
Concept explainers
Interpretation: “The condensed structural formula and IUPAC name of two structural isomers of
Concept introduction:
- Isomers: Compounds which have the same molecular formula, but different physical or chemical properties are known as isomers and the phenomenon is known as isomerism.
- Structural isomerism: The isomers with same molecular formula but different structural formula or different arrangement of atoms in a molecule are known as structural isomers.
- Condensed structural formula: The complete structural formula can be abbreviated by omitting some or all the covalent bonds and by indicating the number of identical groups attached to an atom by a subscript. This is known as condensed structural formula.
- IUPAC: The term IUPAC is International union of pure and applied chemistry. It provides the set of rules for assigning names to organic compounds.
- Rules for determining the IUPAC names
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atom is taken as the parent chain on which the various alkyl groups are considered side chain.
- Numbering is done from that side where
functional group is near. - If more than one functional group is present, then preference is given to that functional group which is senior in the seniority table group
If a side chain occurs more than once, the numerical prefixes di(for two),tri(for three) etc are added before the names of the group.
When there are two identical side chains at one position, numbers are given for each.
To draw and explain: The condensed structural formula, IUPAC name of the isomers of carboxylic acid having molecular formula
Solutions:
The condensed structural formula and IUPAC name of the structural isomers of carboxylic acid having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The carboxylic acid having molecular formula
Let us first draw the two structural isomers of carboxylic acid having molecular formula
a) 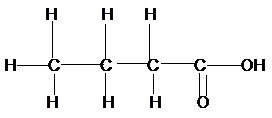
b) 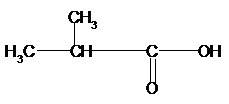
Now for (a), if we count the
Again for (b), if we count the
Therefore, the condensed structural formula, IUPAC name of the structural isomers of carboxylic acid having formula
a)
b)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life (5th Edition)
- scratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forwardA compound has the molecular formula CH40, and shows a strong IR absorption at 2850-3150 cm. The following signals appear in the 'H NMR spectrum: 1.4 ppm (triplet, 6H), 4.0 ppm (quartet, 4H), 6.8 ppm (broad singlet, 4H). Which of the following structures is consistent with these data? Select the single best answer. OCH CH₂ x OCH2CH3 CH₂OCH3 OH CH₂OCH OH CH, OCH₁ CH₂OCH, CH₂OCH HO OH ° CH₂OCH3arrow_forward
- predict the major product while showing me the intermidiate products from each reagent/reagent grouparrow_forwardWhy is it desirable in the method of standard addition to add a small volume of concentrated standard rather than a large volume of dilute standard? An unknown sample of Cu2+ gave an absorbance of 0.262 in an atomic absorption analysis. Then 1.00 mL of solution containing 100.0 ppm (= µg/mL) Cu2+ was mixed with 95.0 mL of unknown, and the mixture was diluted to 100.0 mL in a volumetric flask. The absorbance of the new solution was 0.500. Calculate the concentration of copper ion in the sample.arrow_forwardWhat is the relation between the standard deviation and the precision of a procedure? What is the relation between standard deviation and accuracy? The percentage of an additive in gasoline was measured six times with the following results: 0.13, 0.12, 0.16, 0.17, 0.20, 0.11%. Find the 90% and 99% confidence intervals for the percentage of the additive.arrow_forward
- If you measure a quantity four times and the standard deviation is 1.0% of the average, can you be 90% confident that the true value is within 1.2% of the measured average?arrow_forwardWrite down three most common errors in thermogravimetric analysis. Identify them as systematic or random errors and discuss how you can minimize the errors for better results.arrow_forwarda) A favorable entropy change occurs when ΔS is positive. Does the order of the system increase or decrease when ΔS is positive? (b) A favorable enthalpy change occurs when ΔH is negative. Does the system absorb heat or give off heat when ΔH is negative? (c) Write the relation between ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS. Use the results of parts (a) and (b) to state whether ΔG must be positive or negative for a spontaneous change. For the reaction, ΔG is 59.0 kJ/mol at 298.15 K. Find the value of K for the reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





