
Concept explainers
(a)
The force exerted on the boulder to move it up the mountain with constant velocity.
(a)
Answer to Problem 102A
The force exerted on the boulder to move it up the mountain with constant velocity is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass
The coefficient of kinetic friction
The angle made by the surface of the mountain with the horizontal is
Formula used:
The expression for the kinetic friction acting on a moving object is as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
For the given specifications, the free body diagram of the situation is shown below.
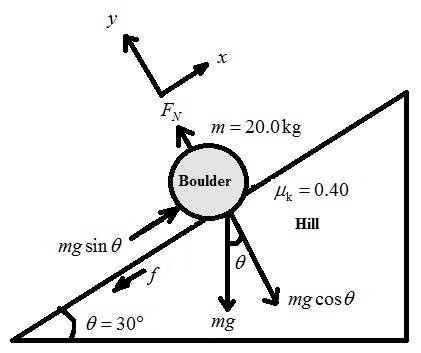
Find the normal force
The kinetic frictional force acting on the person is,
The person has to apply force equal to the kinetic friction to move the boulder up the hill.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted by the person S on the boulder to move it up the mountain with constant velocity is
(b)
The height of the mountain.
(b)
Answer to Problem 102A
The height of the mountain is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass
The coefficient of kinetic friction w
The angle made by the surface of the mountain with the horizontal is
The initial velocity of the person S is
The time taken by the person S to reach the top of the hill is
Formula used:
The distance travelled according to second equation of motion is,
Here,
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity of Earth is
Consider the height of the hill is denoted by
The height of the hill as follows:
Conclusion:
Therefore, the height of the hill is
Chapter 5 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
College Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics (10th Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





