
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
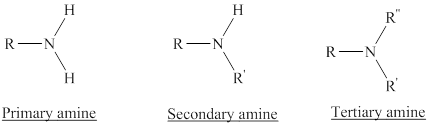
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
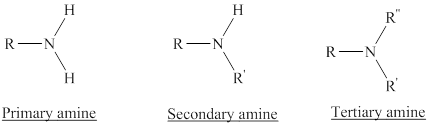
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
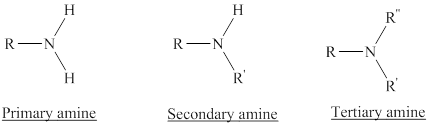
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
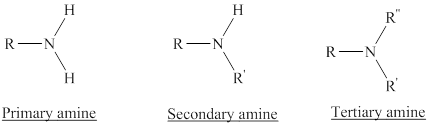
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Write the formulas of the four singly chlorinated isomers formed when 2-methylbutane reacts with Cl2 in the presence of light.arrow_forwardEthylene glycol, the main ingredient in antifreeze, contains 38.7% carbon, 9.7% hydrogen and 51.6 % oxygen. Calculate the empirical and molecular formulas for ethylene glycol. Given the molar mass is approximately 60 g/mol. A) Empirical formula: B)Molecular formula: Explain how you obtained the Molecular formula (b)?arrow_forwardWhat prefixes are used in naming the following?(a) A 1,3-disubstituted benzene(b) A 1,4-disubstituted benzenearrow_forward
- Propose a scheme to separate and isolate a mixture containing 4-aminobenzoate, 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene, and napthalene. Isolate two of the three solids by extraction. (please explain what solvents to use and the process step by step)arrow_forwardDraw the structures of the following compounds. (Includes both new and old names.) 3-cyclopentylhexan-3-olarrow_forwardConsider the following acids and their ionization constant, determine which conjugate base is HCOOH Ka = 1.7 x 10-4 (b) HCN Ka = 4.9 x 10-10arrow_forward
- what is the crystallinity of phenazopyridine? with illustationarrow_forwardCompound A undergoes a reaction with hydrogen bromide, HBr to produce2-bromobutane. A exists as cis-trans isomers and decolourises brominesolution in methylene chloride, CH2Cl2. a)Draw and name the structure of compound D. b)Draw two (2) constitutional isomers of compound Darrow_forwardDetermine the weight/volume of the chemicals needed to prepare the following solutions: a) 100 ml of 0.9% (w/v) saline (NaCl) b) 30 ml of 50% glycerol (v/v) c) Electrophoresis requires TAE, which is a specific mixture of Tris base, acetic acid, and EDTA. TAE is normally made as a 50X concentrated stock. Provide a recipe to make 40 ml of 50X TAE. The recipe for one liter of 50X TAE is as follows: 242g Tris base, 57.1 ml glacial acetic acid, 100 ml 0.5 M EDTAarrow_forward
- Draw the skeletal structure of the alkene that is needed as a starting material to prepare each of the following alcohols. Part 1 of 2 CH3CH(OH)CH3 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☑ :arrow_forwardIsobutylene, CH2=C(CH3)2, is used to prepare cold-flow rubber. Draw a structure for the addition polymer formed from this alkene.arrow_forwardScott test is one of the methods used for screening for Cocaine in Forensic Chemistry. The multi step method consists of a) reacting the sample drug with cobaltous thiocyanate (Co(SCN)2) b) dissolving of the formed precipitate by adding HCl and c) extraction of coordination compound with Chloroform d) measurement of absorbance of extracted coordination compound at 627 nm What is the type of chemical equilibria involved in first step of the method? a.Solubility Product equilibria b.Bronsted Lowry acid – Bronsted Lowry base equilibria c.Complex ion formation d.Coordination compound formationarrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





