
a.
The reading of ammeter connected in the given circuit.
a.
Answer to Problem 54A
The ammeter reads the current flowing through the circuit and it shows a value
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A circuit consists of two resistors of value,
Formula Used:
The ammeter in a circuit measures the current through the element in series with it. Here, the ammeter measures the total current through the circuit which can be calculated using Ohm’s law as,
Calculation:
Consider the potential divider circuit shown in Figure 1.
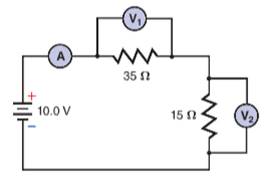
Figure 1
Here, the supply voltage is 10-V and the two resistors have values
Conclusion:
The value read by the ammeter is 0.2 A.
b
The reading of voltmeter 1 connected across a given resistance.
b
Answer to Problem 54A
The voltmeter 1 reads a voltage of value
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A circuit consists of two resistors of value,
Formula Used:
The voltmeter connected across a resistor reads the voltage drop across it. Here, for a given supply voltage and resistors in series, the voltage across each of them can be calculated using the voltage division rule as,
Calculation:
Consider the potential divider circuit shown in Figure 1. Here, the supply voltage is 10-V and the two resistors have values,
Conclusion:
The reading of voltmeter 1 is 7 V.
c.
The reading of voltmeter 2 connected across a given resistance.
c.
Answer to Problem 54A
The voltmeter 2 reads a voltage of value
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A circuit consists of two resistors of value,
Formula Used:
The voltmeter connected across a resistor reads the voltage drop across it. Here, for a given supply voltage and resistors in series, the voltage across each of them can be calculated using the voltage division rule as,
Calculation:
Consider the potential divider circuit shown in Figure 1. Here, the supply voltage is 10-V and the two resistors have values,
Conclusion:
The reading of voltmeter 2 is 3 V.
d.
The energy supplied by the battery in a given time.
d.
Answer to Problem 54A
The energy supplied by the battery in one minute is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A circuit consists of two resistors of value,
Formula used:
The energy supplied by a source E can be expressed in terms of the power dissipation and the time for which power is drawn, t, as
The power drawn by the circuit is a function of its resistance R and current flowing through it, I which can be expressed as,
Calculation:
Since the circuit has two resistors in series, the equivalent resistance value is
Substituting the current and resistance value, the power can be obtained as,
The energy supplied is to be calculated for a duration of one minute. Now, substituting the value of power and time, the energy can be calculated as,
Conclusion:
The energy supplied by the battery for a given time is 120 J.
e.
The equivalent resistance of the circuit.
e.
Answer to Problem 54A
The equivalent resistance of the circuit is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
A circuit consists of two resistors of value,
Formula used:
The equivalent resistance of two resistors in a series circuit is given by,
Calculation:
Substituting the individual resistance values, the equivalent resistance value is
Conclusion:
The equivalent resistance of the circuit is
Chapter 23 Solutions
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
College Physics (10th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





