
Concept explainers
Estimating Cost Behavior Using Scattergraph and High-Low Methods
Camp Rainbow offers overnight summer camp programs for children ages 10 to 14 every summer during June and July. Each camp session is one week and can accommodate up to 200 children. The camp is not coed, so boys attend during the odd-numbered weeks and girls attend during the even-numbered weeks. While at the camp, participants make crafts, participate in various sports, help care for the Camp’s resident animals, have cookouts and hayrides, and help assemble toys for local underprivileged children.
The camp provides all food as well as materials for all craft classes and the toys to be assembled. One cabin can accommodate up to 10 children, and one camp counselor is assigned to each cabin. Three camp managers are on-site regardless of the number of campers enrolled.
Following is the cost information for Camp Rainbow s operations last summer
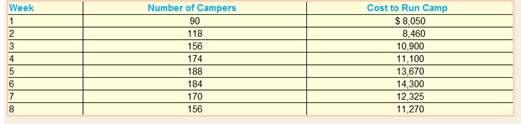
1. For each of the following items. Identify, whether the cost is variable, fixed, mixed, step-variable, or step-fixed. State any assumptions you make.
a. Cost of meals for campers.
b. Cost of camp counselor wanes.
c. Cost of crafting materials.
d.
e. Feed for the camp animals.
f. Electricity for the camp.
g. Camp managers’ salaries.
h. Cost of toys to be assembled by campers.
I. Housekeeping (e.g. cleaning cabins between sessions, laundering bed linens).
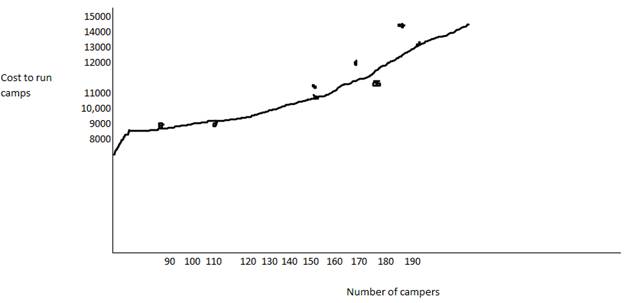
2. Prepare a scattergraph of Camp Rainbows operating cost and draw the line you believe best fits the data.
3. Based on this graph, estimate Camp Rainbow s total fixed costs per month.
4. Using the high-low method, calculate Camp Rainbow s total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per child.
5. Using the high-low method results, calculate the camps expected operating cost if 170 children attend a session.
(a)
Concept introduction:
Variable cost:
Variable costs are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Example: Cloth (i.e., the raw material) used for producing shirt is a variable costs.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost is the cost which remains fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost is the cost which has some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example includes some production cost which remains fixed at $800 and also increases by $2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increases in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
The nature of given expenses.
Answer to Problem 10E
| a. | variable |
| b | step-fixed |
| c | step-variable |
| d | fixed |
| e | fixed |
| f | step-fixed |
| g | fixed |
| h | variable |
Explanation of Solution
| a. | Cost of meal will vary on the number of participants. |
| b | Camp counselor wages vary slightly depending on the number of participants. |
| c | Camp counselor wages will vary highly on the number of participants |
| d | Depreciation will remain fixed |
| e | feed of the camp animals will remain fixed |
| f | Electricity expenses remain fixed upto a certain limit |
| g | Camp manager's salary will remain fixed |
| h | Variable based on the number of participants |
Thus, thenature of expenses has been determined.
(b)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
To prepare:
The scatter-graph and estimate the fixed costs.
Answer to Problem 10E
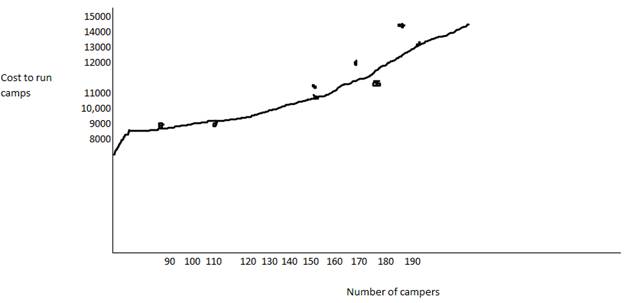
Explanation of Solution
The points have been plotted and a straight line has been drawn near the points.
Thus, the scatter-graph has been prepared
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
Requirement 3
To provide
The estimated fixed costs
Answer to Problem 10E
The estimated fixed cost is $7,000.
Explanation of Solution
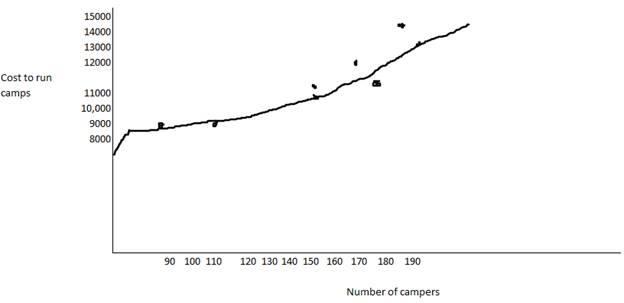
The intercept is at hence the fixed cost is estimated
Thus, the estimated fixed cost has been provided.
(d)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The fixed and variable cost using high low method.
Answer to Problem 10E
The fixed operating cost is $2839
The variable operating cost is $57.35/camper
Explanation of Solution
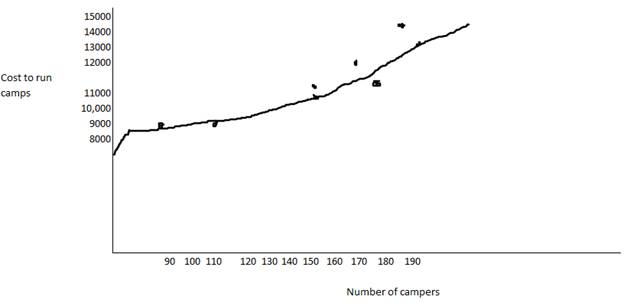
The highest point is 188campers with total cost $13,670
The lowest point is 90 campers with total cost $8050
So, variable cost per camper =
So, fixed cost for 90 camper=8050-(90*57.37) = 8050-5161.22=$2839
Hence, the fixed cost and variable cost has been determined.
(e)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The estimated cost at given number of units.
Answer to Problem 10E
The expected operating cost of 170 children using high-low method is $12,587
Explanation of Solution
The cost of 170 campers = 2839+(170*57.35) = $12,588
Hence, the estimated costs has been determined
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- aces Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Camp Rainbow offers overnight summer camp programs for children ages 10 to 14 every summer during June and July Each camp session is one week and can accommodate up to 200 children. The camp is not coed, so boys attend during the odd-numbered weeks and girls attend during the even-numbered weeks. While at the camp, participants make crafts, participate in various sports, help care for the camp's resident animals, have cookouts and hayrides, and help assemble toys for local underprivileged children. The camp provides all food as well as materials for all craft classes and the toys to be assembled. One cabin can accommodate up to 10 children, and one camp counselor is assigned to each cabin. Three camp managers are on-site regardless of the number of campers enrolled. Following is the cost information for Camp Rainbow's operations last summer Number of Cost to Run Week Campers Camp 1 190 2 100…arrow_forwardCalculating costs using traditional and activity-based systems Bubba and Danny are college friends planning a skiing trip to Killington before the new year. They estimated the following for the trip: Requirements Bubba suggests that the costs be shared equally. Calculate the amount each person would pay. Danny does not like the idea of sharing the costs equally because he plans to stay in the room rather than ski. Danny suggests that each type of cost be allocated to each person based on the above-listed allocation bases. Using the activity allocation for each person, calculate the amount that each person would pay based on his own consumption of the activity.arrow_forwardACE Math Academy provides math help for high school students. The organizations believes a small group learning environment allows students to become more comfortable in asking questions while being able to learn from other students. As a result, each instructor is expected to have a class of six students and each session is two hours long. There are four instructors and they are each being paid $35 per hour. Each session is expected to cost $30 for the student. For the month of June, the company expects 120 sessions. By the end of the month the company noticed everything has met expectations expect the following Instructors were being paid at $40 per hour There were a total of 100 sessions in the month students paid 34 per session A) Calculate the selling price variance for the month. B) Calculate the rate and efficiency variance per hour for direct labor C) Calculate the total direct labor flexible budget variancearrow_forward
- A home builder needs to schedule labor for the construction of 24 homes in a subdivision. In the past the builder has noted a 90% learning rate. If the first home requires 2000 labor hours to build, estimate the time required to build: a. The 4th house b. The 15th house c. All 24 housesarrow_forwardObjectives of Allocation Samantha and Rashida are planning a trip to Padre Island, Texas, during spring break. Members of the varsity volleyball team, they are looking forward to four days of beach volleyball and parasailing. They will drive Samantha's car and estimate that they will pay the following costs during the trip: Motel (4 nights at $160) Food (each) Gas in total Parasailing and equipment rental (each) They have reservations at the Seascape Motel, which charges $135 per night for a single, $160 per night for a double, and an additional $15 per night if a rollaway bed is added to a double room. Samantha's little sister, Kallie, wants to go along. She isn't into sports but thinks that four days of partying and relaxing on the beach would be a great way to unwind from the rigors of school. She figures that she could ride with Samantha and Rashida and share their room. $640 155 123 120 Required: 1. Using incremental costs only, what would it cost Kallie to accompany Samantha and…arrow_forwardCosts assigned to an activity pool for teaching children to swim at the county park are $2,700 per month. Number of students is chosen as the cost driver. On average, 300 students take swim lessons monthly. What is the ABC allocation rate for this activity? O Not enough information given $27.00 $9.00 O s0.90arrow_forward
- Cost Definitions Luisa Giovanni is a student at New York University. To help pay her way through college, Luisa started a dog walking service. She has 12 client dogssix are walked on the first shift (6:30 A.M. and 5:00 P.M.), and six are walked on the second shift (7:30 A.M. and 6:00 P.M.). Last month, Luisa noted the following: 1. Purchase of three leashes at 10 each (she carries these with her in case a leash breaks during a walk). 2. Internet service cost of 40 a month. This enables her to keep in touch with the owners, bill them by email, and so on. 3. Dog treats of 50 to reward each dog at the end of each walk. 4. A heavy-duty raincoat and hat for 100. 5. Partway through the month, Luisas friend, Jason, offered her a chance to play a bit role in a movie that was shooting on location in New York City. The job paid 100 and would have required Luisa to be on location at 6:00 A.M. and to remain for 12 hours. Regretfully, Luisa turned it down. 6. The dog owners pay Luisa 250 per month per dog for her services. Required: 1. At the end of the month, how would Luisa classify her Internet payment of 40as a cost on the balance sheet or as an expense on the income statement? 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which of the above items is an opportunity cost? Why? 3. What price is charged? What is Luisas total revenue for a month?arrow_forwardA professional division at a business school provides several development programs that have been tailored to the specific training needs of both the public and private sectors. The program director is planning to offer a one-full-day course in risk management to be sold at $2,250 plus orientation fee (5%) per participant. The division incurs a cost of $45,000 for promotion, classroom space, staff and instructor’s salary, as well as a cost of $240 per participant for refreshments, lunch, course material, a gift package, and a framed certificate of completion. How many participants need to register in the course for it to be worthwhile to offer it? Round to two decimal places. Group of answer choices 21.20 26.86 36.72arrow_forwardAlter's Home Center (AHC) sells renovation and remodeling products to both contractors and individual home owners. One of the services AHC offers is delivery of the purchased products to the customer's work site. Because not all customers take advantage of the delivery service option, ACH adds 10 percent to the cost of the products purchased to cover the delivery cost. A business intern spent the summer at ACH. The intern's assignment was to analyze the delivery service and recommend a better way to charge customers for using it. The intern, who had studied activity-based costing, identified the following activities and the data related to them: Activity Picking order Delivering order Handling complaints Total delivery cost Cost Driver Number of items Number of orders Number of complaints Annual Cost $ 308,125 720,000 40,000 Annual Driver Volume 362,500 items 30,000 orders 160 complaints $ 1,068,125 The intern selected two customers, who were frequent customers, to use as an…arrow_forward
- Alter's Home Center (AHC) sells renovation and remodeling products to both contractors and individual home owners. One of the services AHC offers is delivery of the purchased products to the customer's work site. Because not all customers take advantage of the delivery service option, ACH adds 10 percent to the cost of the products purchased to cover the delivery cost. A business intern spent the summer at ACH. The intern's assignment was to analyze the delivery service and recommend a better way to charge customers for using it. The intern, who had studied activity-based costing, identified the following activities and the data related to them: Activity Picking order Delivering order Handling complaints Total delivery cost Cost Driver Number of items Number of orders Number of complaints Annual Cost $ 353,875 1,190,000 40,500 $ 1,584,375 Total order value (before delivery charge) Number of orders Total number of items Number of delivery complaints The intern selected two customers,…arrow_forwardAlter's Home Center (AHC) sells renovation and remodeling products to both contractors and individual home owners. One of the services AHC offers is delivery of the purchased products to the customer's work site. Because not all customers take advantage of the delivery service option, ACH adds 10 percent to the cost of the products purchased to cover the delivery cost. A business intern spent the summer at ACH. The intern's assignment was to analyze the delivery service and recommend a better way to charge customers for using it. The intern, who had studied activity-based costing, identified the following activities and the data related to them: Activity Cost Driver Annual Cost Annual Driver Volume Picking order Number of items $ 353,875 372,500 items Delivering order Number of orders 1,190,000 35,000 orders Handling complaints Number of complaints 40,500 150 complaints Total delivery cost $ 1,584,375 The intern selected two customers, who were frequent customers,…arrow_forwardAlter's Home Center (AHC) sells renovation and remodeling products to both contractors and individual home owners. One of the services AHC offers is delivery of the purchased products to the customer's work site. Because not all customers take advantage of the delivery service option, ACH adds 10 percent to the cost of the products purchased to cover the delivery cost. A business intern spent the summer at ACH. The intern's assignment was to analyze the delivery service and recommend a better way to charge customers for using it. The intern, who had studied activity-based costing, identified the following activities and the data related to them: Activity Picking order Delivering order Handling complaints Total delivery cost Cost Driver Number of items Number of orders Number of complaints Annual Cost $ 286,000 522,500 32,400 $ 840,900 Total order value (before delivery charge) Number of orders The intern selected two customers, who were frequent customers, to use as an illustration of…arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



