
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259700903
Author: Leland Hartwell Dr., Michael L. Goldberg Professor Dr., Janice Fischer, Leroy Hood Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 39P
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by a relatively rare X-linked recessive allele. It results in progressive muscular wasting and usually leads to death before age 20. In this problem, an affected person is one with the severe form of DMD caused by hemizygosity or homozygosity for the disease allele.
| a. | What is the probability that the first son of a woman whose brother is affected will be affected? |
| b. | What is the probability that the second son of a woman whose brother is affected will be affected, if her first son was affected? |
| c. | What is the probability that a child of an unaffected man whose brother is affected will be affected? |
| d. | An affected man mates with his unaffected first cousin; there is otherwise no history of DMD in this family. If the mothers of this man and his mate were sisters, what is the probability that the couple’s first child will be an affected boy? An affected girl? An unaffected child? |
| e. | If the two related parents of the couple in part (d) were brother and sister (instead of sisters), what is the probability that the couple’s first child will be an affected boy? An affected girl? An unaffected child?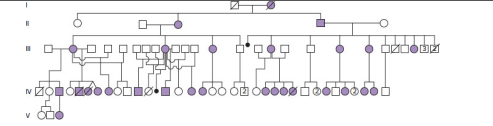 |
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Which of the following is the process that is "capable of destroying all forms of microbial life"?
Question 37 options:
Surgical scrub
Sterilization
Chemical removal
Mechanical removal
After you feel comfortable with your counting method and identifying cells in the various stages of mitosis, use the four images below of whitefish blastula to count the cells in each stage until you reach 100 total cells, recording your data below in Data Table 1. (You may not need to use all four images. Stop counting when you reach 100 total cells.)
After totaling the cells in each stage, calculate the percent of cells in each stage. (Divide total of stage by overall total of 100 and then multiply by 100 to obtain percentage.)
Data Table 1Stage Totals PercentInterphase Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Totals 100 100%
To find the length of time whitefish blastula cells spend in each stage, multiply the percent (recorded as a decimal, in other words take the percent number and divide by 100) by 24 hours. (Example: If percent is 20%, then Time in Hours = .2 * 24 = 4.8) Record your data in Data…
What are Clathrin coated vesicles and what is their function?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Ch. 4 - Choose the best matching phrase in the right...Ch. 4 - Humans have 46 chromosomes in each somatic cell....Ch. 4 - The figure that follows shows the metaphase...Ch. 4 - Human XX males who are sex-reversed because they...Ch. 4 - Researchers discovered recently that the sole...Ch. 4 - One oak tree cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes...Ch. 4 - Indicate which of the cells numbered iv matches...Ch. 4 - a. What are the four major stages of the cell...Ch. 4 - Answer the questions that follow for each stage of...Ch. 4 - Can you think of anything that would prevent...
Ch. 4 - One oak tree cell with 14 chromosomes undergoes...Ch. 4 - Which types of cell division mitosis, meiosis I,...Ch. 4 - Complete the following statements using as many of...Ch. 4 - The five cells shown in figure a e are all from...Ch. 4 - One of the first microscopic observations of...Ch. 4 - A person is simultaneously heterozygous for two...Ch. 4 - Assuming i that the two chromosomes in every...Ch. 4 - In the moss Polytrichum commune, the haploid...Ch. 4 - Can you think of anything that would prevent...Ch. 4 - Sister chromatids are held together through...Ch. 4 - The pseudoautosomal regions PARs of the X and Y...Ch. 4 - Remarkably, the platypus has 10 sex chromosomes,...Ch. 4 - Somatic cells of chimpanzees contain 48...Ch. 4 - In humans: a. How many sperm develop from 100...Ch. 4 - Women sometimes develop benign tumors called...Ch. 4 - In a certain strain of turkeys, unfertilized eggs...Ch. 4 - Imagine you have two pure-breeding lines of...Ch. 4 - A system of sex determination known as...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, the autosomal recessive brown eye...Ch. 4 - Barred feather pattern is a Z-linked dominant...Ch. 4 - When Calvin Bridges observed a large number of...Ch. 4 - In a vial of Drosophila, a research student...Ch. 4 - In 1919, Calvin Bridges began studying an X-linked...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, a cross was made between a...Ch. 4 - As we learned in this chapter, the white mutation...Ch. 4 - The following is a pedigree of a family in which a...Ch. 4 - Each of the four pedigrees that follow represents...Ch. 4 - The pedigree that follows indicates the occurrence...Ch. 4 - Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is caused by a...Ch. 4 - The X-linked gene responsible for DMD encodes a...Ch. 4 - Males have hemophilia when they are hemizygous for...Ch. 4 - In the Fast Forward Box Visualizing X Chromosome...Ch. 4 - Consider the following pedigrees from human...Ch. 4 - Several different antigens can be detected in...Ch. 4 - The ancestry of a white female tiger bred in a...Ch. 4 - The pedigree that follows shows the inheritance of...Ch. 4 - In 1995, doctors reported a Chinese family in...Ch. 4 - In cats, the dominant O allele of the X-linked...Ch. 4 - In marsupials like the opposum or kangaroo, X...Ch. 4 - The pedigree diagram below shows a family in which...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Describe the role and impact of microbes on the earth.
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
On what molecule does the anticodon appear? Explain the role of this molecule in protein synthesis.
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How is a protein destined for the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), imported into the ER? Be concise.arrow_forwardFind out about the organisations and the movements aimed at the conservation of our natural resources. Eg Chipko movement and Greenpeace. Make a project report on such an organisation.arrow_forwardWhat are biofertilizers and mention the significancearrow_forward
- PCBs and River Otters: Otters in Washington State’s Green-Duwamish River have high levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in their livers. PCBs can bind to the estrogen receptors in animals and disrupt the endocrine system of these otters. The PCBs seem to increase the estrogen to androgen ratio, skewing the ratio toward too much estrogen. How would increased estrogen affect the river otter population? Based on your reading of the materials in this unit, what factors can affect fertility in humans? Explain how each of the factors affecting human fertility that you described can disrupt the human endocrine system to affect reproduction.arrow_forwardOther than oil and alcohol, are there other liquids you could compare to water (that are liquid at room temperature)? How is water unique compared to these other liquids? What follow-up experiment would you like to do, and how would you relate it to your life?arrow_forwardSelection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forward
- Competition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forwardmagine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How to solve genetics probability problems; Author: Shomu's Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Beyond Mendelian Genetics: Complex Patterns of Inheritance; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EmvmBuK-B8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY