
Interpretation:
Two isomeric ethyl esters that have six carbon atoms and saturated carbon chain has to be given with their IUPAC names.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are represented shortly by the molecular formula and structural formula. Each and every compound has its own molecular formula. Compounds can have same molecular formula but not same structural formula.
Isomers are the compounds that have same molecular formula but different structural formula. The main difference lies in the way the atoms are arranged in the structure. Isomers have different chemical and physical properties even when they have same molecular formula.
For naming an ester, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains an acyl group and an alkyl group.
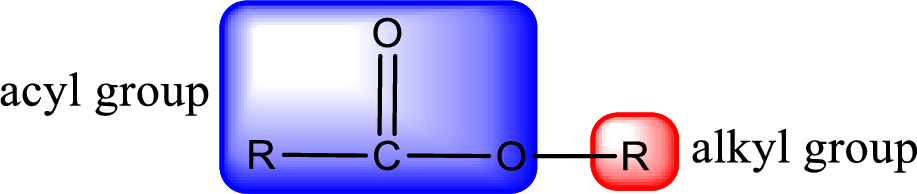
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an ester:
- Alkyl part appears first in the IUPAC name and it is followed by the acyl part of ester as a separate word.
- Name of the alkyl part in the ester is just a name of R group. It can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, or aryl group.
- Acyl part present in the ester is named by considering the acid name and replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
- To obtain the common name the alkyl part name is the same while the acyl part name is derived from the common name of the acid by replacing the suffix “-ic acid” with “-ate”.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Select to Edit Arrows H H Select to Add Arrows > H CFCI: Select to Edit Arrows H Select to Edit Arrowsarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





