
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781305087408
Author: Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please need answer
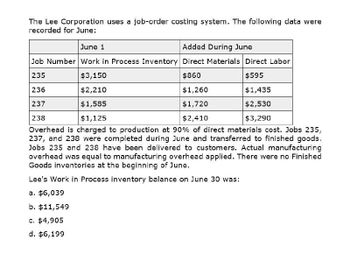
Transcribed Image Text:The Lee Corporation uses a job-order costing system. The following data were
recorded for June:
June 1
Added During June
Job Number Work in Process Inventory Direct Materials Direct Labor
235
$3,150
236
$2,210
237
$1,585
238
$1,125
$860
$595
$1,260
$1,435
$1,720
$2,530
$2,410
$3,290
Overhead is charged to production at 90% of direct materials cost. Jobs 235,
237, and 238 were completed during June and transferred to finished goods.
Jobs 235 and 238 have been delivered to customers. Actual manufacturing
overhead was equal to manufacturing overhead applied. There were no Finished
Goods inventories at the beginning of June.
Lee's Work in Process inventory balance on June 30 was:
a. $6,039
b. $11,549
c. $4,905
d. $6,199
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Channel Products Inc. uses the job order cost system of accounting. The following is a list of the jobs completed during March, showing the charges for materials issued to production and for direct labor. Assume that factory overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor costs and that the predetermined rate is 200%. Required: Compute the amount of overhead to be added to the cost of each job completed during the month. Compute the total cost of each job completed during the month. Compute the total cost of producing all the jobs finished during the month.arrow_forwardLorrimer Company has a job-order cost system. The following debits (credits) appeared in the Work-in-Process account for the month of June. During the month of June, direct labor totaled 30,000 and 24,000 of overhead was applied to production. Finished Goods was debited 100,000 during June. Lorrimer Company applies overhead at a predetermined rate of 80% of direct labor cost. Job number 83, the only job still in process at the end of June, has been charged with manufacturing overhead of 3,400. What was the amount of direct materials charged to Job number 83? a. 3,400 b. 4,250 c. 8,350 d. 7,580arrow_forwardLeen Production Co. uses the job order cost system of accounting. The following information was taken from the companys books after all posting had been completed at the end of May: a. Compute the total production cost of each job. b. Prepare the journal entry to transfer the cost of jobs completed to Finished Goods. c. Compute the selling price per unit for each job, assuming a mark-on percentage of 40%. d. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale of Job 1065.arrow_forward
- Kokomo Kayak Inc. uses the process cost system. The following data, taken from the organizations books, reflect the results of manufacturing operations during the month of March: Production Costs Work in process, beginning of period: Costs incurred during month: Production Data: 18,000 units finished and transferred to stockroom. Work in process, end of period, 3,000 units, two-thirds completed. Required: Prepare a cost of production summary for March.arrow_forwardDublin Brewing Co. uses the process cost system. The following data, taken from the organizations books, reflect the results of manufacturing operations during October: Production Costs Work in process, beginning of period: Costs incurred during month: Production Data: 13,000 units finished and transferred to stockroom Work in process, end of period, 2,000 units one-half completed Required: Prepare a cost of production summary for October.arrow_forwardTerrills Transmissions uses a job order cost system. A partial list of the accounts being maintained by the company, with their balances as of November 1, follows: The following transactions were completed during November: a. Materials purchases on account during the month, 74,000. b. Materials requisitioned during the month: 1. Direct materials, 57,000. 2. Indirect materials, 11,000. c. Direct materials returned by factory to storeroom during the month, 1,100. d. Materials returned to vendors during the month prior to payment, 2,500. e. Payments to vendors during the month, 68,500. Required: 1. Prepare general journal entries for each of the transactions. 2. Post the general journal entries to T-accounts. 3. Balance the accounts and report the balances of November 30 for the following: a. Cash b. Materials c. Accounts Payablearrow_forward
- Schumacher Industries Inc. manufactures recreational vehicles. Schumacher Industries uses a job order cost system. The time tickets from June jobs are summarized as follows: Factory overhead is applied to jobs on the basis of a predetermined overhead rate of 23 per direct labor hour. The direct labor rate is 29 per hour. a. Journalize the entry to record the factory labor costs. b. Journalize the entry to apply factory overhead to production for June.arrow_forwardThe following information, taken from the books of Herman Brothers Manufacturing represents the operations for January: The job cost system is used, and the February cost sheet for Job M45 shows the following: The following actual information was accumulated during February: Required: 1. Using the January data, ascertain the predetermined factory overhead rates to be used during February, based on the following: a. Direct labor cost b. Direct labor hours c. Machine hours 2. Prepare a schedule showing the total production cost of Job M45 under each method of applying factory overhead. 3. Prepare the entries to record the following for February operations: a. The liability for total factory overhead. b. Distribution of factory overhead to the departments. c. Application of factory overhead to the work in process in each department, using direct labor hours. (Use the predetermined rate calculated in Requirement 1.) d. Closing of the applied factory overhead accounts. e. Recording under- and overapplied factory overhead and closing the actual factory overhead accounts.arrow_forwardBarnes Company uses a job order cost system. The following data summarize the operations related to production for October: a. Materials purchased on account, 315,500. b. Materials requisitioned, 290,100, of which 8,150 was for general factory use. c. Factory labor used, 489,500 of which 34,200 was indirect. d. Other costs incurred on account for factory overhead, 600,000; selling expenses, 150,000; and administrative expenses, 100,000. e. Prepaid expenses expired for factory overhead were 18,000; for selling expenses, 6,000; and for administrative expenses, 5,000. f. Depreciation of office building was 30,000; of office equipment, 7,500; and of factory equipment, 60,000. g. Factory overhead costs applied to jobs, 711,600. h. Jobs completed, 1,425,000. i. Cost of goods sold, 1,380,000. Instructions Journalize the entries to record the summarized operations.arrow_forward
- Gerken Fabrication Inc. uses the job order cost system of accounting. The following information was taken from the companys books after all posting had been completed at the end of March: a. Compute the total production cost of each job. b. Prepare the journal entries to charge the costs of materials, labor, and factory overhead to Work in Process. c. Prepare the journal entry to transfer the cost of jobs completed to Finished Goods. d. Compute the unit cost of each job. e. Compute the selling price per unit for each job, assuming a mark-on percentage of 50%.arrow_forwardPrepare Job-Order Cost Sheets, Predetermined Overhead Rate, Ending Balance of WIP, Finished Goods, and COGS At the beginning of March, Mendez Company had two jobs in process, Job 86 and Job 87, with the following accumulated cost information: During March, two more jobs (88 and 89) were started. The following direct materials and direct labor costs were added to the four jobs during the month of March: At the end of March, Jobs 86, 87, and 89 were completed. Only Job 87 was sold. On March 1, the balance in Finished Goods was zero. Required: 1. Calculate the overhead rate based on direct labor cost. (Note: Round to three decimal places.) 2. Prepare a brief job-order cost sheet for the four jobs. Show the balance as of March 1 as well as direct materials and direct labor added in March. Apply overhead to the four jobs for the month of March, and show the ending balances. 3. Calculate the ending balances of Work in Process and Finished Goods as of March 31. 4. Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold for March.arrow_forwardMonterrey Products Co. uses the process cost system. A record of the factory operations for the month of October follows: Required: Prepare a cost of production summary, assuming that the production losses are considered to be normal.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College