
Concept explainers
QUANTITATIVE The Calcium Pump of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. Muscle cells use calcium ions to regulate the contractile process. Calcium is both released and taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). Release of calcium from the SR activates muscle contraction, and ATP-driven calcium uptake causes the muscle cell to relax afterward. When muscle tissue is disrupted by homogenization, the SR forms small vesicles called microsomes that maintain their ability to take up calcium. To obtain the data shown in Figure 8-17, a reaction medium was prepared to contain 5 mM ATP and 0.1 M KCl at pH 7.5. An aliquot of SR microsomes containing 1.0 mg protein was added to 1 mL of the reaction mixture, followed by 0.4 mmol of calcium. Two minutes later, a calcium ionophore was added. (An ionophore is a substance that facilitates the movement of an ion across a membrane.) ATPase activity was monitored during the additions, with the results shown in the figure.
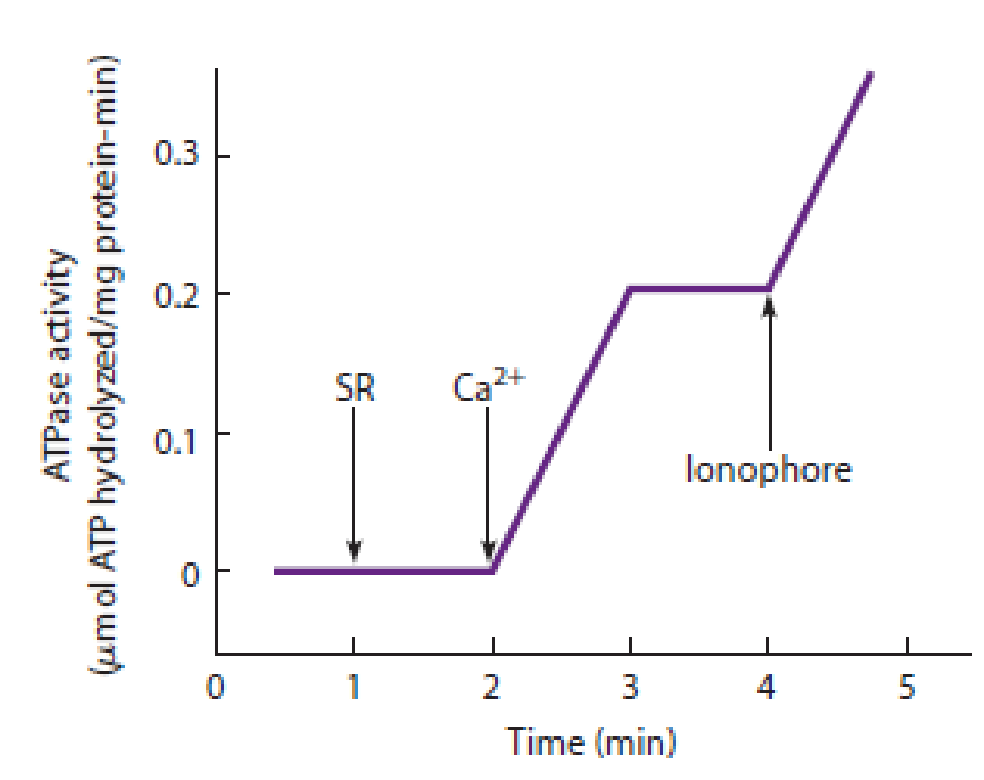
Figure 8-17 Calcium Uptake by the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. See Problem 8-10.
- (a) What is the ATPase activity, calculated as micromoles of ATP hydrolyzed per milligram of protein per minute?
- (b) The ATPase is calcium-activated, as shown by the increase in ATP hydrolysis when the calcium was added and the decrease in hydrolysis when all the added calcium was taken up into the vesicles 1 minute after it was added. How many calcium ions are taken up for each ATP hydrolyzed?
- (c) The final addition is an ionophore that carries calcium ions across membranes. Why does ATP hydrolysis begin again?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- The subunits of which filament bind to GTP, a condition that favors the polymerization of the cytoskeletal subunits? O Intermediate filaments Microfilaments O Microtubulesarrow_forwardIntermediate filaments have identical ends and lack polarity, whereas microtubules have two distinct ends with defined polarity. What is the molecular cause of these differences? Please keep brief - 2 sentences/dot points max.arrow_forwardActin filaments, microtubules, and bacterial flagella are all built from small subunits. Describe three advantages of assembling long filamentous structures from subunits rather than from single, long proteins.arrow_forward
- Inside of skeletal muscle cells are voltage-controlled calcium ion (Ca2+) gate proteins. These are integral for the contraction mechanisms of skeletal muscle. A picture of them is shown below. These are regulated by voltage, as indicated above. How would voltage serve to open or close these gates? Voltage is a component of hydrogen bonds, which is necessary to maintain the secondary structure of the protein; without voltage, the protein starts to chemically degrade. Voltage actually does not serve as the direct mechanism of opening or closing gated proteins. Changing the voltage changes whether the R groups are charged or not, which alters the actual primary structure of the protein Changing voltage changes the nature of the tertiary structure, causing the protein to change its shape to open or close.arrow_forwardWhat is a property that is shared by microtubules and actin filaments? Polymer assembly requires that subunits contain a bound ATP Polymer assembly requires that subunits contain a bound GTP The polymer is assembled from subunits that are protein monomers Assembly and disassembly occurs only at one end of the polymer Subunit assembly is followed by nucleotide hydrolysisarrow_forwardNeurofilament proteins assemble into long, intermediate filaments , found in abundance running along the length of nerve cell axons. The C-terminal region of these proteins is an unstructured polypeptide, hundreds of amino acids long and heavily modified by the addition of phosphate groups. The term “polymer brush” has been applied to this part of the neurofilament. can you suggest why?arrow_forward
- Dynamic instability causes microtubules to either grow or shrink. Consider a microtubule that is in its shrinking phase. What must happen at the end of the microtubule in order for it to stop shrinking and to start growing again?arrow_forward+ 1. What are the components of the cytoskeleton in an animal cell? Fill in the table below to explain: Type of Cytoskeletal Structure Subunits and Shape Size (smallest, intermediate, largest) Function(s) Associated Motor Proteins Microtubules Intermediate Filaments n/a Microfilaments 0arrow_forwardSome muscle cells contain several nuclei per cell. Which of the following provides the most likely explanation for the way in which these cells came to have more than one nucleus? A B с D They underwent repeated mitosis simultaneously with cytokinesis. They underwent repeated mitosis but not cytokinesis. They underwent multiple S phases before entering mitosis. They underwent repeated cytokinesis but not mitosis.arrow_forward
- Muscle cells require a lot of energy to operate normally. Thus, muscle cells likely contain a high number of: [Select the best answer. ] mitochondria lysosomes vacuoles nuclei transport vesicles smooth endoplasmic reticulum rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi complexes ribosomesarrow_forwardMatch each of the following to its role in the cell. Microtubules Actin Tubulin Intermediate filaments Kinesin Dynein Myosin Centrosome A. Cytoskeletal fiber that is intermediate in diameter and very sturdy. Does not form from polymerization of protein monomers like the other ones we discussed in class, but consists of polypeptide strands. Keratin and Lamin A are examples. B. The structure that initiates polymerization of new microtubules and anchors microtubules in the center of the cell near the Golgi Complex. C. Motor protein whose activity results in contraction of muscle. D. Thinnest cytoskeletal filament. Responsible for initiation of amoeboid cell movement via pseudopod formation. E. The "monomer" unit of the thickest cytoskeletal polymer; a dimer of two polypeptide subunits. F. Cytoskeletal structure with the…arrow_forwardDetermine whether the following statements apply to microtubules, intermediate filaments, or actin filaments."a. Thinnest cytoskeletal filaments; are associated with the motor protein myosinb. Consist of proteins twisted together into a ropelike formc. Allow certain cells to “crawl” and change the shape and size of the celld. Consist of protein subunits surrounding a hollow coree. Help a cell to resist mechanical stressf. Grow from the cell’s centrosome"arrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

