
(a)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and halogen.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and halogen is 1, 1.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkali metal belongs to Group 1. It has electronic configuration as
The halogens belong of Group 7. It has electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and halogen ion, it will be written as

Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and non metal from group 16.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkali metal and non metal from group 16 is 2, 1
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkali metal belongs to Group 1. It has electronic configuration as
The elements of Group 16 have electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as

Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 2, 1
(c)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and halogen
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(c)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and halogen
is 1, 2.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkaline earth metal belongs to Group 2. It has electronic configuration as
The halogens belong of Group 7. It has electronic configuration as
Combining alkali metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as
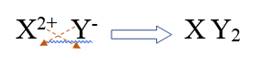
Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 2
(d)
Interpretation:
The subscripts most likely to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and non metal from group 16.
Concept introduction:
The naming of ionic compound is such that the cation comes first and anion comes next. The subscripts are numeric indicating number of atoms that are involved in bonding. To get electrically neutral compound, there is balancing of the polyatomic ions that forms ionic bonds.
(d)
Answer to Problem 39SSC
The subscript to be used if ionic compound is formed between alkaline earth metal and non metal form group 16 is 1, 1.
Explanation of Solution
The binary ionic compound is written with the metal ion first and then the nonmetal next. The charge of the metal ion and non metal ion is balanced by cancelling out each other depending on the number of ions of each.
The alkaline earth metal belongs to Group 2. It has electronic configuration as
The elements of Group 16 have electronic configuration as
Combining alkaline earth metal ion and non metal ion of group 16, it will be written as
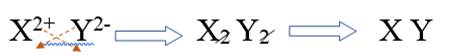
Therefore, the subscripts for this ionic compound is 1, 1
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
Introductory Chemistry (5th Edition) (Standalone Book)
Organic Chemistry
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





