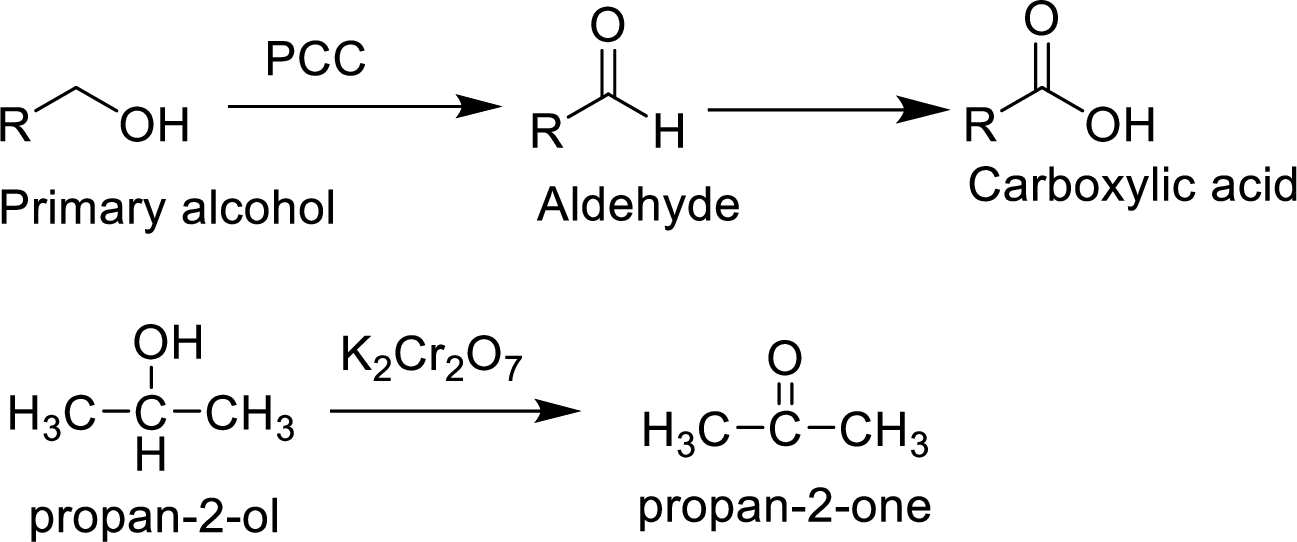
Oxidation of alcohols:
Oxidation of alcohol gives
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of a compound with the given formula upon oxidation by potassium dichromate in aqueous sulphuric acid gives carboxylic acid has to be drawn.
Concept-Introduction:
Oxidation:
Loss of electrons or loss of hydrogen from an atom ion or molecule during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation. Oxidation state of atom ion or molecule will increase in this process. In simple it is the gain of oxygen.
Example:
Here
Oxidation of alcohols:
Oxidation of alcohol gives aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid Primary alcohols on oxidation yield carboxylic acid. Secondary alcohol on oxidation gives ketone. If mild oxidizing agents are used the the reaction will end with an aldehydic product. In the formation of carboxylic acid the alcohol is first oxidized to aldehyde which is then oxidized to form carboxylic acid. Oxidation is not possible in tertiary alcohol because there is no reactive
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of a compound with the given formula upon oxidation by potassium dichromate in aqueous sulphuric acid gives carboxylic acid has to be drawn.
Concept-Introduction:
Oxidation:
Loss of electrons from an atom ion or molecule during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation. Oxidation state of atom ion or molecule will increase in this process. Oxidizing agent is getting reduced in oxidation. In simple it is the addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen.
Example:
Here
Oxidation of alcohols:
Oxidation of alcohol gives aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid Primary alcohols on oxidation yield carboxylic acid. Secondary alcohol on oxidation gives ketone. In the formation of carboxylic acid the alcohol is first oxidized to aldehyde which is then oxidized to form carboxylic acid. Oxidation is not possible in tertiary alcohol because there is no reactive
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- why n-hexanol has higher boiling point than n-hexane. why acetic acid is more acidic then butanoic acid. why sugar is soluble in water in terms of their molecular interactions.arrow_forwardProvide the IUPAC name and common name of the following carboxylic acids:arrow_forwardDoes methanol behave as an acid or a base when it reacts with methylamine?arrow_forward
- 1) To identify which contains more acid vinegar or lemon juice neutralization with sodium hydroxide can be used. Explain how. 2) The long filaments making up the thread of woven synthetic fabrics are likely polyesters. Describe the special characteristic that the alcohol and carboxylic acid must have so that they can react with each other to produce such long filaments.arrow_forwardconsider the following carboxylic acid and derivatives:arrow_forwardComplete the table provided below for nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid and Derivativesarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





