
Concept explainers
To name:
The pathways diagrammed in parts (a), (b), and (c) of the given figure.
Introduction:
Cellular mechanisms involved in many reactions in which the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another take place by means of
Explanation of Solution
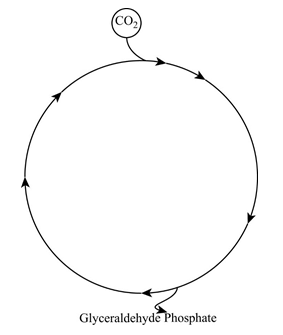
- The given diagram is the Calvin-Benson cycle. In this cycle, three molecules of carbon dioxide are fixed and one molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is produced. After that, it leaves the cycle is shown in the below diagram.
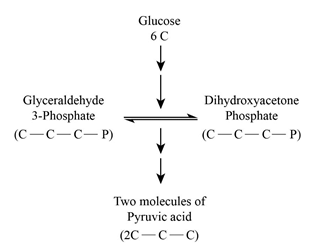
- The given b diagram resembles the Glycolysis pathway. In this pathway, the oxidation of glucose yields two molecules of pyruvic acid as its end product.
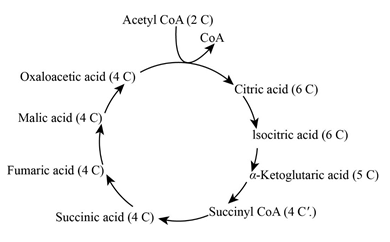
- The below-given diagram is the Kreb’s cycle. Here, the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid produces one carbon dioxide molecule and one acetyl group.
To review:
The anabolic and catabolic mechanisms in the given pathways.
Introduction:
The cellular mechanism of all living organisms requires the energy for its
Explanation of Solution
Glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle are the major pathways for anabolic and catabolic mechanisms of all organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Glycerol is catabolized as Dihydroxyacetone phosphate in the Glycolysis pathway (a) and fatty acids are catabolized as acetyl CoA int he TCA cycle (b).
Glutamic acid is catabolized in the Krebs cycle (c). Glutamic acid is an amino acid which is catabolized by Kreb’s cycle at α-ketoglutaric acid which is formed from isocitric acid.
In the Calvin-Benson cycle, Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is the end product, which enters into glycolysis. In glycolysis, the glucose is oxidized into pyruvate which is decarboxylated to acetyl group and entered into the Kreb’s cycle.
The Calvin cycle requires 18 molecules of ATP between glucose and glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate.
Three molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) is released in the Kreb’s cycle,
- Between pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
- Between isocitric acid to α-ketoglutarate (TCA cycle).
- Between α-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA.
The long chain hydrocarbon like such as acetyl group is catabolized in the TCA cycle at acetyl CoA. This acetyl group like hydrocarbons are catabolized by beta-oxidation which enters into the Kreb’s cycle.
The production of NADH, FADH2 or NADH in glycolysis, Calvin-Benson and TCA cycles are,
The anabolic and catabolic pathways are integrated between,
- In glycolysis, the anabolic and catabolic pathways integrated into dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
- In the TCA cycle, the anabolic and catabolic pathways integrated into acetyl, oxaloacetic acid and ketoglutaric acid.
| Utilizes | Produces | |
| Glycolysis | 2 NADH | |
| Calvin-Benson cycle | 6 NADPH | |
| Pyruvate to acetyl CoA | 1 NADH | |
| Isocitrate to α-ketoglutaric acid | 1 NADH | |
| α-keto-glutaric to succinyl CoA | 1 NADH | |
| Succinate to fumarate | 1 FADH2 | |
| Malate to oxalate | 1 NADH |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
- Below is a list of steps that occur after an exercising muscle cell begins degrading amino acids for ATP production. For each step, choose (A) if the process occurs in the muscle cell and (B) if the process occurs in the liver. It will be easiest to answer this question if you first put the steps in order, then decide in which organ they occur. ______ Alanine is transaminated with a-ketoglutarate.______ Branched chain amino acids are transaminated with a-ketoglutarate.______ Glutamate is deaminated.______ Glutamate is transaminated with pyruvate.______ Ketoacid skeletons resulting from branch chain amino acids enter the CAC.______ Pyruvate enters gluconeogenesis.______ Urea is formed from the nitrogen removed from the original branched chain amino acid.arrow_forwardRegarding phosphofructokinase, which of the following statements is true: a. Low [ATP] stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits. b. High [ATP] stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits. c. The enzyme is more active at low [ATP] than at high, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates the enzyme. d. High [ATP] stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements concerning the enzyme regulation is CORRECT? Select one: A. Citrate is the allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase. B. AMP is the alloseric activator of pyruvate dehydrogenase. C. Glucose-6-phosphate is the allosteric activator for phosphofructokinase. D. ATP is the activator of pyruvate kinase.arrow_forward
- A patient complains of painful muscle cramps when performing strenuous physical exercise. A muscle biopsy indicates a higher than normal concentration of muscle glycogen. a. Which enzyme of glycogen metabolism is affected? b. Discuss how the defect of this enzyme affects glycogen metabolism.arrow_forwardThe following are the negative regulators of phosphofructokinase except Select one: a. AMP +b. H c. Citrate d. ATParrow_forwardThe reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase involves two "sub-reactions", one of which is unfavourable. How is the energy barrier of this unfavourable sub reaction overcome? A. through the formation and hydrolysis of a thioester bond using a cysteine molecule in the enzyme B. through the hydrolysis of an ATP molecule C. through the hydrolysis of a thioester bond in the substrate molecule D. the enzyme catalyzes the formation of a thioester bond E. none of these explanations describe how the energy barrier is overcome Please answer asaparrow_forward
- What are the correct names of the items, I, II and III in the reaction given below? a. Fructose-6P / Phosphofructokinase / Ribose-1,6P b. Glucose-6P / Hexokinase / Glucose-1,6 P c. Fructose-6P / Glucokinase / Glucose-1,6 P d. Fructose-6P/ Phosphofructokinase / Fructose-1,6 P e. Fructose-6P / Phosphoglucose isomerase / Fructose-1,6 Parrow_forwardThe molecule shown below is an important compound involved in glucose metabolism. CH2 OH CH,OH но a. What is the name of this compound? b. Draw the structure of the precursor of this molecule. What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the product? c. Discuss how the hormone glucagon affects the concentration of this molecule. Include in your discussion the role this molecule has in glucose metabolism and its regulation.arrow_forwardWhen transaminated, the three branched-chain amino acids (valine, leucine, and isoleucine) form compounds that have the characteristic odor of maple syrup. An enzyme known as branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase converts these compounds into CoA esters. People who do not have this enzyme have the genetic disease known as maple syrup urine disease, so called because their urine smells like maple syrup. a. Draw the compounds that smell like maple syrup.b. Draw the CoA esters.c. Branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase has five coenzymes. Identify them.d. Suggest a way to treat maple syrup urine disease.arrow_forward
- During cellular respiration, 60 molecules of CO2 were given off as waste. a. How many pyruvate molecules were produced in glycolysis? b. The total amount of ATP produced by complete cellular respiration would be? c. The amount of energy available (Net ATP) to cell as ATP would be?arrow_forwardOrder the steps that results in a triacylglycerol containing two palmitic acids and one stearic acid. a. Diacylglycerol reacts with an fatty-acyl-CoA b. Phosphate is remove from phosphatidic acid to form diacylglycerol c. Two of the fatty acyl-CoAs react with glycerol-3-phosphate d. An elongase produce stearic acid e. Stearoyl-CoA is synthesized…arrow_forwardCyanide is a rapidly acting, potentially deadly chemical that can exist in various forms. If accidentally ingested or inhaled, cyanide can cause rapid death by binding to complex IV (cytochrome oxidase) of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria. A.What is the mechanism by which cyanide stops cellular respiration? Be specific. B.Does cyanide cause an effect at the beginning or the end of the cellular respiration pathway? C.Does this make a difference on the effect that this chemical can have on our cells? Why? D.How does cyanide’s course of action affect the remainder of the cellular respiration pathway? E.If a person accidentally swallows cyanide, mention a potential treatment that is currently available. What is the mechanism of action of this treatment? Be specific. Please answer completely will give rating surely All questions answers neededarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





