
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134604718
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino, Darrell Killian
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 19ESP
Researchers examined a family with an interesting distribution of Leigh syndrome symptoms. In this disorder, individuals may show a progressive loss of motor function (ataxia, A) with peripheral neuropathy (PN, meaning impairment of the peripheral nerves). A mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutation that reduces ATPase activity was identified in various tissues of affected individuals. The accompanying table summarizes the presence of symptoms in an extended family.
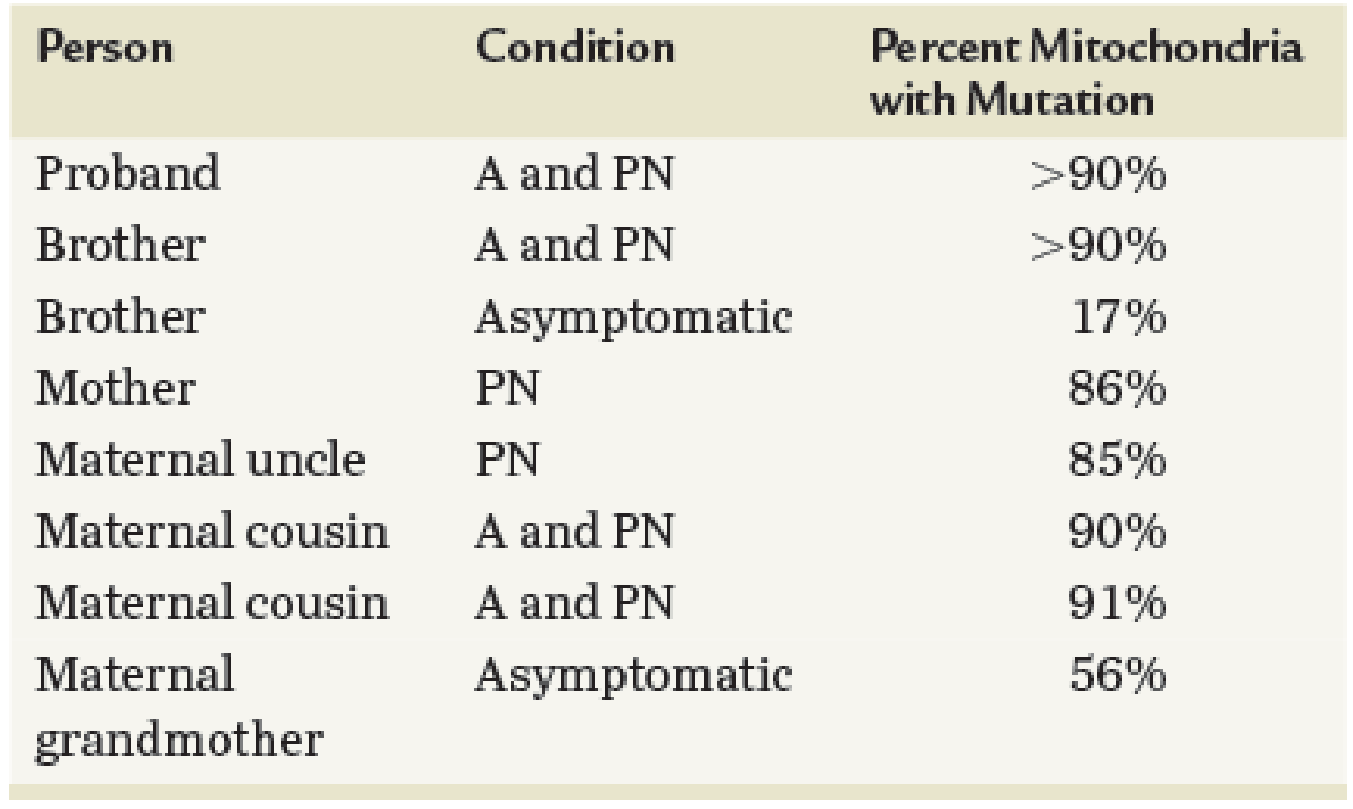
- (a) Develop a pedigree that summarizes the information presented in the table.
- (b) Provide an explanation for the pattern of inheritance of the disease. What term describes this pattern?
- (c) How can some individuals in the same family show such variation in symptoms? What term, as related to organelle heredity, describes such variation?
- (d) In what way does a condition caused by mtDNA differ in expression and transmission from a mutation that causes albinism?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Below is a pedigree of a human genetic disease in which solid color indicates affected individuals. Assume that the disease is caused by a gene that can have the alleles A or a.
a) Based on this pedigree, what is the most likely mode of inheritance?
b) What is/are the possible genotype/s of person 1?
c) What is/are the possible genotype (s) of person 4 ?
Explain your answers.
Take the example of B-thalassemia, an autosomal recessive genetic disease that particularly affects people from around the Mediterranean. This disease is associated with an anomaly of hemoglobin, a protein essential for the transport of oxygen, which is composed of four chains: two alpha (a) and two beta (B). In case of B-thalassemia, the ẞ chains are produced in insufficient or no quantity in an individual homozygous recessive resulting in insufficient production of overall hemoglobin leading to anemia and other physiological challenges.
The gene that controls the synthesis of the ẞ chains is located on chromosome 11. Here is part of the coding portion of this gene (which controls a total of 146 amino acids and of which you only see the portion 36 to 41) and one of the targeted mutations:
1. Give the sequence of amino acids from the template and mutated strands. 2. What type of point mutation is it?
3. Using the principles of the theory of evolution, explain briefly and generally why…
The attached image is a pedigree of a family with a history of sickle cell anemia (the individuals with the filled-in symbols have the disease and no new mutations are occurring in any individual). Sickle cell anemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. What is the probability that the individual with the question mark (?) will get the disease?
a) 1/4
b) 1/2
c) 2/3
d) 1
Chapter 9 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Ch. 9 - Chlamydomonas, a eukaryoric green alga, may be...Ch. 9 - In aerobically cultured yeast, a petite mutant is...Ch. 9 - DNA in human mitochondria encodes 22 different...Ch. 9 - Prob. 4NSTCh. 9 - Why did Marcia choose mitochondrial testing to...Ch. 9 - Marcia saw an ad on television for ancestry DNA...Ch. 9 - How much importance should we place on the results...Ch. 9 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on...Ch. 9 - Review the Chapter Concepts list on page 196. The...Ch. 9 - Streptomycin resistance in Chlamydomonas may...
Ch. 9 - A plant may have green, white, or green-and-white...Ch. 9 - In diploid yeast strains, sporulation and...Ch. 9 - Predict the results of a cross between ascospores...Ch. 9 - In Lymnaea, what results would you expect in a...Ch. 9 - In a cross of Lymnaea, the snail contributing the...Ch. 9 - In Drosophila subobscura, the presence of a...Ch. 9 - A male mouse from a true-breeding strain of...Ch. 9 - Consider the case where a mutation occurs that...Ch. 9 - What is the endosymbiotic theory, and why is this...Ch. 9 - In an earlier Problems and Discussion section (see...Ch. 9 - Mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT) offers a...Ch. 9 - The specification of the anteriorposterior axis in...Ch. 9 - The maternal-effect mutation bicoid (bcd) is...Ch. 9 - (a) In humans the mitochondrial genome encodes a...Ch. 9 - Mutations in mitochondrial DNA appear to be...Ch. 9 - Researchers examined a family with an interesting...Ch. 9 - Payne, B. A. et al. (2013) present evidence that a...Ch. 9 - As mentioned in Section 9.3, mtDNA accumulates...Ch. 9 - Because offspring inherit the mitochondrial genome...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3) Achondroplasia is a common form of hereditary dwarfism that causes very short limbs, stubby hands, and an enlarged forehead. Below are three pedigrees depicting families with this specific type of dwarfism. A. What is the most likely mode of inheritance?arrow_forwardAlbinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait.Determine the genotypes of the parents and offspring for the following families. When two alternative genotypes are possible,list both.(a) Two parents without albinism have five children, four withoutalbinism and one with albinism.(b) A male without albinism and a female with albinism havesix children, all without albinism.arrow_forwardIn humans, the genetic disease cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele (a). The normal (healthy) allele is dominant (A). What is the genotype of someone who has cystic fibrosis? What are the two different genotypes that a healthy person could have? If two people were both heterozygous for the cystic fibrosis gene, what fraction of their children would be likely to have this disease? Hint: Draw a Punnett square to figure it out.arrow_forward
- a. On the basis of this pedigree, what is the most likely mode of inheritance for the disease? Explain your reasoning. b. Based your answer to part a, give the most likely genotypes for all family members in the pedigree.arrow_forwardNow assume that the pedigree shown in question 1 shows the inheritance of a rare genetic disease. a) The disease is most likely autosomal dominant b) The disease is most likely autosomal recessive c) The disease is equally likely to be either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive, but cannot be x-linked d) Cannot be determined from the information givenarrow_forwarda) Which of the four modes of inheritance are consistent with the disease shown in this human pedigrees below? (List the compatible mode or modes) Give an answer for a, b and c b) If the parents in pedigree c have 2 other children, what is the probability that they will carry the disease?arrow_forward
- Hemophilia A is caused by a sex-linked recessive gene in human and in dogs. a. What proportions (and sexes), among their offspring will be hemophiliacs if a hemophilic male is mated to a homozygous nonhemophilic female?b. If a daughter produced by the mating in (a) is mated to a normal male, what proportions and (sexes) will be hemophilic among their offspring?arrow_forwardCystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive trait. A three-generation pedigree is shown below for a family that carries the mutant allele for cystic fibrosis. Note that carriers are not colored in to allow you to figure out their genotypes. Normal allele = F CF mutant allele = f What is the genotype of individual #13? A) ff B) FF C) Ff D) it is impossible to tellarrow_forwardUsing the pedigree chart, explain: a) The number of generations seen. b) If all blue-coloured shapes are affected with disease X- how many males are affected? how many females are affected? c) Does this disease have a dominant or recessive inheritance pattern? Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- Consider the following pedigree. Solid symbols represent individuals affected by the trait. Assume complete penetrance and non-variable expressivity. II 3 4 III 1 2 3 5 6 a) what is the mode of inheritance of this trait? b) Does the ratio of affected to unaffected offspring in generation III-1 to 1II-4 match the expected ratio for this mode of inheritance? Explain your answer in terms of the expected ratio versus the ratio observed. Give a reason for your answer. No mark is assigned for yes or no)arrow_forwardAn unaffected woman for a human disorder marries and unaffected man and they have children. This results in 3 affected sons, and one unaffected daughter, which ends up having children later on with an unaffected man and has 2 affected sons. A) Draw a simple pedigree diagram for this family, including a legend. B) What is the likely mode of inheritance of this trait: Please explain C) Provide the genotypes of the original mother and the daughter. Use a capital letter for the dominant allele and lowercase letter for the recessive allele. D) If one of the affected sons from the original marriage marries a 2nd cousin that is a carrier of this trait and has children, what is the probability that they will have 3 affected sons?arrow_forwardThe complete absence of one or more teeth (tooth agenesis) is a common trait in humans—indeed, more than 20% of humans lack one or more of their third molars. However, more severe tooth agenesis, defined as the absence of six or more teeth, is less common and is frequently an inherited condition. L. Lammi and colleagues examined tooth agenesis in the Finnish family shown in the pedigree below. Q.If IV-2 married a man who had a full set of teeth, what is the probability that their child would have tooth agenesis?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY