
Concept explainers
(a)
The value of mean, median and mode of the data set.
(a)
Answer to Problem 10E
Mean=−$0.4016Median = $0.86Mode = None
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is:
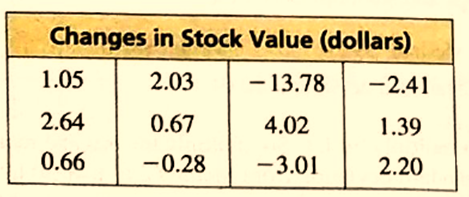
Calculation:
The value of mean will be:
Mean = 1.05+2.03−13.78−2.41+2.64+0.67+4.02+1.39+0.66−0.28−3.01+2.2012Mean=−4.8212Mean=−$0.4016
The value of median will be:
Order the given data set and get the middle value.
The ordered set will be:
−13.78,−3.01,−2.41,−0.28,0.66,0.67,1.05,1.39,2.03,2.20,2.64,4.02
Hence,
Median = 0.67+1.052Median = 1.722Median = $0.86
The value of mode will be:
Get the most occurring value. Hence,
Mode = None
(b)
The measure of center describing the data set in the most efficient way.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10E
Median
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is:
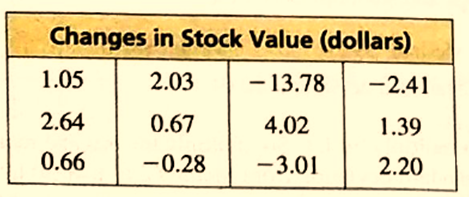
Calculation:
The data is skewed and asymmetrical; median will be preferred in representing the data. The mean is greater than most of the data and mode is less than most of the data. Hence, median will represent this data.
(c)
The effect of additional value on mean, median and mode.
(c)
Answer to Problem 10E
Mean=−$0.0415Median = $1.05Median = None
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is:
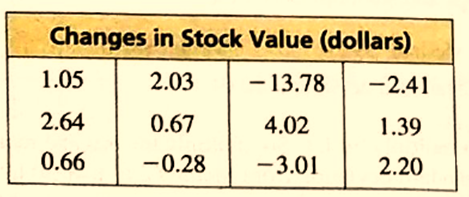
Calculation:
The value of mean will be:
Mean = 1.05+2.03−13.78−2.41+2.64+0.67+4.02+1.39+0.66−0.28−3.01+2.20+4.2813Mean=−0.5413Mean=−$0.0415
The value of median will be:
Order the given data set and get the middle value.
The ordered set will be:
−13.78,−3.01,−2.41,−0.28,0.66,0.67,1.05,1.39,2.03,2.20,2.64,4.02,4.28
Hence,
Median = $1.05
The value of mode will be:
Get the most occurring value. Hence,
Mode = None
Chapter 7 Solutions
BIG IDEAS MATH Integrated Math 1: Student Edition 2016
- 2011 listing by carmax of the ages and prices of various corollas in a ceratin regionarrow_forwardس 11/ أ . اذا كانت 1 + x) = 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 + x) هي متعددة حدود محسوبة باستخدام طريقة الفروقات المنتهية (finite differences) من جدول البيانات التالي للدالة (f(x . احسب قيمة . ( 2 درجة ) xi k=0 k=1 k=2 k=3 0 3 1 2 2 2 3 αarrow_forward1. Differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables, providing examples for each type. 2. Consider a discrete random variable representing the number of patients visiting a clinic each day. The probabilities for the number of visits are as follows: 0 visits: P(0) = 0.2 1 visit: P(1) = 0.3 2 visits: P(2) = 0.5 Using this information, calculate the expected value (mean) of the number of patient visits per day. Show all your workings clearly. Rubric to follow Definition of Random variables ( clearly and accurately differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables with appropriate examples for each) Identification of discrete random variable (correctly identifies "number of patient visits" as a discrete random variable and explains reasoning clearly.) Calculation of probabilities (uses the probabilities correctly in the calculation, showing all steps clearly and logically) Expected value calculation (calculate the expected value (mean)…arrow_forward
- t 56 65 33arrow_forwardCalculating probability for the Standard Normal Curve 1. Assume the mean is zero, the standard deviation is one, and it is associated with the distribution of z values. Each problem is worth 2 points, 1 point for drawing out the curve and shading the area requested and 1 point for the answer. a. What is the P(z > 0)? b. What is the P(z < 1.0)? C. What is the P(z <-1.0)?arrow_forwarda) x(t) = rect(t − 3) b) x(t) = −3t rect(t) . c) x(t) = 2te 3u1(t) d) x(t) = e−2|t| 2. Sketch the magnitude and phase spectrum for the four signals in Problem (1).arrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





