
Interpretation:
A structure for atropine (C17H23NO3) is to be proposed from the following observations: i) On basic hydrolysis atropine yields tropic acid C6H5CH(CH2OH)COOH and tropine (C8H15NO). ii) Tropine is an optically inactive alcohol that yields tropidene on dehydration with H2SO4.
Concept introduction:
Esters when hydrolyzed with bases yield alcohols and
To predict:
A structure for atropine (C17H23NO3) from the following observations: i) On basic hydrolysis atropine yields tropic acid C6H5CH(CH2OH)COOH and tropine (C8H15NO). ii) Tropine is an optically inactive alcohol that yields tropidene on dehydration with H2SO4.
Answer:
Structure of atropine is
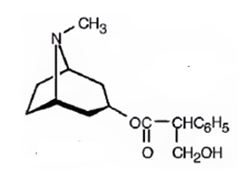
Explanation:
Atropine gives tropic acid and an alcohol, tropine when hydrolyzed in the presence of bases. Hence it must be an ester. Tropine upon dehydration gives tropidene. Hence structure of tropine (optically inactive) can be obtained by adding water to the structure of tropidene.
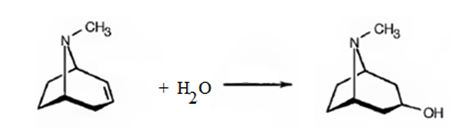
The formation of the ester linkage between the OH of atropine and COOH of tropic acid gives atropine. The reactions can be represented as below.
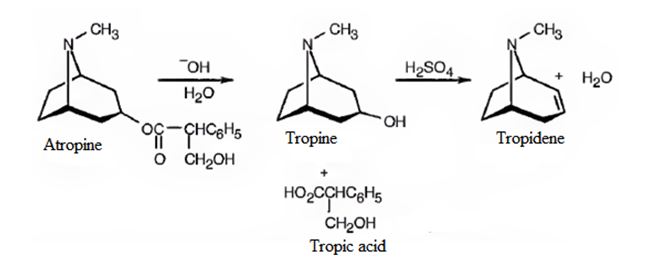
Conclusion:
Structure of atropine is

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- (f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning




