
(a)
Interpretation:
The compound that neutralizes
Concept introduction:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction between acid and base in order to produce salt and water.
(b)
Interpretation:
The compound that neutralizes
Concept introduction:
The neutralization reaction is defined as the reaction between acid and base in order to produce salt and water.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(c)
Interpretation:
The compound that forms amide with ethanoic acid should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Amine reacts with a
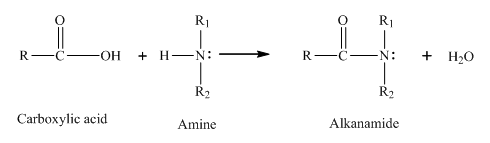
(d)
Interpretation:
The compound reacts with ammonia should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(e)
Interpretation:
The compound that reacts with
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- I2 (aq) + CH3COCH3 (aq) HI (aq) + ICH2COCH3 (aq)Iodine in solution has a yellow-brown color, whereas the acetone and both products are colorless. This means that we can run the reaction using iodine as the limiting reagent, and when we see that the yellow-brown color of the iodine has disappeared, we know that the reaction has stopped and all of the iodine has been consumed. Recall that to calculate a rate of reaction, we would like toknow the change in concentration of a reactant or product during a fixed amount of time. Wewill choose the reactant iodine in this case, because its brown color allows us to determinewhen its concentration has fallen to zero. Rate = –Δ[I2] / Δt = – ([I2]final – [I2]initial) / ([tfinal – tinitial) = – (0 – [I2]initial) / (tfinal – 0) = [I2]initial / tfinal Run several trials at different concentrations of reactants and use themethod of initial rates to obtain values for k, x, y, and z in the rate law. Rate = k [I2]x [acetone]y [H+]z Run the…arrow_forwardWrite the reaction between ammonia, NH3, and hydrosulfuric acid, H2S. NH3 + + In this reaction completes the reactant side while and complete the products side. а. NH3 b. NH4+1 с. HS-1 d. H2S е. Н20 f. H30+1 9. ОН-1arrow_forwardWhich statement best describes the products of this reaction?arrow_forward
- 6. Given the reactions below, provide the missing products and explain the differences among the hydride reactions. Where is stereochemistry is present, does it change or stay the same? 1. LİAIH4, THF 1. NaBH4, EtOH 2. H;O* 2. H3O* + NH 1. LİAIH4, THF 1. NABH4, EtOH 2. H3O* 2. H;O* ОН 1. LİAIH4, THF 1. NaBH4, ETOH 2. H3O* 2. H3O*arrow_forwardAt night, almost all NOx is present as NO2. (Ie the NO/NOx concentration is very small). Explain whyarrow_forwardComplete the following equations. If no reaction occurs, write no reaction. a. b. c. d. e.arrow_forward
- Bleach (sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl, a strong oxidizing agent) neutralizes and inactivates mustard gas. Bleach is also effective on organic stains because it oxidizes coloredcompounds to colorless compounds. Propose products that might be formed by thereaction of mustard gas with bleacharrow_forwardplease make the explanation clear and thank you for your helparrow_forwardWhat is the structures of the compounds here?arrow_forward
- 33. The reaction that occurs will give as a product:arrow_forwardPredict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. NH₂ NH 1 eq. HBrarrow_forwardThe Ka value for chlorous acid (HCIO₂) is 1.1 × 10-2, while the Ka for nitrous acid (HNO₂) is 4.6 x 10-4. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the reaction of HCIO₂ with NO₂. Predict whether the reaction equilibrium favors reactants or products. You have calculated the Keq to be equal to 24. Predict whether the reaction equilibrium favors reactants or products. A) Reactants B) Products C) The reaction produces an equal mixture of reactants and products.arrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning






