
Concept explainers
(a)
The definition of two-cart system.
The speed of the cart C at the bottom of the incline.
(a)
Answer to Problem 31SSC
The velocity of the cart C at the bottom of the incline is
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The weight of the cart at the top of the ramp is
The weight of the cart at the bottom of the ramp is
The angle made by the ramp with the horizontal is
The length of the ramp is
Calculation:
Show the system of the carts as shown in the Figure below:
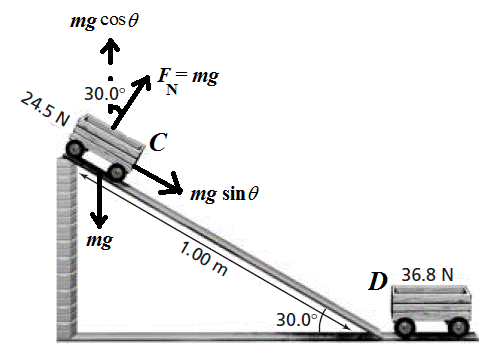
Refer the Figure,
Two Cart System:
Consider the cart at the top of the ramp is denoted by cart C.
Consider the cart at the bottom of the ramp is denoted by cart D.
The cart D is initially at rest.
The cart C which is initially at rest, start moving down the ramp.
Find the acceleration of the cart C using the relation:
Show the relation between the velocity and acceleration of the cart C as follows:
Here,
The initial velocity of the cart C is
Find the final velocity of the cart C as follows:
Hence, the velocity of the cart C at the bottom of the incline is
Conclusion:
Thus, the velocity of the cart C at the bottom of the incline is
(b)
The initial velocity of the carts which stick together.
(b)
Answer to Problem 31SSC
The velocity of the carts which are stick together is
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The weight of the cart at the top of the ramp is
The weight of the cart at the bottom of the ramp is
The angle made by the ramp with the horizontal is
The length of the ramp is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
The initial velocity of the cart C is denoted by
The initial velocity of the cart D is denoted by
The mass of the cart C is denoted by
The mass of the cart D is denoted by
Find the velocity of the cart which stick together, using the relation:
Multiply both sides of the Equation by the acceleration due to gravity
Conclusion:
Thus, the velocity of the cart which are stick together is
Chapter 9 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- A beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .arrow_forwardAn aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?arrow_forwardROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forward
- Question B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forwardPage 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Iarrow_forwardHow would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?arrow_forward14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





