
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781259883989
Author: by Janice Smith
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 13, Problem 72P
Interpretation Introduction
(a)
Interpretation:
The name of the aromatic compound given below needs to be deduced:
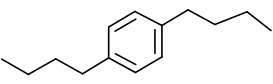
Concept Introduction:
Aromatic compounds are predominantly characterized by the presence of a benzene (C6H6)ring- The parent ring can be identified based on the principal
functional groups attached to the carbon atoms in the ring. These groups could be methyl (-CH3 which gives toluene), amino (-NH2 which forms aniline), hydroxyl (-OH which forms phenol) and so on. - If two or more substituents are present in the ring, the substituents are named in alphabetical order and the ring is numbered such that the first substituent gets the lowest number order.
Interpretation Introduction
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of the aromatic compound given below needs to be deduced:
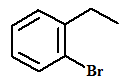
Concept Introduction:
- Aromatic compounds are predominantly characterized by the presence of a benzene (C6H6)ring
- The parent ring can be identified based on the principal functional groups attached to the carbon atoms in the ring. These groups could be methyl (-CH3 which gives toluene), amino (-NH2 which forms aniline), hydroxyl (-OH which forms phenol) and so on.
- If two or more substituents are present in the ring, the substituents are named in alphabetical order and the ring is numbered such that the first substituent gets the lowest number order.
Interpretation Introduction
(c)
Interpretation:
The name of the aromatic compound given below needs to be deduced:
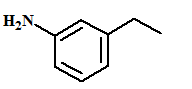
Concept Introduction:
- Aromatic compounds are predominantly characterized by the presence of a benzene (C6H6)ring
- The parent ring can be identified based on the principal functional groups attached to the carbon atoms in the ring. These groups could be methyl (-CH3 which gives toluene), amino (-NH2 which forms aniline), hydroxyl (-OH which forms phenol) and so on.
- If two or more substituents are present in the ring, the substituents are named in alphabetical order and the ring is numbered such that the first substituent gets the lowest number order.
Interpretation Introduction
(d)
Interpretation:
The name of the aromatic compound given below needs to be deduced
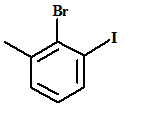
Concept Introduction:
- Aromatic compounds are predominantly characterized by the presence of a benzene (C6H6)ring
- The parent ring can be identified based on the principal functional groups attached to the carbon atoms in the ring. These groups could be methyl (-CH3 which gives toluene), amino (-NH2 which forms aniline), hydroxyl (-OH which forms phenol) and so on.
- If two or more substituents are present in the ring, the substituents are named in alphabetical order and the ring is numbered such that the first substituent gets the lowest number order.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Laser. Indicate the relationship between metastable state and stimulated emission.
The table includes macrostates characterized by 4 energy levels (&) that are
equally spaced but with different degrees of occupation.
a) Calculate the energy of all the macrostates (in joules). See if they all have
the same energy and number of particles.
b) Calculate the macrostate that is most likely to exist. For this macrostate,
show that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann
distribution.
macrostate 1 macrostate 2 macrostate 3
ε/k (K) Populations
Populations
Populations
300
5
3
4
200
7
9
8
100
15
17
16
0
33
31
32
DATO: k = 1,38×10-23 J K-1
Don't used Ai solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Ch. 13.1 - Convert each condensed structure to a complete...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.1PCh. 13.1 - Complete the structure of zingiberene, a component...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.2PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3PPCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.4PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.5PPCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.4PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.6PP
Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.5PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.6PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.7PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.8PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.7PPCh. 13.6 - Prob. 13.9PCh. 13.6 - What products is formed in each of the following...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 13.9PPCh. 13.6 - What product is formed when l-pentene (CH3CH2CH2CH...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 13.11PCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13.10PPCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13.12PCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13.13PCh. 13.10 - Prob. 13.11PPCh. 13.10 - Prob. 13.14PCh. 13.11 - Prob. 13.15PCh. 13.12 - Prob. 13.16PCh. 13.13 - Prob. 13.17PCh. 13.13 - Prob. 13.18PCh. 13 - Anethole, the major constituent of anise oil, is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 20PCh. 13 - What is the molecular formula for a hydrocarbon...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22PCh. 13 - Prob. 23PCh. 13 - Prob. 24PCh. 13 - Prob. 25PCh. 13 - Prob. 26PCh. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each molecule depicted in...Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each molecule depicted in...Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a....Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. d....Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each alkene.Ch. 13 - Give the I UP AC name for each alkene.Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each cyclic compound.Ch. 13 - Give the IUPAC name for each cyclic compound.Ch. 13 - Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC...Ch. 13 - Prob. 36PCh. 13 - Each of the following IUPAC names is incorrect....Ch. 13 - Each of the following IUPAC names is incorrect....Ch. 13 - Prob. 39PCh. 13 - Prob. 40PCh. 13 - Prob. 41PCh. 13 - Prob. 42PCh. 13 - Prob. 43PCh. 13 - Label the carbon-carbon double bond as cis or...Ch. 13 - Prob. 45PCh. 13 - Prob. 46PCh. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - Prob. 48PCh. 13 - Prob. 49PCh. 13 - Prob. 50PCh. 13 - Prob. 51PCh. 13 - Prob. 52PCh. 13 - Prob. 53PCh. 13 - Prob. 54PCh. 13 - What alkyd halide is formed when each alkene is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 56PCh. 13 - Prob. 57PCh. 13 - Prob. 58PCh. 13 - What alkene is needed as a starting material to...Ch. 13 - Prob. 60PCh. 13 - Prob. 61PCh. 13 - Prob. 62PCh. 13 - Prob. 63PCh. 13 - Prob. 64PCh. 13 - Prob. 65PCh. 13 - Prob. 66PCh. 13 - Prob. 67PCh. 13 - Prob. 68PCh. 13 - Prob. 69PCh. 13 - Prob. 70PCh. 13 - Prob. 71PCh. 13 - Prob. 72PCh. 13 - Prob. 73PCh. 13 - Are o-bromochlorobenzene and m-bromochlorobenzene...Ch. 13 - Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC...Ch. 13 - Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC...Ch. 13 - Prob. 77PCh. 13 - Prob. 78PCh. 13 - Prob. 79PCh. 13 - Prob. 80PCh. 13 - Prob. 81PCh. 13 - Prob. 82PCh. 13 - Prob. 83PCh. 13 - Prob. 84PCh. 13 - Prob. 85PCh. 13 - Eleostearic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid...Ch. 13 - Prob. 87PCh. 13 - Prob. 88PCh. 13 - Prob. 89PCh. 13 - Prob. 90PCh. 13 - Prob. 91PCh. 13 - Prob. 92PCh. 13 - Prob. 93PCh. 13 - Prob. 94PCh. 13 - Answer the following questions about compound A,...Ch. 13 - Prob. 96PCh. 13 - Answer the following questions about alkene C,...Ch. 13 - Prob. 98PCh. 13 - Prob. 99PCh. 13 - Prob. 100PCh. 13 - Prob. 101CPCh. 13 - Prob. 102CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In an experiment, the viscosity of water was measured at different temperatures and the table was constructed from the data obtained. a) Calculate the activation energy of viscous flow (kJ/mol). b) Calculate the viscosity at 30°C. T/°C 0 20 40 60 80 η/cpoise 1,972 1,005 0,656 0,469 0,356arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forward
- A laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardThe number of microstates corresponding to each macrostate is given by N. The dominant macrostate or configuration of a system is the macrostate with the greatest weight W. Are both statements correct?arrow_forward
- For the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forwardHow many grams of C are combined with 3.75 ✕ 1023 atoms of H in the compound C5H12?arrow_forwarde. f. CH3O. יון Br NaOCH3 OCH 3 Br H₂Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
07 Physical Properties of Organic Compounds; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UjlSgwq4w6U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY