
Concept explainers
Figure 4.15 Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
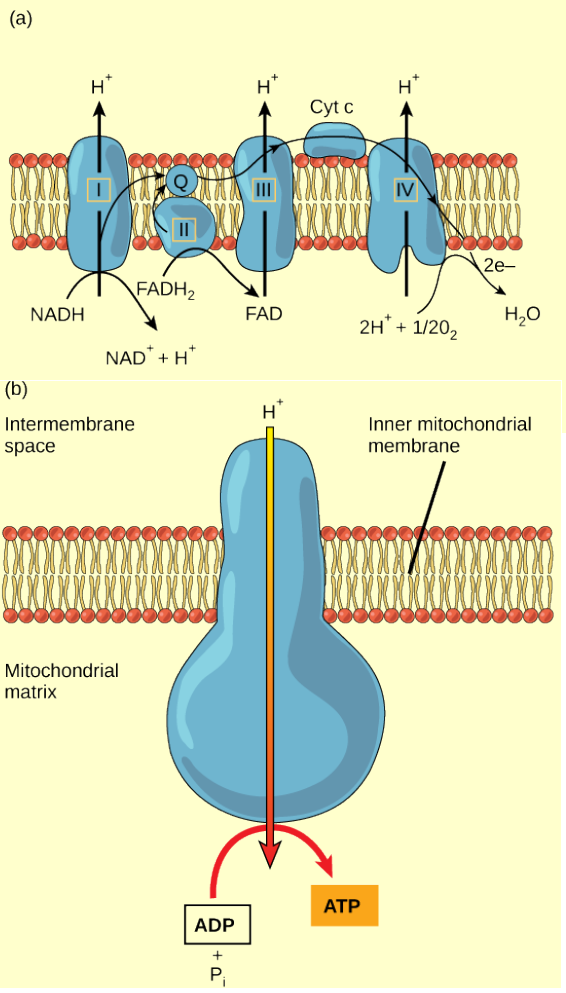
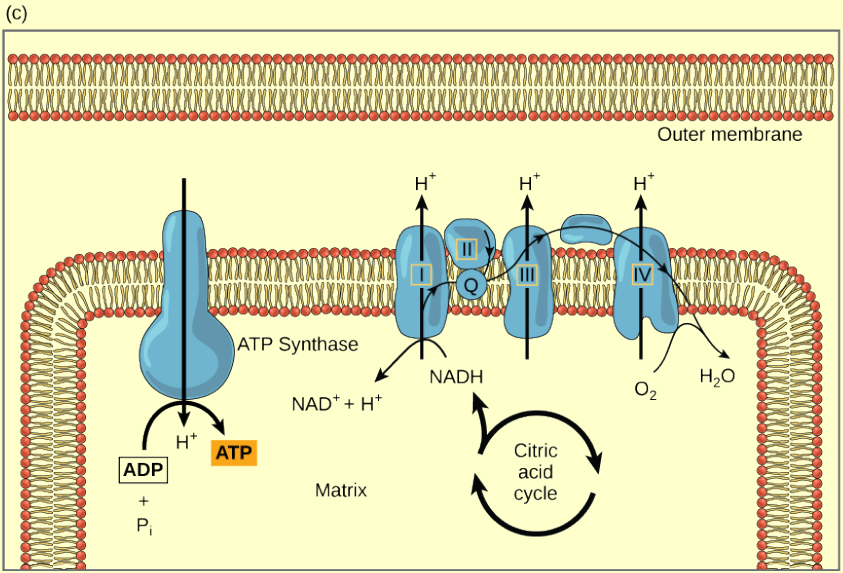
Figure 4.15 (a) The electron transport chain is a set of molecules that supports a series of
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Concepts of Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- Figure 7.12 Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?arrow_forwardMuch of our understanding of ATP synthase is derived from research on aerobic bacteria. What makes these organisms useful for this research? Where do the reactions of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron-transport chain occur in these organisms?arrow_forwardCyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?arrow_forward
- Discuss the composition of the transition state for the formation of ATP by ATP Synthase. a) Where is the active site for this enzyme located? b) How are the amino acid side chains from the α and β subunits of ATP Synthase involved? c) Discuss the importance of Mg+2 in the mechanism of this enzyme.arrow_forwardFigure 7.11 Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an "uncoupler" that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane "leaky" to protons. It was used until 1938 as a weight- loss drug. What effect would you expect DNP to have on the change in pH across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Why do you think this might be an effective weight-loss drug? Intermembrane space Mitochondrial matrix ATP Synthase ADP Inner mitochondrial membrane ATP Figure 7.11 ATP synthase is a complex, molecular machine that uses a proton (H) gradient to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). (Credit: modification of work by Klaus Hoffmeier)arrow_forwardCytochrome B5 is one of many cytochrome molecules in Electron Transport Chain. How would electron transport be affected if the cell had a defective cytochrome B5 gene and did not produce functional cytochrome B5? (It will help to discuss the function of cytochromes in Electron Transport Chain in your answer!)arrow_forward
- The following statements describe the path of electrons from NADH through the electron transport chain. Please arrange them in order: Cytochrome c (Fe2+) carries electrons to Complex IV. Cytochrome c (Fe3+) is reduced to cytochrome c (Fe2+) QH2 carries electrons to Complex III Oxygen is reduced to water Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q) is reduced to ubiquinol (QH2)arrow_forwardWhich of these molecules associated with electron transport is in the reduced state? Choose from the following: (A) cytochrome a3+++ (b) cytochrome a3++arrow_forwardDCCD (diocyclohexylcarbodiimide) inhibits oxidative phosphorylation when the substrate is mitochondrial NADH. DCCD is a drug that binds to ATP synthase and blocks proton transport through the ion channel. a) Explain what the consequences of DCCD on cellular energy production are. b) Suggest at least one other cellular effect of DCCD and explain this effect.arrow_forward
- A proton gradient is created during the electron transport chain using the energy released from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2. The protons then cross the membrane through ATP synthase down their electrochemical gradient, and ATP is produced. This is an example of A) energy coupling B) cotransport C) allosteric regulation.arrow_forwardHow much fat (in grams) would the body have to burn to produce the daily minimum requirement of 40 kg ATP from ADP and phosphate? Assume that: 1. The fat is metabolized completely to water and carbon dioxide. 2. The energy that is released can be used entirely for ATP production. 3. Complete oxidation of 1 g of fat to water and CO2 releases 9 kcal or 37 kJ. 4. The Delta G for ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 kJ/mol. You will have to look up one more value online to answer this question, but you do not need to know anything about lipid metabolism. A) approx. 16 to 17 g of fat B) approx. 65 to 66 g of fat C) approx 22 to 23 kg of fat D) approx. 267 to 268 g of fat E) approx. 5 to 6 kg of fatarrow_forwardWhat is the direct mechanism of ATP synthesis during the electron transport phase of cellular respiration? (what is the potential energy source that drives ATP production?) b) Why is oxygen needed for this phase? c) What is the role of ATP synthasearrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

