
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
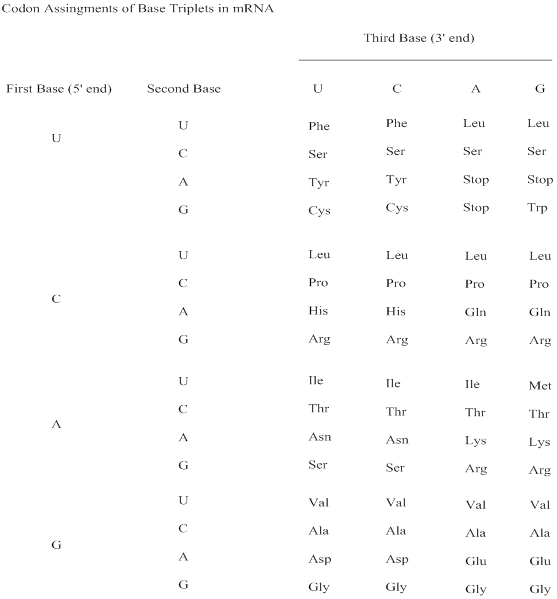
The amino acids those have most codons and least codons; reason for multiple codons for certain amino acids has to be interpreted.
Concept Introduction:
Codon: A sequence of three ribonucleotides in the mRNA chain that codes for a specific amino acid; also a three-
Genetic code: The sequence of nucleotides, coded in triplets (codons) in mRNA that determines the sequence of amino acids in protein synthesis.
Translation: A tRNA molecule is a single polynucleotide chain held together by regions of base pairing in a partially helical structure. An amino acid is bonded to its specific tRNA by an ester linkage. Connecting specific amino acid at end of the tRNA is known as charging tRNA. Once done, tRNA is ready to be used in the protein synthesis.
At the other end of the tRNA, three anticodons are present which are complementary to the codons present in mRNA. Once the anticodons pairs off with codons, the amino acid at terminal end of the tRNA is delivered and attached to the growing protein chain.
Illustrated relationships are:
DNA informational strand: 5’ ATG CCA GTA GGC CAC TTG TCA 3’
DNA Template strand: 3’ TAC GGT CAT CCG GTG AAC AGT 5’
mRNA: 5’ AUG CCA GUA GGC CAC UUG UCA 3’
protein: Met Pro Val Gly His Leu Ser
Notice: 5’ end of the mRNA strand codes for the N-terminal amino acid, whereas the 3’ end of the mRNA strand codes for the C-terminal amino acid. Proteins are always written N-terminal to C-terminal, reading left to right.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- What amino acid sequence is encoded by the codon sequence ACGCAGCGCCCGGUC? Use the 3 letter abbreviation with hyphens and no spaces in between.arrow_forwardHow many codons are there? How many amino acids are coded by these codons?arrow_forward64 codons specify 20 amino acids. There are two characteristics of codons: 1. No ambiguity: Each codon specifies only one amino acid 2. Redundancy: One amino acid is specified by more than one codon Question: What advantage we get from codon redundancy?arrow_forward
- The genetic code is thought to have evolved to maximize genetic stability by minimizing the effect on protein function of most substitution mutations (single-base changes). We will use the six arginine codons to test this idea. Consider all of the substitutions that could affect all of the six arginine codons.(a) How many total mutations are possible?(b) How many of these mutations are “silent,” in the sense that the mutantcodon is changed to another Arg codon?(c) How many of these mutations are conservative, in the sense that an Argcodon is changed to a functionally similar Lys codon?arrow_forwardSince among the 64 codons of mRNA 61 codify amino acids that form polypeptide chains what are the functions of the three remaining codons?arrow_forwardCompare the codons with a pyrimidine, either U or C, as the second base. Do the majority of the amino acids specified by these codons have hydrophobic or hydrophilic side chains?arrow_forward
- Is it reasonable that codons for the same amino acid have one or two nucleotides in common? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHow many cases are there in which it would be possible to identify the first two nucleotides of a codon if the amino acid specified by it is known?arrow_forwardUsing a table that shows which codon represents which amino acid determine the following: A) The possible codons that encode Serine: B) The amino acids that could be encoded if the 2nd position of the UCA codon that encodes Serine was changed to one of the other 3 bases: C) The amino acids that could be encoded if the 3rd position of the UCA codon that encodes Serine was changed to one of the other 3 bases: D) The amino acids that could be encoded if the 1st position of the UCA codon that encodes Serine was changed to one of the other 3 bases:arrow_forward
- Why are 3 nucleotides needed for a codon? Because one nucleotide is redundant Because there are 3 different aminoacetyl TRNA synthetase enzymes Because there are 64 amino acids to code for, and 4X4X4 = 64 Because there are 20 amino acids, 3 nucleotides provides enough combinations to code for 20 amino acidsarrow_forwardIt is possible for the codons for a single amino acid to have the first two bases in common and to differ in the third base. Why is this experimental observation consistent with the concept of wobble?arrow_forwardFor each codon, provide the anticodon and the three-letter abbreviation of the amino acid for which it codes. Consult the codon table as needed. 5'-AUU-3' anticodon: 3'- -5' amino acid: 5' -UCU-3' anticodon: 3'- -5' amino acid: 5' -CAG-3' anticodon: 3'- -5' amino acid:arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
