
Concept explainers
Temperature and pH Effects. Figure 6-4 illustrates enzyme activities as functions of temperature and pH. In general, the activity of a specific enzyme is highest at the temperature and pH that are characteristic of the environment in which the enzyme normally functions.
- (a) Explain the shapes of the curves in Figure 6-4 in terms of the major chemical or physical factors that affect enzyme activity.
- (b) For each enzyme in Figure 6-4, suggest the adaptive advantage of having the enzyme activity profile shown in the figure.
- (c) Some enzymes have a very flat pH profile—that is, they have essentially the same activity over a broad pH range. How might you explain this observation?
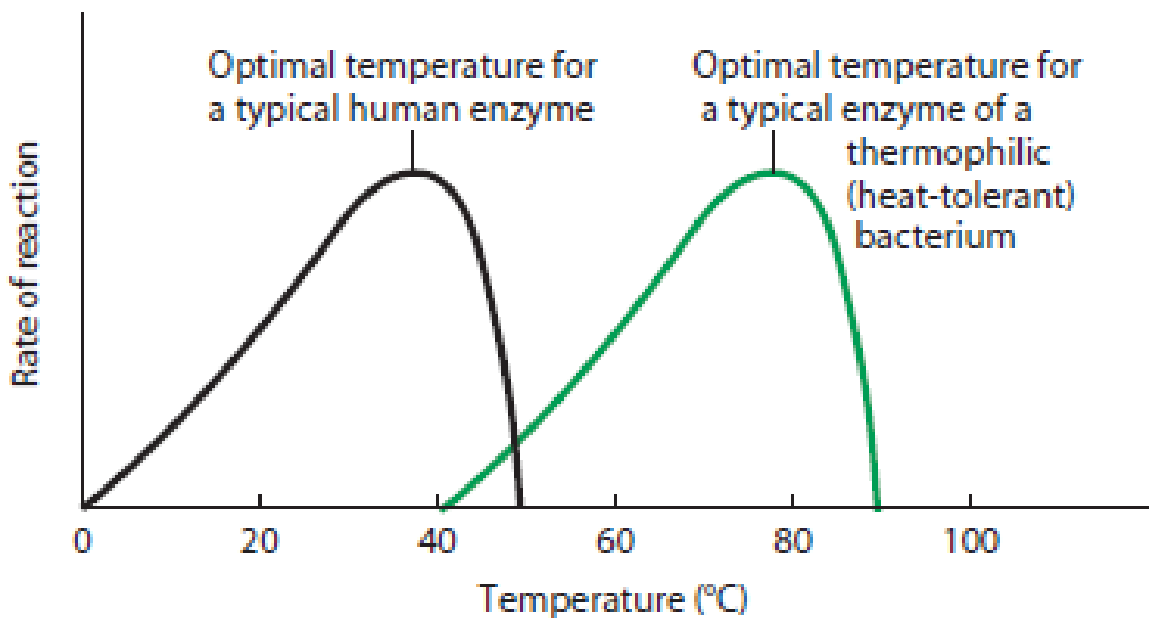
(a) Temperature dependence. The reaction rate for both a typical human enzyme (black) and a typical enzyme from a thermophilic bacterium (green) varies with temperature. It is highest at the optimal temperature, which is about 37°C (body temperature) for the human enzyme and about 75°C (the temperature of a typical hot spring) for the bacterial enzyme. Above the optimal temperature, the enzyme is rapidly inactivated by denaturation.
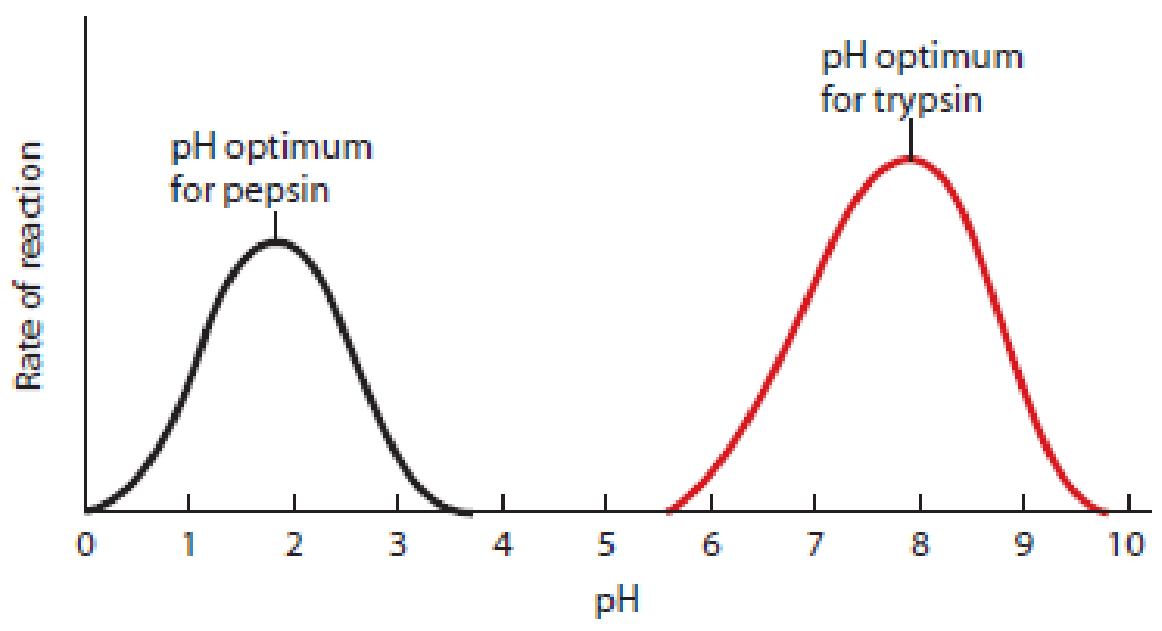
(b) pH dependence. The reaction rate of an enzyme is highest at its optimal pH, which is about 2.0 for pepsin (stomach pH) and near 8.0 for trypsin (intestinal pH). At the pH optimum for an enzyme, ionizable groups on both the enzyme and the substrate molecules are in the most favorable form for reactivity.
Figure 6-4 The Effect of Temperature and pH on the Reaction Rate of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions. Every enzyme has an optimum temperature and pH that usually reflect the environment where that enzyme is found in nature.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- QIV. Determine if the level of organization is molecular or cellular. Tick True if molecular. Tick False if cellular. The membrane proteins are mostly glycoproteins in association with enzymes to hasten the biochemical process. Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forwardEnzymes catalyze chemical reactions. What constitutes the active site of an enzyme? What are the turnover number (kcat), the Michaelis constant (Km), and the maximal velocity (Vmax) of an enzyme? The kcat (catalytic rate constant) for carbonic anhydrase is 5 × 105 molecules per second. This is a “rate constant,” but not a “rate.” What is the difference? By what oncentration would you multiply this rate constant in order to determine an actual rate of prod- uct formation (V)? Under what circumstances would this rate become equal to the maximal velocity (Vmax) of the enzyme?arrow_forwardFill in the blanks.: Write Cif only statement A is correct, Hif only statement B is correct, E if both statements are correct, M if both statements are incorrect. A. An enzyme catalyzes a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway that has a lower energy of activation. B. The enthalpy of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction decreases significantly as compared to the uncatalyzed reaction.arrow_forward
- Enzyme Properties The effect of temperature on enzyme activity. Temperature °C 10 Reaction rate 1.0 15 1.5 20 2.5 25 3.5 30 5.5 35 7.5 40 9.5 45 50 8.5 7.0 55 4.0 60 0.0 a. "DRAW A LINE GRAPH OF THE RESULTS OF THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON A TYPICAL ENZYME REACTION RATE." b. WHAT IS THE BEST TEMPERATURE FOR THIS ENZYME TO WORK? c. MOST ENZYMES WORK AT THIS TEMPERATURE IN HUMANS, WHY DO YOU THINK THIS IS?arrow_forwardModified TRUE or FALSE. Write the word TRUE if the statement is correct. If the statement is false, write the incorrect underlined word/s and indicate the correct word/s to make the statement true. Extreme temperatures and pH can cause permanent disruption of the protein primary structure(s) of enzymes that leads to loss of active site shape, loss of binding efficiency and activity.arrow_forwardTrend observed in graph and conclusion about the effect of temperature on enzyme activity. In your answer i) include a concise description of the trend observed in the graph shown , and ii) explain this trend using the language presented in this unit and your biochemical knowledge of enzymes and reactions. In your conclusion, provide a logical argument supported by molecular theory that would explain any change observed in enzyme activityarrow_forward
- Understanding how enzymes work 1) Excluding enzymes, for example, that work in the stomach's low pH, describe the working conditions for most enzymes in the human body. 2) Describe the effect of enzymes on the rate of reactions that they catalyze. 3) Define the transition state in a chemical reaction and how an enzyme functions during the transition state.arrow_forwardModified TRUE or FALSE. Write the word TRUE if the statement is correct. If the statement is false, write the incorrect underlined word/s and indicate the correct word/s to make the statement true. The Michaelis-Menten Constant (Km) of an enzyme is equal to the enzyme concentration at which the initial velocity of the reaction is one half of maximum velocity (Vmax).arrow_forwardPlease ASA. Thanku. In the reaction Na + Cl à Na+ + Cl-, which component is said to become ‘oxidized’ and which is considered reduced? Na, Cl Cl, Cl Na, Na Cl, Naarrow_forward
- I. Active site analysis. Below is a diagram of a putative active site for Monoamine oxidase. As we learned, the purpose of tertiary structure is to form a scaffold so you can orient just a few amino acids in the right orientation to promote binding and/or catalysis. The position where this occurs is the active site. The amino acid architecture of an active site is designed to bind substrates. Amino acid side chains are capable of hydrogen bonding, ionic and hydrophobic interactions. Fill in each amino acid that you think is suitable for interacting with the part of the substrate it is closest to. Assume the pH will be at 7.0 a.a.#1 a.a.#2 a.a.#6 HO Lond NH₂ НО a.a.#5 OH a.a.#3 a.a.#4arrow_forwardAsap. Explanation. Wellarrow_forwardCan you help me, please? Enzyme specificity (list the different types of enzyme specificities)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





