
Concept explainers
(a)
To construct: a suitable display for the growth rates.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
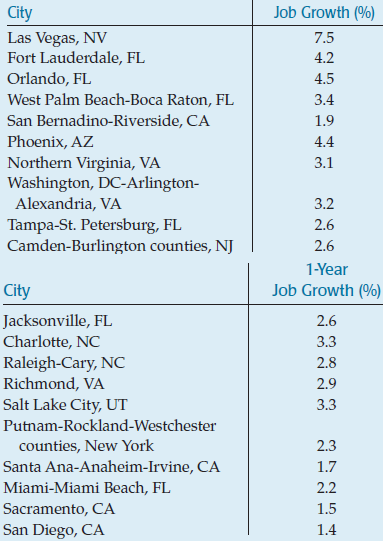
Graph:
By seeing the data, it is observed that the data is quantitative so the histogram is the appropriate to display the data. On the basis of given data plot the histogram.
(b)
To find: the summary the growth rate among these cities with a
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Formula used:
Calculation:
Arranging in the ascending order
1.4, 1.5, 1.7, 1.9, 2.2, 2.3, 2.6, 2.6, 2.6, 2.8, 2.9, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.3, 3.4, 4.2, 4.4, 4.5, 7.5 (in percent)
These are 20 values so median is the average of 10th and 11th values. therefore median would be
Sum of all the job growth percentages is 61.4% so mean would be
Hence, median is 2.85% and mean is 3.1%. Distribution is skewed to right so mean is higher than median.
(c)
To find: the better job of summarizing the growth rates.
(c)
Answer to Problem 48E
Median is better
Explanation of Solution
Median would be better than mean because the distribution is skewed to right. The distribution has outliers’ therefore median works better to explain the growth rates of job.
(d)
To find: the summary of the spread of the growth rate distribution with a standard deviation and with an IQR.
(d)
Answer to Problem 48E
Standard deviation of the distribution is 1.4% and IQR is 1.1%.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Formula used:
Calculation:
So standard deviation will be
So standard deviation is 1.4%.
To find IQR let us first find
Lower half of data has 10 values. Lower half of data is
1.4, 1.5, 1.7, 1.9, 2.2, 2.3, 2.6, 2.6, 2.6, 2.6, 2.8
So the lower quartile is
Upper half of data has 10 values. Upper half of data is
2.9, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.3, 3.4, 4.2, 4.4, 4.5, 7.5
So the lower quartile is
Therefore IQR is
Hence, standard deviation of the distribution is 1.4% and IQR is 1.1%.
(e)
To find: the measures in (d) the better job of summarizing the growth rates.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Inter
(f)
To find: the change the values of the summary statistics calculated above.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Suppose first median, Subtracting 1.20% from every value of data does not change the order of data vales. Therefore the median would also be decrease by 1.20%. Therefore the new median would be 2.85% - 1.20% = 1.65%.
Now taking the standard deviation, Mean decreases by 1.20% and every value also decreases by 1.20% so deviation would not change. Therefore standard deviation remains unchanged.
Therefore, new standard deviation is 1.4%.
Lower and upper
(g)
To Explain: the expected the mean, median, standard deviation and IQR to change.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
1.4, 1.5, 1.7, 1.9, 2.2, 2.3, 2.6, 2.6, 2.6, 2.8, 2.9, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.3, 3.4, 4.2, 4.4, 4.5
Total number of values is odd so median is the 10th value that is 2.8%.
So new mean is equal to 2.8%
Standard deviation decreases. Las Vegas job growth percentage works as an outlier in the distribution so omitting Las Vegas decreases standard deviation also.
Las Vegas value is last in order data set so omitting it does not change IQR.
(h)
To Explain: the report about all of these growth rates.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The distribution is skewed to right and has an outlier so median shows the data correctly. Las Vegas job growth is significantly larger than any other city. Spread of the correctly represents by IQR. Almost 20 states have scores between 240 and 244. One of the state has scores less than 225.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Stats: Modeling the World Nasta Edition Grades 9-12
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- le Chrome dent/PlayerHomework.aspx?homeworkId=687785871&questionid=15&flushed=true&cld=8066907¢erwin=yes 2024 FabtizioMendez fabrizio 12/12/24 8:00 AM B 不 X Question 15, 5.4.13 Part 6 of 6 HW Score: 93.86%, 17.83 of 19 points ct: 0 Points: 0.83 of 1 Save For the following situation, find the mean and standard deviation of the population. List all samples (with replacement) of the given size from that population and find the mean of each. Find the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution and compare them with the mean and standard deviation of the population. The scores of three students in a study group on a test are 90, 98, 94. Use a sample size of 3. The mean of the population is 94 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The standard deviation of the population is 3.27 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify all samples of size 3 with the correct accompanying means below. A. 94,98,90 x=94 B. 90,98,90 x=92.67 D. 98,90,98 x = 95.33 E. 90,94,94 x = 92.67…arrow_forwardSample opticalDens lot run westernBlot 1 1.053 A A 1.708 A A 2.99 0.977 A A 1.67 4 0.881 AB 1.47 0.788 A B 2.25 6 0.788 A B 0.15 7 0.896 AC 1.41 1.038 AC 2.51 9 0.963 AC 1.85 10 0.971 A D 1.7 11 1.234 AD 1.49 12 1.089 A D 1.92 13 0.984 A E 0.96 14 0.986 A E 1.64 15 1.067 A E 16 0.996 BA 1.77 17 1.129 BA 1.69 18 1.016 BA 3.01 19 1.019 B B 1.03 20 1.088 B B 1.94 21 1.28 BB 2.1 22 1.12 BC 0.83 23 1.054 BC 2.52 24 1.235 BC 1.78 1.327 BD 2.2 26 1.361 BD 2.08 27 1.233 BD 1.84 1.079 BE 0.9 29 1.12 B 1.29 30 0.959 BE 1.79 31 1.229 CA 1.46 32 1.027 CA 1.97 33 1.109 CA 2.29 34 1.118 CB 35 1.066 CB 2.06 36 1.146 CB 1.51 37 1.053 CC 1.47 38 1.082 CC 2.19 39 1.113 CC 2 40 1.14 CD 1.7 41 1.172 CD 2.87 0.966 CD 0.3 43 0.963 CE 2.18 44 1.064 CE 1.65 45 1.086 CE 2.59 46 0.985 DA 1.96 47 0.894 DA 2.43 48 1.109 DA 1.56 49 0.847 D B 1.51 50 0.799 DB 1.3 51 0.918 DB 0.7 52 1.033 DC 2.31 0.943 DC 1.85 54 1.089 DC 0.71 55 0.988 DD 1.12 1.169 D D 1.47 57 1.106 D D 2.9 58 1.308 DE 2.08 1.498 DE 1.94 60 1.271…arrow_forwardNot use ai bhffidjsis88sdjcbdudufuivfuarrow_forward
- Could you please help me with it. Thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help me with this. Thank you!arrow_forwardConstruct a frequency distribution for the given data set using 6 classes. In the table, include the midpoints, relative frequencies, and cumulative frequencies. Which class has the greatest frequency and which has the least frequency? Question Viewer Amount (in dollars) spent on books for a semester 422 106 355 400 381 411 106 50 62 511 394 54 381 505 437 359 267 311 268 115 407 413 192 252 80 454 107 330 486 Complete the table, starting with the lowest class limit. Use the minimum data entry as the lower limit of the first class. (Type integers or decimals. Round the class limits to the nearest whole number. Round all other values to the nearest thousandth as needed.) Class 50-126 Frequency 9 Midpoint 88 Relative Frequency Cumulative Frequency 0.333 9arrow_forward
- To assure 99% confidence another poll is conducted, again asking whether or nothuman cloning should be allowed. 5,000 randomly selected adults from across thenation are surveyed. Of those surveyed 4,388 respond that they are against humancloning. Construct a 99% confidence interval estimate for the proportion of adults whoare against human cloning. Does this interval support the newspaper’s claim?arrow_forwardCould you help me please. Thank you!arrow_forwardCan you help me with it please.arrow_forward
- In a recent national poll consisting of 1012 randomly selected adults. Participants wereasked whether or not human cloning should be allowed. Of those surveyed 900indicated human cloning should not be allowed. A newspaper releases and articleclaiming 90% of those across the nation are against human cloning based on thenational poll. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the proportion of adultswho are against human cloning. Does this interval support the newspaper’s claim? What sample size would be needed to assure 99% confidence with an error bound of 0.02?arrow_forwardIn a recent national poll consisting of 1012 randomly selected adults. Participants wereasked whether or not human cloning should be allowed. Of those surveyed 900indicated human cloning should not be allowed. A newspaper releases and articleclaiming 90% of those across the nation are against human cloning based on thenational poll. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the proportion of adultswho are against human cloning. Does this interval support the newspaper’s claim?arrow_forwardIt is known that 30% of all households still have landlines. If we randomly select 10 households, let X = number that have landlines a) FInd the probability that X = 3. b) Find the mean and standard deviation of X.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





