
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Can be oxidized to an aldehyde _______
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an aldehyde or to ketone. Product obtained may depend on the oxidizing agent used. Therefore, in presence of mild oxidizing agent, one gets aldehyde or ketone. In the presence of strong oxidizing agent,
Thus, Can be oxidized to an aldehyde: BoxAandBoxG_.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Segment of a condensation polymer molecule _______.
The
Thus, segment of a condensation polymer molecule Box H_.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an aldehyde or to ketone. Product obtained may depend on the oxidizing agent used. Therefore, in presence of mild oxidizing agent, one gets aldehyde or ketone.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid _____.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an aldehyde or to ketone. Product obtained may depend on the oxidizing agent used. Therefore, in presence of mild oxidizing agent, one gets aldehyde or ketone. In the presence of strong oxidizing agent, carboxylic acid is obtained.
Thus, Can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid BoxA,BoxE,BoxIandBoxG_.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of alcohols: primary, secondary and tertiary. The type of alcohols depends upon the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A primary alcohol_____.
The compound given in Boxes A and G is a primary alcohol. The hydroxyl group is attached with a carbon atom that is attached with one carbon atom.
Thus, a primary alcohol BoxAandBoxG_.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The fatty acid can react with glycerol to form triglyceride with the formation of ester linkages. The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester group is derived by a carboxylic acid group in which the acidic hydrogen is replaced by an alkyl group.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A triglyceride_____.
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box F contains a triglyceride.
Thus, A triglyceride BoxF_
(f)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which monomer units are linked together with no side product formation. Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Addition polymerization monomer_____.
Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond. Compounds in Box C contain a double bond.
Thus, addition polymerization monomer is BoxC_.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an amide linkage_____.
An amide linkageis formed between a carboxylic acid and an amine. The carboxylic acid group of one amino acid reacts with an amino group of another amino acid to form an amide linkageby removing a water molecule. Compound in Box D and Box H contains an amide bond.
Thus, contains an amide linkage BoxDandBoxH_.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. To get an aldehyde or ketone, oxidation of acohol must takes place in the presence of mild oxidizing agent such as copper at 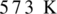 . Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
. Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Oxidized to form a ketone_____.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. Secondary alcohols undergo oxidation to form ketones. Compound in Box E and Box I are the secondary alcohols.
Thus, oxidized to form a ketone BoxE and Box I_.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester is derived by a carboxylic acid group in which the acidic hydrogen is replaced by an alkyl group.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an ester linkage_____.
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box F contains a triglyceride.
Thus, contains an ester linkage BoxF_.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Polymers are the high molecular mass compounds. The small monomers units joined together to form large molecule and this reaction is known as polymerization reaction. When two small molecules condense together to form a polymer with elimination of water molecule, the reaction is known as condensation polymerization.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Condensation polymerization monomer_____.
Box B contains a compound in which two amine groupsare present. These two amine groups can undergo condensation polymerization which is characterized by the loss of hydrogen molecule.
Thus, Condensation polymerization monomer BoxB_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- 75.0 grams of an unknown metal was heated to 95.0°C, it was then placed into 150.0 grams of water at23.1°C, when the metal and water reached thermal equilibrium, the temperature was 27.8°C. Calculatethe specific heat of the metal. (Assume that the specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g °C)arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardA 25.0 g sample of water was cooled from 23.9°C to 12.7°C, how much heat was released? (Assume thatthe specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g °C)arrow_forward
- Zeolites: environmental applications.arrow_forward" is The structure of the bicarbonate (hydrogen carbonate) ion, HCO3-, HCO3 best described as a hybrid of several contributing resonance forms, two of which are shown here. HO :0: :Ö: HO + Bicarbonate is crucial for the control of body pH (for example, blood pH: 7.4). A more self-indulgent use is in baking soda, where it serves as a source of CO2 CO₂ 2 gas, which gives bread and pastry their fluffy constituency. (i) Draw at least one additional resonance form. = (ii) Using curved "electron-pushing" arrows, show how these Lewis structures may be interconverted by movement of electron pairs. (iii) Determine which form or forms will be the major contributor(s) to the real structure of bicarbonate, explaining your answer on the basis of the criteria in Section 1-5.arrow_forwardWhich of these is the best use of a volumetric flask? measuring how much liquid it contains delivering a precise amount of liquid to another container holding solutions making solutions of precise concentrationarrow_forward
- You're competing on a Great British television game show, and you need to bake a cake. The quantity for each ingredient is given in grams, but you haven't been given a kitchen scale. Which of these properties would correlate with the mass of a baking ingredient like eggs or milk? Check all that apply. depth of color viscosity volume densityarrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for each of the following species. Again, assign charges where appropriate. a. H-H¯ b. CH3-CH3 c. CH3+CH3 d. CH3 CH3 e. CH3NH3+CH3NH3 f. CH30-CH3O¯ g. CH2CH2 - h. HC2-(HCC) HC2 (HCC) i. H202×(HOOH) H₂O₂ (HOOH) Nortonarrow_forwardIs molecule 6 an enantiomer?arrow_forward
- Show work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





