
1.
Prepare the worksheet to develop Company S’s financial statements for the first 6 months of 2016.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: A worksheet is a tool that is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form, having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process.
Prepare the worksheet to develop Company S’s financial statements for the first 6 months of 2016:
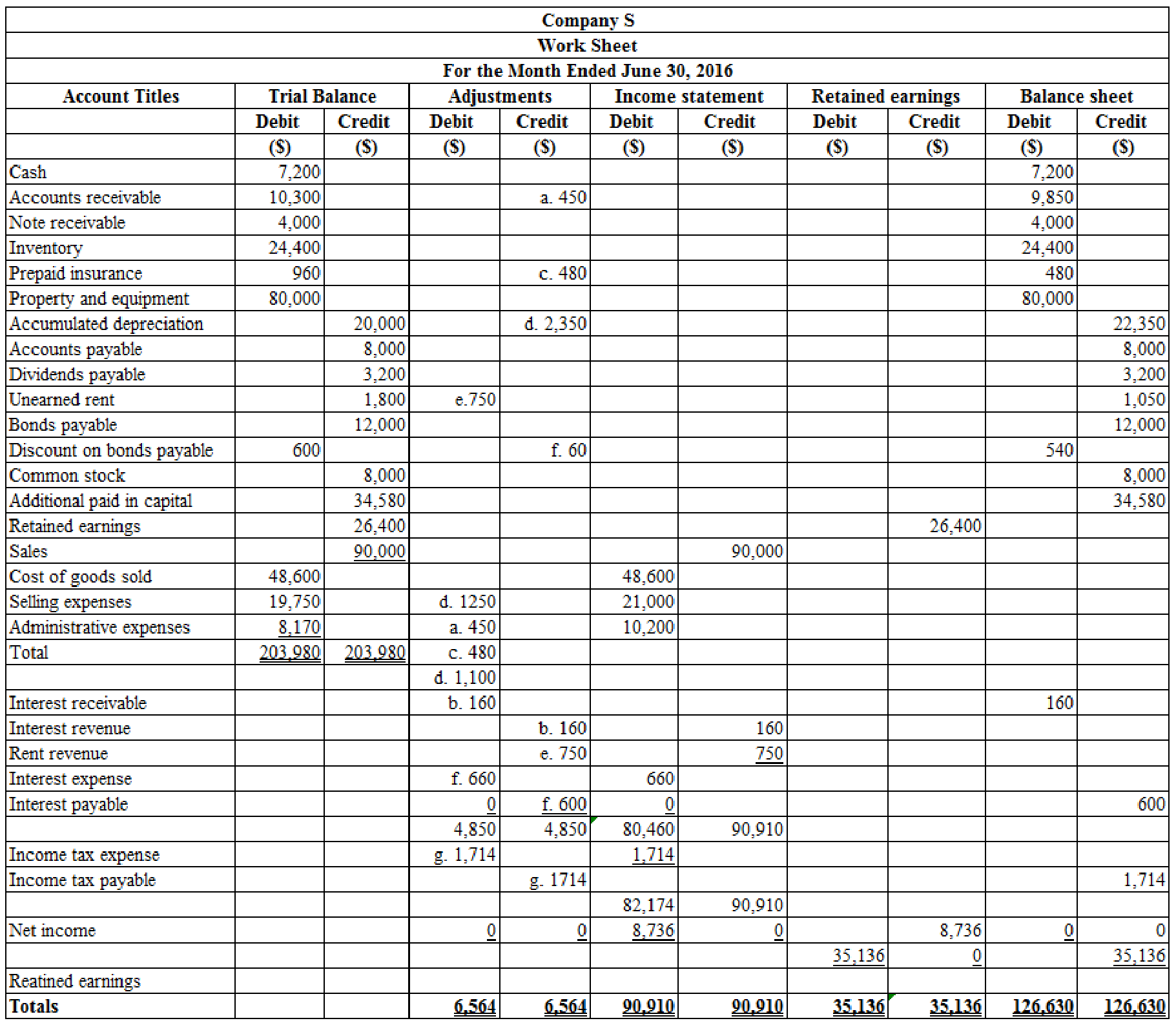
Table (1)
Working notes:
a. Calculate the amount of
Bad debt expense = Net sales amount×Average uncollectible accounts=$90,000×.5%=$450
b. Calculate the amount of interest revenue:
Interest revenue = (Note receivable amount×12%×Period from March 1 to June 30)=$4,000×12%×412=$160
c. Calculate the amount of insurance expense:
Insurance expense = (Amount of prepaid insurance×Payment for 6 months)=($960×612)=$480
d. Calculate the amount of
Depreciation expense on Building =[(Building amountEstimated life) × 612 months]= [($55,00025) × 612 months]= $1,100
Depreciation expense on Building =[(Equipment amountEstimated life) × 612 months]= [($20,0008 years) × 612 months]= $1,250
Depreciation expense=($1,100+$1,250)=$2,250
e. Calculate the amount of rent revenue:
Rent revenue = (Amount of unearned rent×Period from 1/2/2016 to 30/6/2016)= $1,800×512=$750
f. Calculate the amount of interest expense:
Interest expense = (Amount of discount on bonds payable+ 10% of discount on bonds payable)=$600+60=$660
g. Calculate the amount of income tax expense for first 6 months:
Calculate estimated annual pre-tax income:
Estimated annual pretax income = (Pre-tax income for 6 months + Pre-tax income for2nd half )= ($90,910−$80,460)+$11,550= $10,450 + $11,550=$22,000
Calculate estimated effective income tax rate:
Estimated effective income tax rate = [(15% on taxable income + 30% on Balance $2,000 income)Estimated annual pretax income]= [($3,000 + $600)$22,000]=16.4
Calculate the amount of income tax expense for first 6 months:
Income tax expensefor first 6 months} = (Pre-tax income for 6 months×Estimated effective income tax rate)=$10,450×16.4%=$1,714
2 (a)
Prepare the income statement for the first 6 months of 2016.
2 (a)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement for the first 6 months of 2016:
| Company S | ||
| Interim Income statement | ||
| For the period ended June 30, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 90,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (48,600) | |
| Gross profit | 41,400 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Selling expenses | 21,000 | |
| Administrative expenses | 10,200 | |
| Total operating expenses | (31,200) | |
| Pre-tax operating income | 10,200 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Interest revenue | 160 | |
| Rent revenue | 750 | |
| Interest expense | (660) | |
| Total other revenues and expenses | 250 | |
| Income before income taxes | 10,450 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | (1,714) | |
| Net income | $8,736 | |
| Earnings per share | $1.09 | |
Table (2)
Working notes:
h. Calculate earnings per share for 6 months:
Earnings per share for first 6 months = Net income Number of Common stock oustanding= $8,7368,000 Shares=$1.09
2 (b)
Prepare the income statement for the second quarter of 2016.
2 (b)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement for the second quarter of 2016:
| Company S | ||
| Interim Income statement | ||
| For the period ended June 30, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 50,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (25,600) | |
| Gross profit | 24,400 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Selling expenses | 12,200 | |
| Administrative expenses | 5,990 | |
| Total operating expenses | (18,190) | |
| Pre-tax operating income | 6,210 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Interest revenue | 120 | |
| Rent revenue | 450 | |
| Interest expense | (330) | |
| Total other revenues and expenses | 240 | |
| Income before income taxes | 6,450 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | (1,014) | |
| Net income | $5,436 | |
| Number of shares | 8,000 shares | |
| Earnings per share | $0.68 | |
Table (3)
Working notes:
i. Calculate the amount of sales for second quarter:
Sales for second quarter = (Amount of sales in trial balance as of June 30, 2016−Amount of sales at the end of first quarter of 2016)= $90,000−$40,000=$50,000
j. Calculate the amount of cost of goods sold for 3 months:
Cost of goods sold for second quarter = (Amount of cost of goods sold in trial balance as of June 30, 2016−Amount of cost of goods sold at the end of first quarter of 2016)= $48,600−$23,000=$25,600
k. Calculate the amount of selling expenses for second quarter:
Selling expenses for 3 months = (Amount of selling expenses in the worksheet−Amoutn of selling expense at the end of first quarter of 2016)= ($19,750+$1,250)−$8,800= $21,000 −$8,800=$12,200
l. Calculate the amount of administrative expenses for second quarter:
Administrative expenses for second quarter = (Amount of Administrative expenses in the worksheet−Amoutn of administrative expense at the end of first quarter of 2016)= ($8,170+$450+$480+$1,100)−$4,210= $10,200−$4,210=$5,990
m. Calculate the amount of interest revenue for second quarter:
Interest revenue for second quarter = (Note receivable amount×12%×Revenue earned for 3 months)=$4,000×12%×3/12=$120
n. Calculate the amount of rent revenue for second quarter:
Rent revenue for 3 months =(Amount of unearned rent×Revenue earned for 3 months)=($1,800×312)=$450
o. Calculate the amount of interest expense for second quarter:
Interest expense for 3 months= [(Amount of discount on bonds payable+ 10% of discount on bonds payable)2]=[$600+602]=$330
p. Calculate the amount of income tax expenses for second quarter:
Income tax expenses for 3 months = (Amount of income tax expense in the worksheet−Amoutn of incoem tax expense at the end of first quarter of 2016)= $1,714−$700=$1,014
q. Calculate earnings per share for second quarter:
Earnings per share for 3 months = Net income Number of Common stock oustanding= $5,4368,000 Shares=$0.68
3.
Prepare the statement of
3.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of Retained Earnings: Statement of retained earnings shows, the changes in the retained earnings, and the income left in the company after payment of the dividends, for the accounting period.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings for the first 6 months:
| Company S | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For First 6 Months Ended June 30, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, January 1, 2016 | 29,600 | |
| Add: Net income | 8,736 | |
| Subtotal | 38,336 | |
| Less: Dividends | (3,200) | |
| Retained earnings at June 30, 2016 | $35,136 | |
Table (4)
Working note:
r. Calculate the amount of retained earnings, January 1, 2016:
Retained earnings, January 1, 2016 = (Retained earnings amount in trial balance as of June 30, 2016 + Dividend)= $26,400+$3,200=$29,600
4.
Prepare the
4.
Explanation of Solution
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements which summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Interim financial reports: these are the financial reports prepared by the company between the two annual reports.
Prepare the balance sheet as on June 30, 2016 of Company S:
| Company S | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As on June 30, 2016 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 7,200 | |
| Accounts receivable | 9,850 | |
| Note receivable | 4,000 | |
| Interest receivable | 160 | |
| Inventory | 24,400 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 480 | |
| Total current assets | 46,090 | |
| Property and equipment | 80,000 | |
| (22,350) | ||
| Net property, plant and equipment | 57,650 | |
| Total assets | $103,740 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 8,000 | |
| Interest payable | 600 | |
| Dividends payable | 3,200 | |
| Income tax payable | 1,714 | |
| Unearned rent | 1,050 | |
| Bonds payable | 12,000 | |
| Less: Discount on bonds payable | (540) | 11,460 |
| Total liabilities | 26,024 | |
| Shareholders’ Equity | ||
| Contributed Capital: | ||
| Common stock | 8,000 | |
| Additional paid in capital on common stock | 34,580 | |
| Retained earnings | 35,136 | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | 77,716 | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $103,740 | |
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis
- Yost received 300 NQOs (each option gives Yost the right to purchase 10 shares of Cutter Corporation stock for $19 per share). At the time he started working for Cutter Corporation three years ago, Cutter's stock price was $19 per share. Yost exercised all of his options when the share price was $38 per share. Two years after acquiring the shares, he sold them at $59 per share. Note: Input all amounts as positive values. Leave no answer blank. Enter zero if applicable. c. Assume that Yost is "cash poor" and needs to engage in a same-day sale in order to buy his shares. Due to his belief that the stock price is going to increase significantly, he wants to maintain as many shares as possible. How many shares must he sell in order to cover his purchase price and taxes payable on the exercise? Number of shares to be soldarrow_forwardMark received 10 ISOs (each option gives him the right to purchase 14 shares of Hendricks Corporation stock for $6 per share) at the time he started working for Hendricks Corporation five years ago, when Hendricks's stock price was $5 per share. Now that Hendricks's share price is $35 per share, Mark intends to exercise all of his options and hold all of his shares for more than one year. Assume that more than a year after exercise, Mark sells the stock for $35 a share. Note: Enter all amounts as positive values. Leave no answers blank. Enter zero if applicable. a. What are Mark's taxes due on the grant date, the exercise date, and the date he sells the shares, assuming his ordinary marginal rate is 32 percent and his long-term capital gains rate is 15 percent? Grant date Exercise date Sale date Taxes Duearrow_forwardOn January 1, year 1, Dave received 2,500 shares of restricted stock from his employer, RRK Corporation. On that date, the stock price was $13 per share. On receiving the restricted stock, Dave made the 83(b) election. Dave's restricted shares will vest at the end of year 2. He intends to hold the shares until the end of year 4, when he intends to sell them to help fund the purchase of a new home. Dave predicts the share price of RRK will be $33 per share when his shares vest and $54 per share when he sells them. Assume that Dave's price predictions are correct, and answer the following questions: Note: Leave no answers blank. Enter zero if applicable. Round your final answer to the nearest whole dollar value. Enter all amounts as positive values. b. What are the tax consequences of these transactions to RRK? Grant date Tax consequences Vesting date $ 0 Sale date $ 0arrow_forward
- Meg works for Freedom Airlines in the accounts payable department. Meg and all other employees receive free flight benefits (for the employee, family, and 10 free buddy passes for friends per year) as part of its employee benefits package. If Meg uses 15 flights with a value of $6,975 this year, how much must she include in her compensation this year? Amount includedarrow_forwardSeiko's current salary is $101,000. Her marginal tax rate is 32 percent, and she fancies European sports cars. She purchases a new auto each year. Seiko is currently a manager for Idaho Office Supply. Her friend, knowing of her interest in sports cars, tells her about a manager position at the local BMW and Porsche dealer. The new position pays $84,600 per year, but it allows employees to purchase one new car per year at a discount of $19,400. This discount qualifies as a nontaxable fringe benefit. In an effort to keep Seiko as an employee, Idaho Office Supply offers her a $10,500 raise. Answer the following questions about this analysis. a. What is the annual after-tax cost to Idaho Office Supply if it provides Seiko with the $10,500 increase in salary? Note: Ignore payroll taxes. After-tax costarrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Nicole's employer, Poe Corporation, provides her with an automobile allowance of $42,000 every other year. Her marginal tax rate is 32 percent. Answer the following questions relating to this fringe benefit. b. What is Poe's after-tax cost of providing the auto allowance? > Answer is complete but not entirely correct. After-tax cost $ 28,560arrow_forward
- 100%, equity, ending inventory. On January 1, 2015, 100% of the outstanding stock of Solo Company was purchased by Plato Corporation for $3,300,000. At that time, the book value of Solo’s net assets equaled $3,000,000. The excess was attributable to equipment with a 10-year life. The following trial balances of Plato Corporation and Solo Company were prepared on December 31, 2015: Plato Corporation Solo Company Cash 735000 37000 Accounts Receivable 400000 365000 Inventory 600000 275000 Property,Plato and Equipment 4000000 2300000 Investment in Solo company 3510000 Accounts Payable (35000) (100000) Common stock ($10 par) (1000000) (400000) Paid-in capital in excess of par (1500000) (200000) Retained earnings, Jan 1, 2015 (5,500,000) (2,400,000) Sales (12,000,000) (1,000,000) Cost of goods sold 7,000,000 750,000 Other expenses 4,000,000 40,000 Subsidiary income…arrow_forwardMarino Snacks Co. had its highest total cost of $84,000 in July and its lowest total cost of $60,000 in November. The company produces a single product. Production volume was 14,000 units in July and 9,000 units in November. What is the fixed cost per month? Answerarrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using the proper financial approach.arrow_forward
- E4-8 Plevin Company ended its fiscal year on July 31, 2014. The company's adjusted trial balance as of the end of its fiscal year is shown below. PLEVIN COMPANY Adjusted Trial Balance July 31, 2014 (b) Tota Journal entries, closing (LO 2, No. Account Titles Debit Credit 101 Cash $ 9,840 112 Accounts Receivable 8,780 157 Equipment 15,900 158 Accumulated Depreciation-Equip. $ 7,400 201 Accounts Payable 4,220 208 Unearned Rent Revenue 1,800 301 Owner's Capital 45,200 306 Owner's Drawings 16,000 400 Service Revenue 64,000 6,500 429 Rent Revenue 711 Depreciation Expense 8,000 726 Salaries and Wages Expense 55,700 732 Utilities Expense 14,900 $129,120 $129,120 Instructions (a) Prepare the closing entries using page J15. (b) Post to Owner's Capital and No. 350 Income Summary accounts. (Use the three-column form.) (c) Prepare a post-closing trial balance at July 31.arrow_forwardGeneral accounting questionarrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





