
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134641621
Author: Dean R. Appling, Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill, Christopher K. Mathews
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 15P
The same enzyme as in Problem 14 is studied in the presence of a different inhibitor (inhibitor B). In this case, two different concentrations of inhibitor are used. Data are as follows:
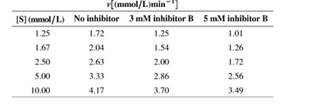
a. What kind of inhibitor is inhibitor B?
b. Determine the apparent Vmax and KM at each inhibitor concentration.
c. Estimate KI from these data.
14. The steady-state kinetics of an enzyme are studied the absence and presence of an inhibitor (Inhibitor A). The initial rate is given as a function of substrate concentration in the following table:
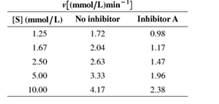
a. What kind of inhibition (competitive, uncompetitive. or mixed) is involved?
b. Determine Vmax and KM the absence and presence of inhibitor.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Note the Michaelis Menton kinetics results of inhibition
by inhibitor A and by B, separately.
Normal enzyme
Inhibitor A
Convert these to lineweaver burke in graphs below.
-5+
-4
Inhibitor B
-3+
-2
Effect of Inhibitor A.
Draw uninhibited first and then draw the result-
ing inhibition for comparison.
What kind of an inhibitor is A? How can you
tell?
Effect of Inhibitor B.
Draw uninhibited first and then draw the result-
ing inhibition for comparison.
What kind of an inhibitor is B? How can you
tell?
The Lineweaver - Burk plot (Figure 1) shows an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the absence and
presence of 0.1µM inhibitor (ketoconazole).
O Estimate Vmax and Km in the absence and presence of the inhibito..
(ii) Determine the type of inhibition shown by the inhibitor. Explain.
0.1-
0.08
0.06 -
With inhibitor
0.04
0.02
Without inhibitor
0.4 -0.2
-0.02
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1/{S\(&M-1)
1/vo (pmol-11 min)
In an enzyme kinetics study, three inhibitors resulted to the following results:
Inhibitor ABC
Inhibitor XYz Inhibitor PQR Without Inhibitor
V
40.2 mM/sec
40.3 mM/sec 12.32 mM/sec
65.43 mM/sec
max
K
24.3 mM
28.5 mM
24.3 mM
15.7 mM
b. What type of inhibitor is inhibitor PQR? Why do you say so?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1PCh. 8 - The enzyme urease catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea...Ch. 8 - An enzyme contains an active site aspartic acid...Ch. 8 - The folding and unfolding rate constants for a...Ch. 8 - In some reactions, in which a protein molecule is...Ch. 8 - Would you expect an “enzyme” designed to bind to...Ch. 8 - The initial rate for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction...Ch. 8 - a. If the total enzyme concentration in Problem 7...Ch. 8 - Prob. 9PCh. 8 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 8 - The following data describe the catalysis of...Ch. 8 - At 37 oC, the serine protease subtilisin has kcat...Ch. 8 - The accompanying figure shows three...Ch. 8 - The steady-state kinetics of an enzyme are studied...Ch. 8 - The same enzyme as in Problem 14 is studied in the...Ch. 8 - Enalapril is an anti-hypertension “pro-drug"...Ch. 8 - Initial rate data for an enzyme that obeys...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PCh. 8 - Suggest the effects of each of the following...Ch. 8 - The inhibitory effect of an uncompetitive...Ch. 8 - Prob. 21PCh. 8 - Prob. 22PCh. 8 - Prob. 23PCh. 8 - In kinetics experiments, the hydrolysis of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The change in the amount of product B in a reaction which is catalyzed by Enzyme A is given in the table below. Determine the Vmax and Km of the enzyme in the absence and presence of C. Is C an inhibitor or an activator of enzyme A? Determine the type of inhibition or activation. Rate of formation of Product B in the presence of 25 mg/mL C (mM/min) Substrate Rate of formation of (mM) Product B (mM/min) 0.5 21.5 14.1 1 30.2 22.2 1.5 34.9 27.0 2.5 39.8 33.1 3.5 42.0 36.3arrow_forwarda. Calculate both Vmax and KM for the control using Lineweaver-Burk curve. b. Provide the type of inhibition for both? Find, KI, for the inhibitor binding to the enzyme, for experiments (2) and (3). d. Calculate the reaction Kcat for the Control in experiment (1). e. Draw a velocity versus [S] showing Michaelis-Menten curve for the Control. Clearly show Vmax and Ky for the enzyme. c. (1) V. [(umol/(ml.s)] 7.6 (2) V- Τ (μmol/ (ml.s)] [S] (mM) (3) V. [(umol/(ml.s)] 6.6 2 4 14.6 26.6 45.8 4.4 8.6 16.4 29.8 11.4 17.8 24.6 28.2 16 24 60 40.8arrow_forwardMatch the different names for inhibition mechanisms (1-5) with a description of their properties 7a-7d: 1. competitive inhibitor. 2. allosteric inhibitor also known as non-competitive inhibitor. 3. un-competitive inhibitor. 4. affinity label also known as active site directed covalent (irreversible) enzyme inhibitor. 5. Kcat inhibitor, also known as a mechanism-based covalent (irreversible) enzyme inhibitor. 4a. An enzyme inhibitor in which a substrate or competitive inhibitor is modified so that it contains a chemically reactive electrophile which can bind to and subsequently react with the enzyme active site: 4b. An enzyme inhibitor that contains latent reactive group that upon binding followed by catalytic turnover at the enzyme active site produces a reactive electrophile that reacts covalently with the enzyme: 4c. A reversible inhibitor that competes with the substrate for binding to the enzyme active site: 4d. A reversible inhibitor that can bind independently of substrate to its…arrow_forward
- 1. Make a Lineweaver-Burk plot and use the plot to complete the information in the table and the following questions. a. Is it possible for the enzyme to overcome the effect of the inhibitor in question from the chart. Explain. b. What prevents this enzyme from being an even more catalytically efficient enzyme? c. What do single molecule data indicate about the validity of ensemble data?d. What is the reason that humans are insensitive to sulfa drugs?arrow_forwarda. What is the Vmax of this enzyme WITHOUT inhibitor? Please show your work. b. What is the Km of this enzyme WITHOUT inhibitor? Please show your work. c. The specificity constant of enzyme X is 8 x 10^7 /(M * seconds) What is the kcat of enzyme X WITHOUT inhibitor? Please show your work d. What was the concentration of enzyme used for measuring the kinetics of enzyme X WITHOUT inhibitor? Please show your workarrow_forwardConsider the given data for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Determine the Vm, Km and the type of inhibition based on the given data below Substrate concentration, uM 30 50 100 300 900 slope y-intercept Complete the table below (include correct units). Experiment A Vm Km Experiment A (Initial velocity without inhibitor, uM-min) Type of Inhibition: 10.4 14.5 22.5 33.8 40.8 Experiment B (Initial velocity with inhibitor, uM-min) 5.1 7.3 13.3 25.7 37.2 Experiment Barrow_forward
- Shown below are Km, and Vmax values obtained for an enzyme A which catalyze the transformation of the following substrates. Enzyme concentration used was 0.01 M. Km, mM 0.02 Vmax, mM/min 5.3 Substrate 1 2 1.5 13.7 3 2.6 100 4 0.1 25 0.05 62 1. Which substrate have the highest affinity for the enzyme? Explain. 2. Which will show higher efficiency of converting the substrate to the product? Show solutions and еxplain.arrow_forwardA. Lineweaver-Burk plot of the enzyme with increasing amounts of substrate in the absence or the presence of the inhibitor is shown below. Graph A : x-intercept Graph B : x-intercept = - 0.012, y-intercept = 0.8 Graph C : x-intercept = - 0.027, y-intercept = 0.8 Graph D : x-intercept = - 0.039, y-intercept = 0.8 - 0.007, y-intercept = 0.8 Graph A 4 Graph B Graph C Graph D 1 -0,04 -0,02 0,00 0,02 0,04 1/[Substrate] (uM) (i) Which graph indicates an enzymatic reaction without inhibitor? (ii) Which type of inhibitor is it? Briefly explain. (iii) Which graph indicates the highest concentration of inhibitor? (iv) Calculate the Vmax and Km of the graph showing an enzymatic reaction with the lowest concentration of inhibitor. Show the steps of calculation and unit in your answers. Keep 2 decimal places in your answers. 1/Rate (umol/min)arrow_forwardIn an enzyme kinetics study, three inhibitors resulted to the following results: Inhibitor ABC Inhibitor XYZ Inhibitor PQR Without Inhibitor Vmax 40.2 mM/ sec 40.3 mM/ sec 12.32 mM/ sec 65.43 mM/ sec Km 24.3 mM 28.5 mM 24.3 mM 15.7 mM d. Draw the estimated Michaelis Menten Curve of Inhibitor ABC and the curve without the inhibitor.arrow_forward
- In pure noncompetitive inhibition: a. Where on the enzyme does the inhibitor bind? b. Does the inhibitor bind to E, ES or both? c. What is the effect of I on Vmax? d. What is the effect of I on Km?arrow_forwardThe Michaelis-Menten rate equation for reversible mixed inhibition is written as Vo = Vmax [S] aKm + a' [S] where Vo is initial velocity, Vmax is maximum velocity, [S] is substrate concentration, a represents the effect of the inhibitor bound to free enzyme (E), a' represents the effect of the inhibitor bound to the enzyme-substrate complex (ES), and Km is the Michaelis constant that represents the [S] at which the reaction reaches/Vm Vmax 2α' Derive an expression for the effect of a reversible inhibitor on apparent Km from the previous equation. Use the alphabet tab to enter a and the basic tab to enter the prime sign in your answer. = Apparent, or observed, Km is equivalent to the [S] at which Vo max. apparent Km =arrow_forwarda. Estimate KM and Vmax for the uninhibited reaction from the first graph. Whatdifficulties do you find in getting accurate values?b. Make a Lineweaver-Burk (double reciprocal) plot to determine KM and Vmax again.What advantages do you see with the second method? c. Use the Lineweaver-Burk method and the table of data for the inhibitors to determine the kind of inhibition for each inhibitor.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON
Enzyme Kinetics; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FXWZr3mscUo;License: Standard Youtube License