
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305687875
Author: Gilbert
Publisher: CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 10.3, Problem 29E
Interpretation Introduction
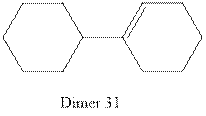
Interpretation:To show the mechanism of formation of dimer 31 from cyclohexene in presence of H3O+ .
Concept introduction: The molecule which is formed when two monomers joined with each other by either strong or weak bond is called dimer.
The structure of dimer 31 is as follows:
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
What is the molarity of a 0.393 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 g/mol
The rate constant for the decay of a radioactive element is 2.28 × 10⁻³ day⁻¹. What is the half-life of this element in days?
Handwritten please
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 10E
Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 13ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 13ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 18ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 20ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 21ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 25ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 26ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 28ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 30ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 32ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 18ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 20ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 23ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 13ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 18ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 20ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 21ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 22ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 23ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 24ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 25ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 26ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 28ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 30ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.7 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 13ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.8 - Prob. 15E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Choose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. What is the half-life for this reaction?arrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. 1. PhNa A 2. H3O+ 1. PhCH2MgBr B 2. H3O+ хё 1. PhMgBr C 2. H3O+ 00 HO Q E D 1. H3O+ 2. PhMgBr PhMgBrarrow_forward
- Please answer all of the questions and provide detailed explanations and include a drawing to show the different signals on the molecule and include which ones should be highlighted.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ Q OH ☑ Select to Drawarrow_forwardHow should I graph my data for the Absorbance of Pb and Fe for each mushroom? I want to compare the results to the known standard curve. Software: Excel Spreadsheets Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/Eb2PfHdfEtBJiWh0ipHZ_kkBW4idWWwvpLPPtqoq2WkgbQ?rtime=HxrF0_tR3Ugarrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly, but do not use italics in Canvas.arrow_forwardThe kinetics of a gas phase reaction of the form A → Products results in a rate constant of 0.00781 M/min. For this reaction, the initial concentration of A is 0.501 M. How many minutes will it take for the concentration of A to reach 0.144 Marrow_forwardWhat is the rate for the second order reaction A → Products when [A] = 0.256 M? (k = 0.761 M⁻¹s⁻¹)arrow_forward
- For reaction N2(g) + O2(g) --> 2NO(g) Write the rate of the reaction in terms of change of NO.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardThe reaction of 2-oxacyclopentanone with hydrochloric acid in water (i.e., "excess") produces which of the following carboxylic acids?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry || Polymers || Full Chapter || By Shiksha House; Author: Best for NEET;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxdJlS0xZ0Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY