
(a)
To Explain: the better relationship between percent made and distance.
(a)
Answer to Problem 47E
Exponential model
Explanation of Solution
Given:
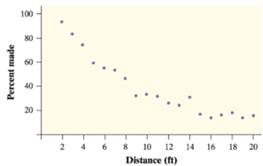
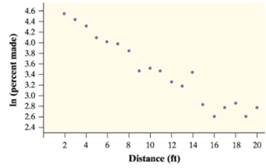
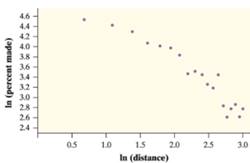
It is observed that the given
General linear model to expect ln(count) from time
Taking the exponential
Therefore the model associate with the model
(b)
To find: the equation of the least-squares regression line on the basis of given computer output.
(b)
Answer to Problem 47E
Explanation of Solution
Given:

Calculation:
General equation for the least square regression line
The calculated of the constant
The calculated of the slope
Putting the value of
Where x shows the distance and y shows the ln(percent made)
Where
(c)
To Explain: the prediction of the percent made for putts of 21 feet on the basis of part (b).
(c)
Answer to Problem 47E
10.7381%
Explanation of Solution
Given:

Calculation:
From the part (b)
Where
Putting the value of
Taking the exponential
Therefore the expected percent made is 10.7381
(d)
To Calculate: here is given linear regression in part (b), is it expected that prediction in part (c) to be too large, too small or about right, justify the answer.
(d)
Answer to Problem 47E
Too small
Explanation of Solution
Given:
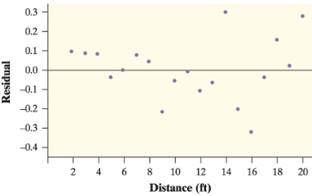
It is observed that, made a prediction for a distance of
Then residual is the difference between the predicted y-value and actual y-value. If a residual is positive, then this means that the actual y-value is larger than the expected y-value and therefore our prediction looks to have been too small.
Chapter 12 Solutions
PRACTICE OF STATISTICS F/AP EXAM
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Essentials of Statistics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Statistical Reasoning for Everyday Life (5th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics Using Excel (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics (10th Edition)
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





