
(a)
Interpretation:
The main product of the mononitration of benzoic acid should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic
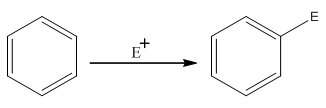
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
The nitration reaction takes place in the presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. In this reaction, the protonation of nitric acid occurs in order to produce the nitronium ion. The nitronium ion will attach on the benzene ring to form nitrobenzene. The general reaction is as follows:
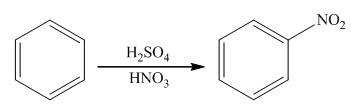
(b)
Interpretation:
The main product of the monosulphonation of phenol should be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of benzene. A general electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of benzene can be written as:
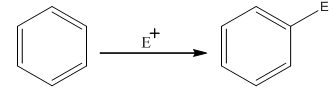
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
The sulfonation takes place in the presence of sulphuric acid. In this reaction, sulfur trioxide is formed that acts as an electrophile. Sulfur trioxide will attach on the benzene ring to form the final product. The general reaction is as follows:
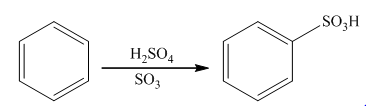
(c)
Interpretation:
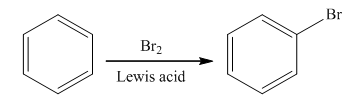
The main product of the monobromination of
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic aromatic substitution is the type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes the hydrogen atom of benzene. A general electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of benzene can be written as:
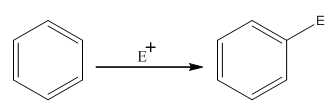
Where,
The activating groups are the groups that have the ability to donate the electron density to the benzene ring.
The deactivating groups are the groups that have the ability to withdraw the electron density to the benzene ring. The ortho and para directing groups are the activating groups while meta direction groups are deactivating groups.
Halogenation is the
The bromination takes place in the presence of Lewis acid and bromine molecule. In this reaction, the bromonium ion is produced that acts as an electrophile. Brominium will attach on the benzene ring to form the final product. The general reaction is as follows:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- Disiamylborane adds only once to alkynes by virtue of its two bulky secondary isoamylgroups. Disiamylborane is prepared by the reaction of BH3 # THF with an alkene.(a) Draw the structural formulas of the reagents and the products in the preparation ofdisiamylboranearrow_forward(a) Draw the structure of the following :(i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde (ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate, (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid.arrow_forwardGive an IUPAC and common name for each of the following naturally occurring carboxylic acids: (a) CH3CH(OH)CO2H (lactic acid); (b) HOCH2CH2C(OH)(CH3)CH2CO2H (mevalonic acid).arrow_forward
- 11) Synthesize 2-methyl-3-hydroxycyclohexone from cyclohexone, methyl iodide, and inorganic precursors.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the following compounds which parent names have been traced to a common name; (a)5-methyl-4-nitroimidazole (b)2-chloro-4-methoxythiazole.arrow_forwardThe ketone 2-heptanone has been identified as contributing to the odor of a number of dairy products, including condensed milk and cheddar cheese. Describe the synthesis of 2-heptanone from acetylene and any necessary organic and inorganic reagents.arrow_forward
- (a) A hydrocarbon isolated from fish oil and from plankton was identified as 2,6,10,14-tetramethyl-2-pentadecene. Write its structure.(b) Alkyl isothiocyanates are compounds of the type RN C S. Write a structural formula for allyl isothiocyanate, a pungent-smelling compound isolated from mustard.(c) Grandisol is one component of the sex attractant of the boll weevil. Write a structural formula for grandisol given that R in the structure shown is an isopropenyl group.arrow_forward4) Give an example of an enol which would tautomerize into a) an aldehyde and b) a ketone.arrow_forwardDimethyl disulfide, CH,S–SCH3, found in the vaginal secretions of female hamsters, acts as a sexual attractant for the male hamster. Write an equation for its synthesis from methanethiol.arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of each of the following molecules. (a) cyclohexyl butanoate; (b) 1,1-dimethylethyl hexanoate; (c) phenyl 4,4-dinitroheptanoatearrow_forward(a) How will you convert:(i) Benzene to acetophenone (ii) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol(b) Give reasons :(i) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.(ii) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and alcohols of comparable molecular masses.(iii) Propanal is more reactive than propanone in nucleophilic addition reactions.arrow_forward(a) Draw the structure of the hemiacetal formed from one mole of benzaldehyde and one mole of ethanol. (b) Draw the structure of the acetal formed from one mole of benzaldehyde and two moles of ethanol. (c) Draw the structure of 2-methoxy-2-butanol. What compounds could you prepare this from?arrow_forward
