
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The major product of the following reaction should be determined.
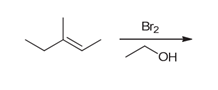
Concept introduction:
(b)
Interpretation: The major product of the following reaction should be determined.
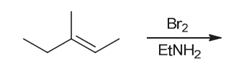
Concept introduction:
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Due to the presence of a double bond, alkenes undergo addition reactions. Some examples of addition reactions of alkenes are hydrohalogenation, halogenation, catalytic hydrogenation, acid-catalyzed hydration, hydroboration-oxidation, oxymercuration-demercuration, etc. The addition reactions mainly occur with the formation of carbocation as an intermediate.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT COMPANION (
- Predict the product and provide a suitable mechanism. The reaction proceeds through a rearrangement. What is the name of the rearrangement? Based on the rearrangement, write the product of the second reaction.arrow_forwardAn electron-deficient carbon atom reacts with a nucleophile, symbolized as: Nu−. Define this ?arrow_forwardIn hydrobromination of 3-hexene, which of the following pairs of species act as nucleophiles? 3-hexene, Br– 3-hexene, HBr HBr, Br– HBr, Br2arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of NaCl with 2- bromo-2-methylhexane in acetone/water. Predict the change in rate if the concentrations of both the 2-bromo-2- methylhexane and the NaCl are doubled. A) The reaction rate stays the same. B) The reaction rate doubles. C) The reaction rate is halved. D) The reaction rate quadruples E) The reaction rate triples.arrow_forwardWhat explains why many aldehydes and ketones can undergo self-condensation reactions in basic conditions? The alpha carbon can lose a proton and act like a nucleophile and the carbonyl carbon is an electrophile. The alpha carbon can gain a proton and act like an electrophile and the carbonyl carbon is a nucleophile. The oxygen of the carbonyl group can attack the carbon of the carbonyl group. Only esters can undergo self-condensation reactions.arrow_forwardBy taking into account electronegativity differences, draw the products formed by heterolysis of the carbon–heteroatom bond in each molecule. Classify the organic reactive intermediate as a carbocation or a carbanion.arrow_forward
- Sketch the reaction mechanism (including the final product) corresponding to the following description. Be prepared to explain the mechanism to your partner. 2-bromo-4-methylpentane is being reacted with sodium cyanide in diethyl ether (set up the reaction – next you will get a description of the mechanism to draw). A lone pair of electrons from the cyanide attacks the carbon bonded to bromine, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. At the same time, the carbon-bromine bond breaks with the electron pair from the carbon-bromine bond moving toward the bromine to form a bromide ion. This will form the product 2,4-dimethylpentanenitrile and sodium bromide. is this reaction following an SN1 or SN2 mechanism? Write out the rate law for this reaction.Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction.arrow_forwardmethanol + CH3OH Suppose you were told that the above reaction was a substitution reaction but you were not told the mechanism. Evaluate the following categories to determine the reaction mechanism and then draw the structure of the major organic product. Type of alkyl halide: Type of nucleophile: Solvent: Is the product racemic?arrow_forwardClassify each of the following species as a nucleophile or an electrophile:arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction of ethyl bromide with each of the following nucleophiles? CH3CH2CH2O- CH3C≡C- (CH3)3Narrow_forwardBr Brz CH3 CH3 H3C CH2CI2 H3C Br Electrophilic addition of bromine, Br2; to alkenes yields a 1,2-dibromoalkane. The reaction proceeds through a cyclic intermediate known as a bromonium ion. The reaction occurs in an anhydrous solvent such as CH,Cl). In the second step of the reaction, bromide is the nucleophile and attacks at one of the carbons of the bromonium ion to yield the product. Due to steric clashes, the bromide ion always attacks the carbon from the opposite face of the bromonium ion so that a product with anti stereochemistry is formed. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions Br: :Br: .CH3 H3C H3C CH3 Br:arrow_forward14. When propylene reacts with hydrogen bromide in the presence of a peroxide initiator, which of the following structures are formed during the mechanism? (A) Br Br (B) (C) Br H• (D)arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

