
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.8, Problem DQ
The following sequence of steps is used to create the
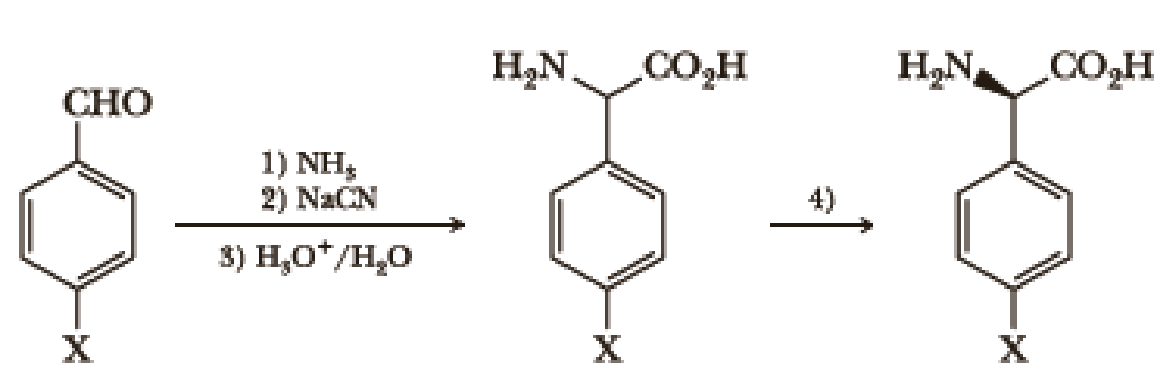
- 1. Step 1 would best be performed at a pH below the pKa of ammonium.
- 2. Step 1 would create an imine that undergoes nucleophilic attack by cyanide in Step 2.
- 3. The hydrolysis of the nitrile created in Step 2 would be better performed in base rather than the acid shown.
- 4. Step 4 is a resolution of a racemic mixture that results from Steps 1–3 and does not require a chiral reagent.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting
Don't used Ai solution
Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.1PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.2PCh. 18.4 - Prob. 18.3PCh. 18.4 - Prob. 18.4PCh. 18.4 - Synthesis of nitriles by nucleophilic displacement...Ch. 18.5 - Complete the following transesterification...Ch. 18.6 - Complete and balance equations for the following...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. AQCh. 18.8 - Several compounds have been found to inhibit...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. CQ
Ch. 18.8 - The following sequence of steps is used to create...Ch. 18.9 - Prob. 18.8PCh. 18.9 - Prob. 18.9PCh. 18.10 - Prob. 18.10PCh. 18.10 - Show how to convert (R)-2-phenylpropanoic acid to...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.12PCh. 18 - Write the IUPAC name for each compound. (a)...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.14PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.15PCh. 18 - Propose a structural formula for compound A,...Ch. 18 - Propose a structural formula for compound B,...Ch. 18 - Propose a structural formula for each compound...Ch. 18 - Draw a structural formula for the principal...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.20PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.21PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.22PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.23PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.24PCh. 18 - Show the product expected when the following...Ch. 18 - The reagent diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBALH)...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.27PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.28PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.29PCh. 18 - Nicotinic acid, more commonly named niacin, is one...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.31PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.32PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.33PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.34PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.35PCh. 18 - Isoniazid, a drug used to treat tuberculosis, is...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.37PCh. 18 - A step in a synthesis of PGE1 (prostaglandin E1,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.39PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.40PCh. 18 - Show how to synthesize 5-nonanone from...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.42PCh. 18 - The following sequence of steps converts...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.44PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.45PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.46PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.47PCh. 18 - Following is a retrosynthetic analysis for the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.50PCh. 18 - Given this retrosynthetic analysis, propose a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.52PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.53PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.54PCh. 18 - In Problem 7.28, we saw this step in Johnsons...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.56PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.57PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.58PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.59PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.60PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.61PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.62PCh. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Minoxidil is a molecule that causes hair growth in...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.69PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.70PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.71P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Why are mutants used as test organisms in the Ames test?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
What process causes the Mediterranean intermediate Water MIW to become more dense than water in the adjacent At...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
More than one choice may apply. Using the terms listed below, fill in the blank with the proper term. anterior ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Differentiate between single links and multicenter links.arrow_forwardI need help on my practice final, if you could explain how to solve this that would be extremely helpful for my final thursday. Please dumb it down chemistry is not my strong suit. If you could offer strategies as well to make my life easier that would be beneficialarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Definition and classification of boranes.arrow_forwardWhich of the terms explain the relationship between the two compounds? CH2OH Он Он Он Он α-D-galactose anomers enantiomers diastereomers epimers CH2OH ОН O он Он ОН B-D-galactosearrow_forwardHi, I need help on my practice final, If you could offer strategies and dumb it down for me with an explanation on how to solve that would be amazing and beneficial.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305446021
Author:Lampman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License