
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781259700903
Author: Leland Hartwell Dr., Michael L. Goldberg Professor Dr., Janice Fischer, Leroy Hood Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 9P
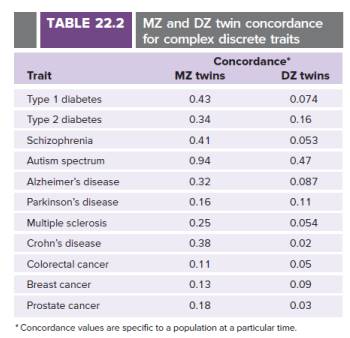
Table 22.2 lists concordance values for MZ and DZ twins with respect to a number of discrete complex traits.
| a. | How do you know at a glance that the heritabilities of all of these traits is less than 1.0? |
| b. | To estimate the heritabilities of these traits, would you use Eq. 22.7 or Eq. 22.8? Explain why |
| c. | Calculate heritability estimates for each trait using the data in Table 22.2. For which trait is the contribution of genetic variance to the total |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A characteristic has a narrow-sense heritability of 0.6.a. If the dominance variance (VD) increases and all other variancecomponents remain the same, what will happen to narrow-senseheritability? Will it increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain.b. What will happen to broad-sense heritability? Explain.c. If the environmental variance (VE) increases and all other variancecomponents remain the same, what will happen to narrow-senseheritability? Explain.d. What will happen to broad-sense heritability? Explain.
In a wild strain of tomato plants, the phenotypic variance fortomato weight is 3.2 g2. In another strain of highly inbred tomatoesraised under the same environmental conditions, the phenotypicvariance is 2.2 g2. With regard to the wild strain,A. Estimate VG.B. What is hB2?C. Assuming that all of the genetic variance is additive, what is hN2?
For each of the following characteristics, indicate whether it would be considered a discontinuous characteristic or a quantitative characteristic. Briefly justify your answer. a. Kernel color in a strain of wheat, in which two codominant alleles segregating at a single locus determine the color. Thus, there are three phenotypes present in this strain: white, light red, and medium red. b. Body weight in a family of Labrador retrievers. An autosomal recessive allele that causes dwarfism is present in this family. Two phenotypes are recognized: dwarf (less than 13 kg) and normal (greater than 23 kg). c. Presence or absence of leprosy. Susceptibility to leprosy is determined by multiple genes and numerous environmental factors. d. Number of toes in guinea pigs, which is influenced by genes at many loci. e. Number of fingers in humans. Extra (more than five) fingers are caused by the presence of an autosomal dominant allele.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Ch. 22 - Choose the best matching phrase in the right...Ch. 22 - Suppose you grew genetically identical dandelion...Ch. 22 - How can each of the following be used in...Ch. 22 - Two different groups of scientists studying a rare...Ch. 22 - Which of the following statements would be true of...Ch. 22 - Studies have indicated that for pairs of twins...Ch. 22 - Prob. 7PCh. 22 - Prob. 8PCh. 22 - Table 22.2 lists concordance values for MZ and DZ...Ch. 22 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 22 - Prob. 11PCh. 22 - Two alleles at one locus produce three distinct...Ch. 22 - In a certain plant, leaf size is determined by...Ch. 22 - Compare and contrast the use of SNP genotyping: i...Ch. 22 - Explain the similarities and differences between...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22.14c, the fw2.2 causal gene was...Ch. 22 - Among the most prevalent pathologies that afflict...Ch. 22 - Human geneticists have found the Finnish...Ch. 22 - Canavan disease, caused by homozygosity for a...Ch. 22 - In GWAS analysis, because of the existence of LD...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22.15: a. Why do some chromosomes in the...Ch. 22 - Consider the triangle diagram shown in Fig. 22.17....Ch. 22 - Prob. 23PCh. 22 - You conduct a Case/Control study comparing the...Ch. 22 - Prob. 25PCh. 22 - ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a rare, fatal...Ch. 22 - Through GWAS explorations, scientists have...Ch. 22 - In domesticated dogs, size has a high...Ch. 22 - Suppose a GWAS investigation found a particular LD...Ch. 22 - In 2008, Time magazine named as its invention of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following applies to the Hardy-Weinberg expression:p2 + 2pq + q2?a. Knowing either p2 or q2, you can calculate all the otherfrequencies.b. It applies to Mendelian traits that are controlled by one pairof alleles.c. 2pq = heterozygous individualsd. It can be used to determine the genotype and allelefrequencies of the previous and the next generations.e. All of these are correct.arrow_forwardTwo loci contribute to eyelash length in angora rabbits (locus A and B). Assuming additive genetic variance and disregarding environmental effects, you determine that the following alleles contribute the following values to the total expression of lash length (in cm) A = 2.3, a=1.5, B=2.4, b=1.7 What would the phenotype of a rabbit with a genotype of AABb be? _________cmarrow_forwardADHD is a highly heritable trait with published broad sense heritability estimates in the range of 0.6- 0.9. Larsson et al. 2014 (doi: 10.1017/S0033291713002493 ) reported the concordance values shown in the table below for pairs of monozygotic (MZ) or dizygotic (DZ) twins with data for male and female pairs shown separately, using data from the Swedish twin register (59,000 twin pairs, born between 1959 and 2001). Male MZ twins Male DZ twins Female MZ twins Female DZ twins 56% 16% 37% 13% Based on the data in this table, does ADHD appear to be more heritable in males or females? Provide one sentence of rationale to support your answer.arrow_forward
- In a cross between two inbred lines of Drosophila, the F1 progeny has the phenotypic variance of 0.87 for the number of abdominal bristles. The F2 generation has the phenotypic variance of 3. a)What is the environmental variance? __________ b)What is the genetic variance of the F2? __________ In a plant, height varies between 6 and 36 cm and is governs by 3 genes with wild-type alleles being additive. What would be the genotype of a plant16 cm in height? there might be multiple possible answers Name one mutation which is a suppressor of bri1-5arrow_forwardTwo different varieties of potato plants produce potatoes with thesame mean weight of 1.5 pounds. One variety has a very low variancefor potato wieght, and the other has a much higher variance. A. Discuss the possible reasons for the differences in variance.B. If you were a potato farmer, would you rather raise a varietywith a low or high variance? Explain your answer from apracticalpoint of view.C. If you were a potato breeder and you wanted to develop potatoeswith a heavier weight, would you choose the variety witha low or high variance? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardWhy are monozygotic twins who are reared apart so useful in the calculation of heritability?arrow_forward
- The narrow-sense heritability of wing length in a population of Drosophila melanogaster is 0.8. The narrow-sense heritability of head width in the same population is 0.9. The genetic correlation between wing length and head width is −0.86. If a geneticist selects for increased wing length in these flies, what will happen to head width?arrow_forwardA genetics researcher determines that the broad-sense heritability of height among Southwestern University undergraduate students is 0.90. Which of the following conclusions would be reasonable? Explain your answer. a. Sally is a Southwestern University undergraduate student, so 10% of her height is determined by nongenetic factors. b. Ninety percent of variation in height among all undergraduate students in the United States is due to genetic differences. c. Ninety percent of the height of Southwestern University undergraduate students is determined by genes. d. Ten percent of the variation in height among Southwestern University undergraduate students is determined by variation in nongenetic factors. e. Because the heritability of height among Southwestern University students is so high, any change in the students’ environment will have minimal effect on their height.arrow_forwardPlease refer to the table below. If only data on the variances for F1, F2 and BC1 populations were available, how will the broad sense heritability estimate change? Show solutions.arrow_forward
- Figure 19-11 shows the expected distributions for thethree genotypic classes if the B locus is a QTL affectingthe trait value.a. As drawn, what is the dominance/additive (D/A)ratio?b. How would you redraw this figure if the B locus hadno effect on the trait value?c. How would the positions along the x-axis of thecurves for the different genotypic classes of the B locuschange if D/A = 1.0?arrow_forwardSuppose that in a population of Peacocks the phenotypic variance for tail length is 2.5 and the heritability for this trait is 0.4. From a long-term captive population you also have data from a line of completely inbred individuals. In this line the phenotypic variance among individuals is 0.50. Assume that there is no epistatic variance (VI) for this trait. Calculate the following: What is the additive genetic variance? What is the dominance genetic variance? What is the environmental variance? What is the broad-sense heritability (H2)?arrow_forwardSuppose that in a population of Peacocks the phenotypic variance for tail length is 2.5 and the heritability for this trait is 0.4. From a long-term captive population you also have data from a line of completely inbred individuals. In this line the phenotypic variance among individuals is 0.50. Assume that there is no epistatic variance (VI) for this trait. Calculate the following: What is the total genetic variance for tail length? What is the additive genetic variance? What is the dominance genetic variance? What is the environmental variance? What is the broad-sense heritability (H2)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Genetic Variation and Mutation | 9-1 GCSE Science Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel; Author: SnapRevise;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bLP8udGGfHU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY