
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 18, Problem 18.58P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The amide formation between the given combination of dicarboxylic acid and diamine will lead to the formation of a polymer has to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Polyamides:
It is a family of
An amide linkage is shown below:
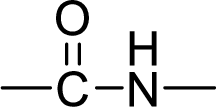
In the polymer nylon-6,6, the carbon atoms are joined together by amide bonds.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Indicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are false
(f) SO:
Best Lewis Structure
3
e group geometry:_
shape/molecular geometry:,
(g) CF2CF2
Best Lewis Structure
polarity:
e group arrangement:_
shape/molecular geometry:
(h) (NH4)2SO4
Best Lewis Structure
polarity:
e group arrangement:
shape/molecular geometry:
polarity:
Sketch (with angles):
Sketch (with angles):
Sketch (with angles):
1.
Problem Set 3b
Chem 141
For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing
bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the
molecule is polar or non-polar (iv)
(a) SeF4
Best Lewis Structure
e group arrangement:_
shape/molecular geometry:
polarity:
(b) AsOBr3
Best Lewis Structure
e group arrangement:_
shape/molecular geometry:
polarity:
Sketch (with angles):
Sketch (with angles):
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 18.1 - Prob. 18.1PCh. 18.2 - Prob. 18.2PCh. 18.4 - Prob. 18.3PCh. 18.4 - Prob. 18.4PCh. 18.4 - Synthesis of nitriles by nucleophilic displacement...Ch. 18.5 - Complete the following transesterification...Ch. 18.6 - Complete and balance equations for the following...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. AQCh. 18.8 - Several compounds have been found to inhibit...Ch. 18.8 - Prob. CQ
Ch. 18.8 - The following sequence of steps is used to create...Ch. 18.9 - Prob. 18.8PCh. 18.9 - Prob. 18.9PCh. 18.10 - Prob. 18.10PCh. 18.10 - Show how to convert (R)-2-phenylpropanoic acid to...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.12PCh. 18 - Write the IUPAC name for each compound. (a)...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.14PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.15PCh. 18 - Propose a structural formula for compound A,...Ch. 18 - Propose a structural formula for compound B,...Ch. 18 - Propose a structural formula for each compound...Ch. 18 - Draw a structural formula for the principal...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.20PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.21PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.22PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.23PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.24PCh. 18 - Show the product expected when the following...Ch. 18 - The reagent diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBALH)...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.27PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.28PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.29PCh. 18 - Nicotinic acid, more commonly named niacin, is one...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.31PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.32PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.33PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.34PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.35PCh. 18 - Isoniazid, a drug used to treat tuberculosis, is...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.37PCh. 18 - A step in a synthesis of PGE1 (prostaglandin E1,...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.39PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.40PCh. 18 - Show how to synthesize 5-nonanone from...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.42PCh. 18 - The following sequence of steps converts...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.44PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.45PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.46PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.47PCh. 18 - Following is a retrosynthetic analysis for the...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.50PCh. 18 - Given this retrosynthetic analysis, propose a...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.52PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.53PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.54PCh. 18 - In Problem 7.28, we saw this step in Johnsons...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.56PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.57PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.58PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.59PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.60PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.61PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.62PCh. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Using your reaction roadmap as a guide, show how...Ch. 18 - Minoxidil is a molecule that causes hair growth in...Ch. 18 - Prob. 18.69PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.70PCh. 18 - Prob. 18.71P
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- reaction scheme for C39H4202 Hydrogenation of Alkyne (Alkyne to Alkene) show reaction (drawing) pleasearrow_forwardGive detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning