
(a)
Interpretation:
Structure of the missing substance that involves in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
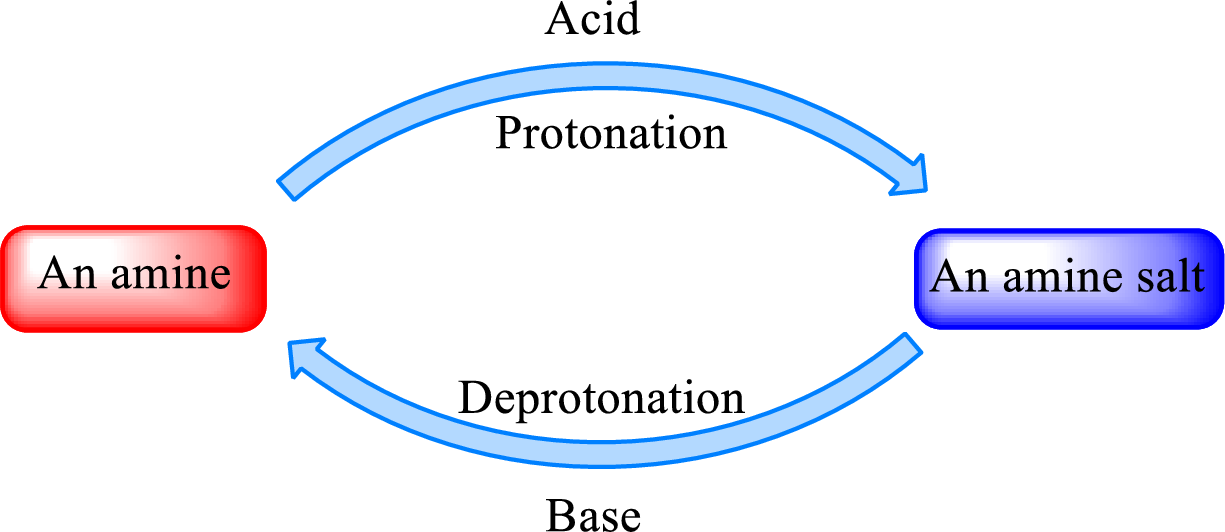
Neutralization reaction is the one that takes place between an acid and a base to give salt as product. As
When a strong base is added to the amine salt, the parent amine can be obtained. This is a reverse reaction of the amine salt formation reaction. These reactions can be represented as shown below,
(b)
Interpretation:
Structure of the missing substance that involves in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
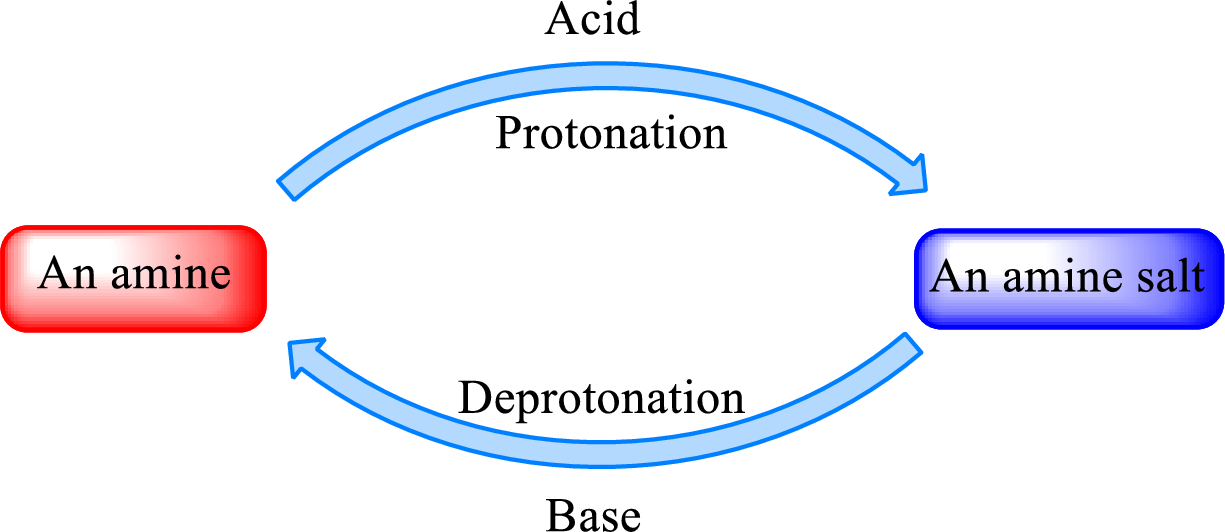
Neutralization reaction is the one that takes place between an acid and a base to give salt as product. As amines are bases due to the amino group in it, the reaction with inorganic acid or carboxylic acid gives salt as product. The salt formed is an amine salt. Proton is donated from the acid to the nitrogen atom which acts as a proton acceptor. In simple words, it can be said that in an amine‑acid reaction, the acid loses a hydrogen ion and amine gains a hydrogen ion.
When a strong base is added to the amine salt, the parent amine can be obtained. This is a reverse reaction of the amine salt formation reaction. These reactions can be represented as shown below,
(c)
Interpretation:
Structure of the missing substance that involves in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
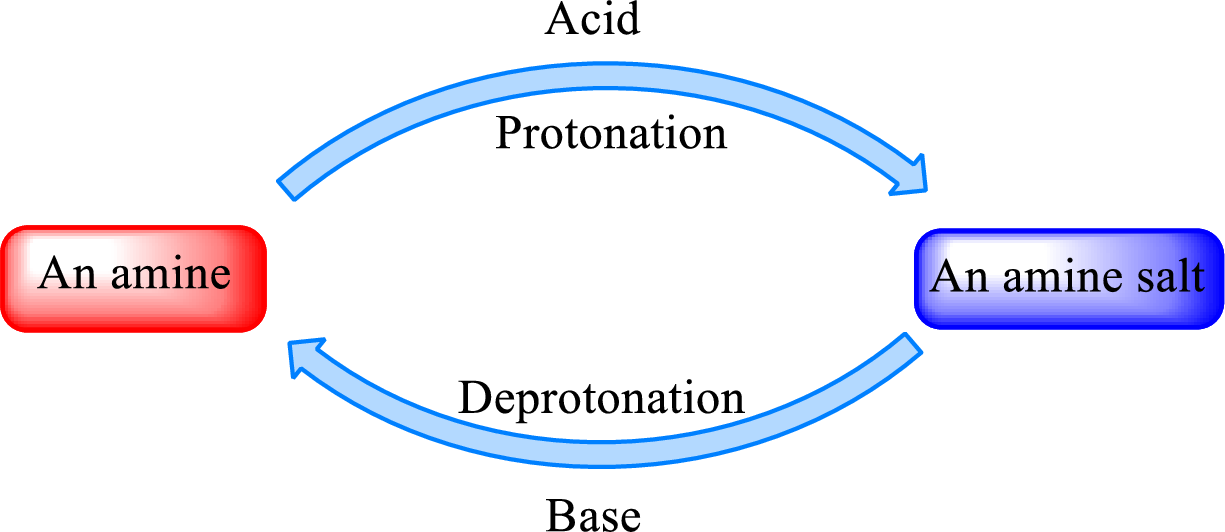
Neutralization reaction is the one that takes place between an acid and a base to give salt as product. As amines are bases due to the amino group in it, the reaction with inorganic acid or carboxylic acid gives salt as product. The salt formed is an amine salt. Proton is donated from the acid to the nitrogen atom which acts as a proton acceptor. In simple words, it can be said that in an amine‑acid reaction, the acid loses a hydrogen ion and amine gains a hydrogen ion.
When a strong base is added to the amine salt, the parent amine can be obtained. This is a reverse reaction of the amine salt formation reaction. These reactions can be represented as shown below,
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of the missing substance that involves in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
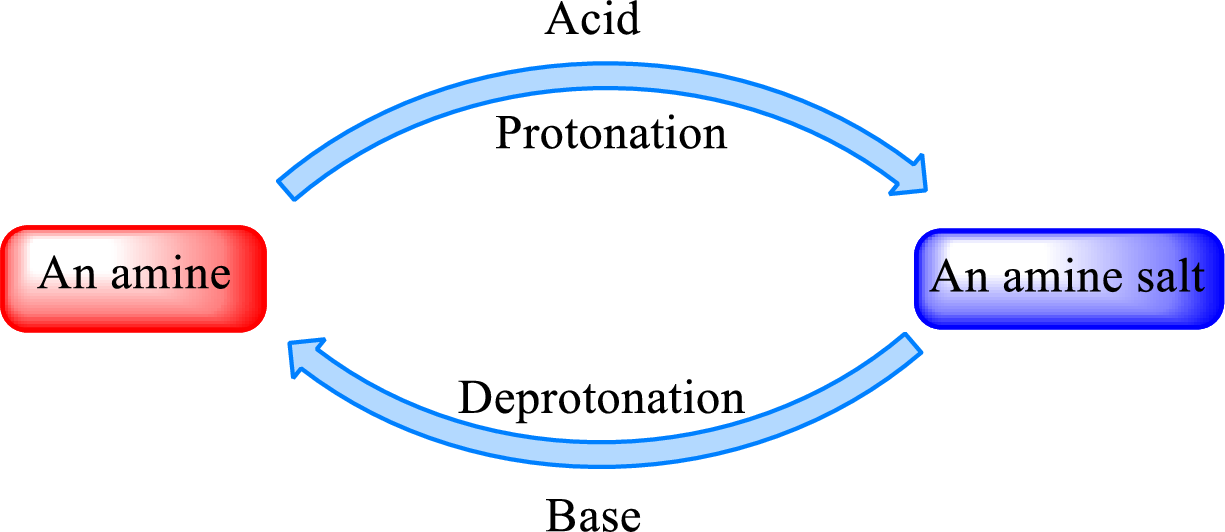
Neutralization reaction is the one that takes place between an acid and a base to give salt as product. As amines are bases due to the amino group in it, the reaction with inorganic acid or carboxylic acid gives salt as product. The salt formed is an amine salt. Proton is donated from the acid to the nitrogen atom which acts as a proton acceptor. In simple words, it can be said that in an amine‑acid reaction, the acid loses a hydrogen ion and amine gains a hydrogen ion.
When a strong base is added to the amine salt, the parent amine can be obtained. This is a reverse reaction of the amine salt formation reaction. These reactions can be represented as shown below,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Write the systematic (IUPAC) names for the amines. The names should have the format alkanamine. H₂C-N-CH3 H3C-CH2-CH-CH3 systematic (IUPAC) name: HC-N-CH2-CH3 HC-CH2-CH2-CH₂ systematic (IUPAC) name: These compounds are amines.arrow_forward< app.101edu.co Classify and describe the properties of the following nitrogen containing compound. O CI O + Question 13.a of 25 CH3 N Classify the following amine. H CH3 A) primary amine B) secondary amine C) tertiary amine @=J D) tertiary amine salt E) quaternary ammonium saltarrow_forwardComplete this table for different amine compounds. Chemical propylamine quaternary ammonium ion methylphenylamine Molecular formula C3H9N C₂H7N C5H13N C4H10N Structural formula (CH3)3N (CH3)2NH CH 3 I (CH₂) 11 | H3C(CH2) 11 -N-(CH₂)11CH3 NHCH3 (CH₂)11 CH3 CH3CH2CH2-NH-CH3 + Classification Tertiary Quaternary Tertiary Secondaryarrow_forward
- Choose the Aromatic compound from the list below: O a) diethyl ether Ob) methanol Oc) benzene d) propanoic acidarrow_forwardamine, (2) an amide, or (3) both an amine and an amide. 17-106 Classify each of the following compounds as (1) an amine, (2) an amide, or (3) both an amine and an NH2 b. `NH a. H2N H d. с.arrow_forwardSketch the product, Then writeh the IUPAC NAME OF THE AMINE PRODUCT and the dominant Intermolecular force for the product. CH, NH, + H -CI O CH3-NH3*Cr, methylammonium chloride (Amine Product: H-Bond) O CH3-CH3-NH3*Cl', ethylammonium chloride (Amine Product: H-Bond) O CH3-NH3*, methylammonium ion (Amine Product: Dipole-Dipole) +. O CH3-NH3*CI , ethylammonium chloride (Amine Product: H-Bond) O CH3-NH3*CI', ethylammonium chloride (Amine Product: Dipole-Dipole) CH3-NH3*Cl", methylammonium chloride (Amine Product: lonic)arrow_forward
- Do not give handwriting solution.arrow_forward13. Write the chemical reaction for the base hydrolysis of each amide sample. Include the condensed structural formulas of the reactants and products. ACETAMIDE BENZAMIDEarrow_forwardWhich functional groups, or functional group and reagent, combine to make an amine? O Alkene O Ketone O Carboxylic acid Amide O Acid O Water O Oxidant Reductantarrow_forward
- Question 16.arrow_forwardWrite structural formulas for these amines. a) Isopropylaminearrow_forwardWhich statements are true about amines? NH3+ is the form found in our blood amines can react with aldehydes to produce ethers amines act as weak acids in aqueous solutions amines can react with carboxylic acid to produce alcoholsarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





