
Concept explainers
Suppose the mature height of a plant is a multifactorial trait under the control of five independently assorting genes, designated A, B, C, D, and E, and five environmental factors. There are two alleles of each gene (
The five environmental factors are (
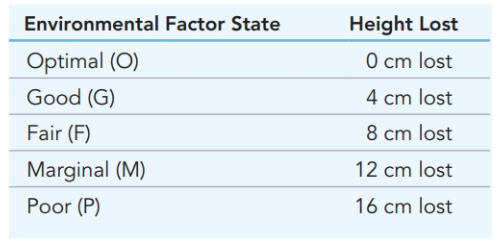
Thus, for example, if one environmental factor is optimal, two are good, one is fair, and one is marginal, the loss of potential height is
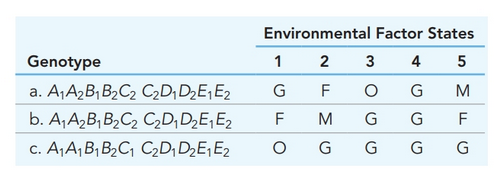
a. Calculate the potential height, based on inherited alleles, and the attained height, based on growth in the environmental circumstances given, for the three plants (a, b, and c) in the accompanying table.
b. How many
c. List two genotypes that have a height potential of
d. If two plants that each have a height potential of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Consider the following hypothetical gene a plant.Gene T produces a protein that impacts stem length.There are two alleles for gene T, T which produces long stems and t which results in short stems. Assume that gene T displays complete dominance, what would be the genotypes (written as two letters-your answer will be case sensitive) that correspond to- homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive and heterozygous. and the phenotypes (what trait will be observed in the plant) for each of the genotypes.arrow_forwardA heterozygous plant with genotype Aa self-pollinates. Find the probability that an offspring is tall for the following genetic systems. Half of heterozygous plants and one fourth of homozygous plants are tall (it depends on their position in the greenhouse)arrow_forwardVariations in Gene Expression In a cross involving polygenic inheritance, three (3) gene pairs control plant height. The shortest and tallest plants are 12 cm and 24 cm, respectively. What height should all F1s display if the shortest and tallest plants were crossed, assuming environmental factors are the same. COMPLETE SOLUTION.arrow_forward
- A heterozygous plant with genotype Aa self-pollinates, and then its offspring also self-pollinate. Find the probability that the offspring of the offspring are tall for the following genetics systems. Half of heterozygous plants and one fourth of homozygous plants are tall (it depends on their position in the greenhouse).arrow_forwardIf an allotetraploid species is made up of two ancestral genomes, A and B, with each of them having a basic chromosome number of seven. The resistance to the pathogen attacking the foliage of plants is controlled by a dominant allele located at the F locus. The recessive alleles F^a and F^b show sensitivity to the pathogen. Plants with at least on F^A allele are resistant to the pathotype 1 and 2 (regardless of the genotype in B genome), and plants with at least one F^B allele are resistant to pathotypes 1 and 3 (regardless of genotype in A genome). What proprtion of the self-progeny of F^AF^a F^BF^b plant will be resistant to pathotype 1, 2 and 3?arrow_forwardOn pea plants, the location of flower growth is an inheritable trait. Axial flower position (A) is dominant over the recessive trait of terminal flower position (a). In the parental generation, a homozygous dominant axial flower position pea plant is crossed with a terminal flower position pea plant. 1. Draw a digital Punnett square of the F1 offspring producing the F2 offspring. 2. In the F2 generation, what is the probability one plant will have a terminal flower position? 3. In the F2 generation, what is the probability two plants will have axial flower positions? Show all work digitally.arrow_forward
- In garden pea plants, tall stem height (T) is dominant over short stem height (t), and green pod colour (G) is dominant over yellow pod colour (g). Some Genotypes of Pea Plants TTGG TTGg TTgg TtGG TtGg Ttgg ttGG ttGg ttgg Identify the correct genotypes listed above for the pea plant phenotypes described below. Phenotype Number Pure breeding tall, green pod pea plant Answer Pea plant used for a test cross Answer Heterozygous tall and green pod pea plant Answer Yellow pod heterozygous tall pea plant Answerarrow_forwardPitcher plants can take many forms. You are interested in understanding the genetic control of pitcher formation in pitcher plants. Which of the following is not likely a result you would expect from your QTL study? AV O a. Variation in pitcher size in your F2 population does not exceed that of your parental generation. O b. You were able to reconstitute the phenotypes of the parental generation by selectively breeding F2 individuals. O c. The variation in phenotypes is greater in the F1 population compared to the F2 population. O d. The phenotypes you are interested exhibit a typical Mendelian inheritance.arrow_forwardIn rice, plants homozygous for the recessive allele sd1 are relatively short in stature; heterozygotes are of normal height. Plants carrying one copy of a dominant allele, Xa4 (corresponding to a second gene located on a different chromosome), are resistant to bacterial blight. Note that both the sd1 and Xa4 alleles would be considered "mutant" alleles in this scenario. A farmer obtained two pureline plants (one is homozygous for the sd1 mutant and the other is homozygous for the Xa4 mutant) and crossed them. Assume both pureline plants have identical alleles at all other loci, and no other mutant alleles are present in these two plants, which of these statements is correct? O All the progeny will be susceptible to bacterial blight and will be short. O When a progeny plant from the cross goes through meiosis, gametes will either contain sd1 or Xa4 alleles, but never both. O When a progeny plant from the cross goes through meiosis, four possible types of gametes that may form, and the…arrow_forward
- Many beautiful varieties of roses have been produced, particularlyin the last few decades. These newer varieties often have verystriking and showy flowers, making them desirable as horticulturalspecimens. However, breeders and novices alike have noticed thatsome of these newer varieties are not very fragrant compared withthe older, more traditional varieties. From a genetic point of view,suggest an explanation why some of these newer varieties withsuperb flowers are not as fragrant.arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothetical gene a plant. Gene T produces a protein that impacts stem length. There are two alleles for gene T, T which produces long stems and t which results in short stems. If gene T displays incomplete dominance, which of the following genotypes above would have a different phenotype? and What would the phenotype be for this genotype?arrow_forwardAssuming you planted bean seeds that have been obtained from the same parent bean plant in three plots where growth conditions are the same except soil pH which varies as shown in the table attached which shows the effects of soil fertility on bean yields obtained from three plots where seeds from the same parent bean plant were obtained. a) is the trait, bean yield, qualitative (monogenic ) or quantitative (polygenic). Supoort tour answer with good reasoning.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





