
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration for the cations
Concept Introduction:
The distribution of electrons in atom into orbitals is said to be electronic configuration. The electronic configuration for every element present in the periodic table is unique or different.
(a)
Answer to Problem 30E
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
The number of electrons that the subshells can hold is:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, subshell is:
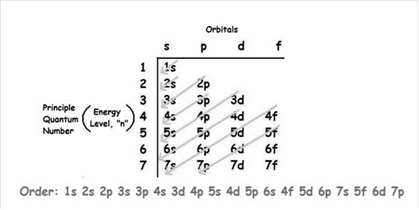
In electronic configuration, the number of electrons present in each sublevel is shown by superscript.
The given cations are:
The atomic number of magnesium = 12, after losing two electrons,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of tin = 50, after losing two electrons,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of potassium= 19, after losing one electron,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of aluminium = 13, after losing three electrons,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of thallium = 81, after losing one electron,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of arsenic = 33, after losing three electrons,
Electronic configuration of
(b)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration for anions:
Concept Introduction:
The distribution of electrons in atom into orbitals is said to be electronic configuration. The electronic configuration for every element present in the periodic table is unique or different. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, which is further equal to the number of electrons for neutral atom.
(b)
Answer to Problem 30E
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
Explanation of Solution
The number of electrons that the subshells can hold is:
s-block - 2
p-block - 6
d-block - 10
f-block - 14
The increasing order of energy of shells, subshell is:
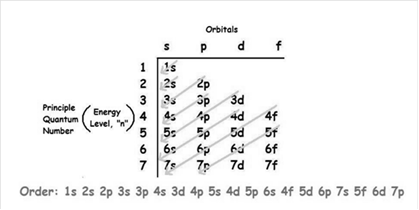
In electronic configuration, the number of electrons present in each sublevel is shown by superscript.
The given anions are:
The atomic number of nitrogen= 7, after gaining three electrons,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of oxygen = 8, after gaining two electrons,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of fluorine = 9, after gaining one electron,
Electronic configuration of
The atomic number of tellurium = 52, after gaining two electrons,
Electronic configuration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- 13. Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing electronegativity: Br, Ca, Ge, K?○ Br<Ge<Ca<K ○ K<Ca<Ge<Br ○ Ge<Br<K<Ca ○ Ge<Ca<K<Br 14. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing electron affinity: Ne, Xe, Rn, Kr,?○ Kr<Ne<Rn<Xe ○ Ne<Kr<Xe<Rn ○ Xe<Rn<Ne<Kr ○ Rn<Xe<Kr<Ne15. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing atomic size: K, Rb, Na, Li?○ Na<Li<K<Rb ○ Li<Na<K<Rb ○ Li<Na<Rb<K ○ Rb<K<Na<Liarrow_forwardCalculate the second ionization energy of the metal M (AH¡on2 in kJ/mol) using the following data: Lattice enthalpy of MO(s), AH = -2278 kJ/mol Bond dissociation enthalpy of O2(g) = +498 kJ/mol %3D First electron affinity of O = -141 kJ/mol Second electron affinity of O = +744 kJ/mol Enthalpy of sublimation of M = + 125 kJ/mol First ionization energy of M = + 309 kJ/mol Standard enthalpy of formation of MO(s), AHf = -341 kJ/molarrow_forward1.Give an example of a one S block element whose valance electrons are in 4th principal quantum number (n=4) 2.Name an element which is in period 3 that has the valence electron configuration of (ns2 np3)arrow_forward
- Use the electronic configuration of zinc to explain why it forms only a +2. From which orbital(s) are the electrons removed?arrow_forwardThe electron configuration of an element, X, is [Ne] 3s¹. The formula of the most probable ionic compound that this element will form with Br is Note: The compound Fe(CIO4)3 should be entered as "Fe(CIO4)3".arrow_forwardThe first three iodization energies of an element X are 590, 1145 and 4912 kJ/mol. What is the most likely stable ion of X? A. X2- B. X3+ C. X+ D. X2+arrow_forward
- 6. Which of the following species is not isoelectronic with sulfide? A. Ar B. Sc3+ C. Kr D. P3–arrow_forwardThe first three ionization energies of a element X are 590, 1145 and 4,912 kJ• mol- 1. what is the most likely formula for the stable ion of X? A. X3+B. X+C. X2+D. X-arrow_forwardWrite the empirical formula for at least four ionic compounds that could be formed from the following ions: 2+ 3+ Fe²+, MnO, CO, Fe³+ 11 0,0,... Xarrow_forward
- 3. Of the elements Nd, Al, and Ar, which will readily form(s) +3 ions? Why? 4. The atomic radii of Na and Cl are 190 and 79 pm, respectively, but the distance between sodium and chlorine in NaCl is 282 pm. Explain this discrepancy.arrow_forwardTwo fourth-period atoms, one of a transition metal, M, and the other of a main-group nonmetal, X, form a compound with the formula M2X3. What is the electron configuration of atom X if M is Fe? What is the configuration of X if M is Co, if X is the same then give the full electron configuration for the Co ion.arrow_forward10)arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





