
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119776741
Author: Klein
Publisher: WILEY CONS
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.7, Problem 16CC
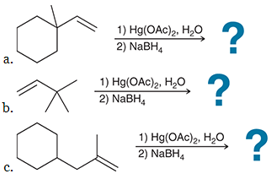
Predict the product for each reaction, and predict the products if an acid-catalyzed hydration had been performed rather than an oxymercuration - demercuration:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
single reaction sequence: a certain ketone undergoes alkylation to give new ketone, when reacted with a base and then an alkylating agent, 1-bromopropane. What is the structure of the final ketone product?
Predict the products of the following acid-base reactions. If the equilibrium would not
result in the formation of appreciable amounts of products, you should so indicate. In
each case label the stronger acid, the stronger base, the weaker acid, and the weaker base:
(a) CH3CH=CH2 + NANH2
(d) CH3C=C: + CH;CH2OH →
(e) CH3C=C:- + NH¾CI –
|
(b) CH;C=CH + NaNH2
(c) CH3CH2CH3 + NANH2 →
|
HAS
Comparing Hydration Products Using Two Different Methods Draw the product formed when CH3CH2C=CH is treated with each of the following sets of reagents: (a) H2O, H2SO4, HgSO4; and (b) R2BH, followed by H2O2, HO−.
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
Ch. 8.3 - Provide a systematic name for each of the...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 2CCCh. 8.3 - Prob. 3CCCh. 8.3 - Prob. 4CCCh. 8.5 - Prob. 5CCCh. 8.5 - Prob. 6CCCh. 8.5 - Prob. 1LTSCh. 8.5 - Prob. 7PTSCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8ATSCh. 8.5 - Prob. 9CC
Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 2LTSCh. 8.5 - Prob. 10PTSCh. 8.5 - Prob. 11ATSCh. 8.6 - Prob. 12CCCh. 8.6 - Prob. 13CCCh. 8.6 - Prob. 3LTSCh. 8.6 - Prob. 14PTSCh. 8.6 - Prob. 15ATSCh. 8.7 - Predict the product for each reaction, and predict...Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 17CCCh. 8.8 - Prob. 18CCCh. 8.8 - Prob. 19CCCh. 8.8 - Prob. 4LTSCh. 8.8 - Prob. 20PTSCh. 8.8 - Prob. 21ATSCh. 8.9 - Prob. 5LTSCh. 8.9 - Prob. 22PTSCh. 8.9 - Prob. 23ATSCh. 8.10 - Prob. 24CCCh. 8.10 - Prob. 6LTSCh. 8.10 - Prob. 25PTSCh. 8.10 - Prob. 26ATSCh. 8.10 - Prob. 27ATSCh. 8.11 - Prob. 7LTSCh. 8 - Prob. 47PP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When cis-2-decalone is dissolved in ether containing a trace of HCl, an equilibrium is established with trans-2-decalone. The latter ketone predominates in the equilibrium mixture. Propose a mechanism for this isomerization and account for the fact that the trans isomer predominates at equilibrium.arrow_forwardWhen 2-iodo-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane is heated in acetic acid, CH3COOH, a mixture of substitution and elimination products is obtained. Provide structures for all possible products, writing [not drawing] the name of the mechanism by which each one is formed.arrow_forwardIn the presence of an appropriate base, esters undergo self-condensation to afford the corresponding B-ketoesters as shown below. Explain in detail using reaction schemes (not mechanisms) why route C and not routes A and B would lead to the expected product. 2 x Ethyl acetate A: NaOH(aq) B: OMe- C: OEt- EtO CH3arrow_forward
- Devise a synthesis of the ketone hexan-3-one, CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3, from CH3CH2Br as the only organic starting material; that is, all the carbon atoms in hexan-3-one must come from CH3CH2Br. You may use any other neededreagents.arrow_forwardWhen cis-2-decalone is dissolved in ether containing a trace of HCI, an equilibrium is established with trans-2-decalone. The latter ketone predominates in the equilibrium mixture. H H HCI cis-2-Decalone trans-2-Decalone Propose a mechanism for this isomerization and account for the fact that the trans iso- mer predominates at equilibrium.arrow_forwardH3C. H3C. CH3 nnc» XT :OH 2 CH₂OH HCI catalyst Aldehydes and ketones react reversibly with two equivalents of alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to give acetals. Alcohols are poor nucleophiles, and so protonation of the carbonyl oxygen is used to make the carbonyl carbon a stronger electrophile. Addition of the first equivalent of alcohol gives a hemiacetal, a hydroxyether. Addition of the second equivalent of alcohol is accompanied by loss of water to yield the product acetal. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 H3C CH3OH H3CQ OCH3 CH3 H3C. H HO: :OCH 3 CH3 46arrow_forward
- H3C OH OH H+ CH3 Esters can be synthesized by an acid-catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid; this process is called the Fischer esterification reaction. Because the alcohol oxygen is a poor nucleophile, the carbonyl carbon is made a better electrophile by protonation of the carbonyl oxygen. The steps of the synthesis are all reversible. The reaction is generally driven to completion by using an excess of the liquid alcohol as a solvent, or by distilling off the product as it forms. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions CIX 10-4 H₂O CH3 H₂O CH3arrow_forward5. For the following compound, provide three different reactions to produce the compound using a Grignard Reaction: OH of H3C CH 3arrow_forwardDraw structural formulas for the isomeric carbocation intermediates formed on treat- ment of each alkene with HCl. Label each carbocation 1°, 2°, or 3° and state which of the isomeric carbocations forms more readily. CH₂CH3 (a) H₂C=C (c) CH3 CH3 (b) (d) H₂C-CH=CH-CH3arrow_forward
- When pent-1-ene is treated with mercury(II) acetate in methanol and the resulting product is reacted with NaBH4, what is the primary organic compound which results? 1-ethoxypentane 1-methoxypentane 3-ethoxypentane 2-ethoxypentane 2-methoxypentanearrow_forward(c) The structures of lycopene, beta-carotene and retinol are shown below. Lycopene Beta-carotene H3C CH; CH3 CH3 OH Retinol (vitamin A) CH3 Using appropriate reaction mechanisms: (i) Show how lycopene is converted into beta-carotene. (ii) Briefly explain how retinol is formed from beta-carotene.arrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for the following reactionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY