
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781285866932
Author: Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:134
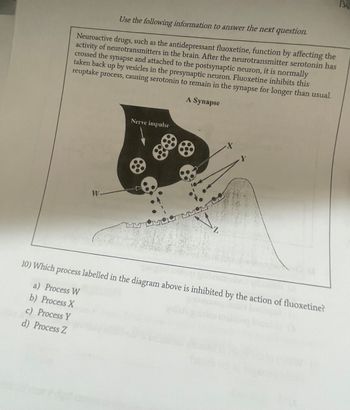
Use the following information to answer the next question.
Neuroactive drugs, such as the antidepressant fluoxetine, function by affecting the
activity of neurotransmitters in the brain. After the neurotransmitter serotonin has
crossed the synapse and attached to the postsynaptic neuron, it is normally
taken back up by vesicles in the presynaptic neuron. Fluoxetine inhibits this
reuptake process, causing serotonin to remain in the synapse for longer than usual.
W-
Nerve impulse
A Synapse
Z
10) Which process labelled in the diagram above is inhibited by the action of fluoxetine?
a) Process W
b) Process X
c) Process Y
d) Process Z
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A common membrane-bound intermediary between the receptor and the effector protein within the plasma membrane is the __________________.arrow_forwardWhat is a synapse? Explain the difference between an excitatory and an inhibitory synapse.arrow_forwardA neuron responds to adequate stimulation with _______, a type of self-propagating signal.arrow_forward
- Assume presynaptic excitatory neuron A terminates on a postsynaptic cell near the axon hillock and presynaptic excitatory neuron B terminates on the same postsynaptic cell on a dendrite located on the side of the cell body opposite the axon hillock. Explain why rapid firing of presynaptic neuron A could bring the postsynaptic neuron to threshold through temporal summation, thus initiating an action potential, whereas firing of presynaptic neuron B at the same frequency and the same magnitude of EPSPs may not bring the postsynaptic neuron to threshold.arrow_forwardWhat neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction? norepinephrine serotonin dopamine acetylcholinearrow_forwardA _______________ is a drug that causes temporary paralysis by blocking the transmis- sion of nerve stimuli to the muscles. neuromuscular blocker skeletal muscle relaxantarrow_forward
- How much of a change in the membrane potential is necessary for the summation of postsynaptic potentials to result in an action potential being generated? +30 mV +15 mV +10 mV -15 mVarrow_forwardView the University of Michigan Webscope (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/nervefiber) to see an electron micrograph of a cross-section of a myelinated nerve fiber. The axon contains microtubules and neurofilaments, bounded by a plasma membrane known as the axolemma. Outside the plasma membrane of the axon is the myelin sheath, which is composed of the tightly wrapped plasma membrane of a Schwann cell. What aspects of the cells in this image react with the stain that makes them the deep, dark, black color, such as the multiple layers that are the myelin sheath?arrow_forwardWhen action potentials arrive at a synapse between a neuron and another cell, they stimulate the release of molecules of a ________ that diffuse over to that cell.arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements best describes saltatory conduction? a. It inhibits direct neurotransmitter release. b. It transmits the action potential at the nodes of Ranvier andthus speeds up impulses on myelinated axons. c. It increases neurotransmitter release at the presynapticmembrane. d. It decreases neurotransmitter uptake at chemically gatedpostsynaptic channels. e. It removes neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft.arrow_forwardWhich of the following neurotransmitters is associated with inhibition exclusively? GABA acetylcholine glutamate norepinephrinearrow_forwardAn example of a synapse could be the site where: a. neurotransmitters released by an axon travel across a gap and are picked up by receptors on a muscle cell. b. an electrical impulse arrives at the end of a dendrite causingions to flow onto axons of presynaptic neurons. c. postsynaptic neurons transmit a signal across a cleft to apresynaptic neuron. d. oligodendrocytes contact the dendrites of an afferent neurondirectly. e. an onoff switch stimulates an electrical impulse in apresynaptic cell to stimulate other presynaptic cells.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781305634350
Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College


Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning