
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
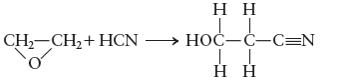
Concept Introduction:
A chemical compound can be formed by either ionic bond or covalent bond between bonded atoms. The ionic compound is formed by opposite charge ions; cations and anions. The covalent compound is formed by sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The bond energy of a chemical bond can be defined as the energy required to break that chemical bond. The bond energy that is needed to break the bonds in reactant molecule and the energy released to form
(a)
Answer to Problem 56E
Explanation of Solution
Given:
 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
For the given reaction:
(b)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept Introduction:
A chemical compound can be formed by either ionic bond or covalent bond between bonded atoms. The ionic compound is formed by opposite charge ions; cations and anions. The covalent compound is formed by sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The bond energy of a chemical bond can be defined as the energy required to break that chemical bond. The bond energy that is needed to break the bonds in reactant molecule and the energy released to form chemical bonds in product can be used to calculate the
(b)
Answer to Problem 56E
Explanation of Solution
Given:
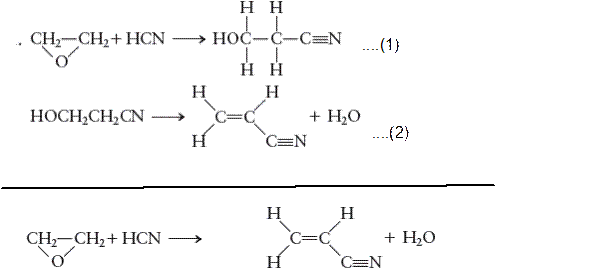
For the given reaction:
(c)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept Introduction:
A chemical compound can be formed by either ionic bond or covalent bond between bonded atoms. The ionic compound is formed by opposite charge ions; cations and anions. The covalent compound is formed by sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The bond energy of a chemical bond can be defined as the energy required to break that chemical bond. The bond energy that is needed to break the bonds in reactant molecule and the energy released to form chemical bonds in product can be used to calculate the
(c)
Answer to Problem 56E
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For the given reaction:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- A Lewis structure obeying the octet rule can be drawn for O2 as follows: Use the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O2 to show that the above Lewis structure corresponds to an excited state.arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures for CO32, HCO3, and H2CO3. When acid is added to an aqueous solution containing carbonate or bicarbonate ions, carbon dioxide gas is formed. We generally say that carbonic acid (H2C03) is unstable. Use bond energies to estimate E for the reaction (in the gas phase) H2CO3CO2+H2O Specify a possible cause for the instability of carbonic acid.arrow_forwardWhat is a driving force? Name two common and important driving forces, and give an example of each. What is entropy? Although the total energy of the universe is constant, is the entropy of the universe constant? What is a spontaneous process?arrow_forward
- Explain why the bond between B and Cl in the molecule BCl3 is shorter than would be expected for a single B—Cl bond.arrow_forwardRegarding the following equation: KClO3 → KCl + O2 What type (classification) of chemical reaction is this?arrow_forwardThe breaking of the O-O bond in peroxydisulfuryl difluoride (FO,SOOSO,F) gives FO,SO: (FO2SO)2 2 2 FO2SO The compound on the left of this equation is a colorless liquid that boils at 67.1°C. Its vapor, when heated to about 100°C, turns brown as the product of the reaction forms. Suppose that, in a sample of the vapor, the intensity of the brown color doubles between 100°C and 110°C and that the total pressure increases only by the 2.7% predicted for an ideal gas. Estimate AH° for the preceding reaction.arrow_forward
- In terms of bond energies and thermodynamics, why do we (as a society) make so much CO2?arrow_forwardHow many kj of heat are needed to produce 6.47 g NH 3 ? 4NO+6H 2 O 4NH 3 +5O 2; triangle H=906 kJarrow_forwardTwo useful organic compounds that contain Cl atoms are vinyl chloride(CH2=CHCl) and chloroethane (CH3CH2Cl). Vinyl chloride is the startingmaterial used to prepare poly(vinyl chloride), a plastic in insulation,pipes, and bottles. Chloroethane (ethyl chloride) is a local anesthetic.Why is the C–Cl bond in vinyl chloride stronger than the C–Cl bond inchloroethane?arrow_forward
- 1. Write the ΔHf ̊ reaction for HNO3, accounting for the enthalpy term in your reaction.arrow_forwardCalculate ΔHo for each oxidation reaction. Each equation is balanced as written; remember to take into account the coefficients in determining the number of bonds broken or formed. [ΔHo for O2 = 497 kJ/mol; ΔHo for one C=O in CO2 = 535 kJ/mol]arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





