
(a)
Interpretation:
The formation of isoleucyl-tRNA proceeds through the reversible formation of the enzyme bound Ile AMP intermediate. Prediction of 32P-labelled ATP formation from 32PPi is to be done by ATP and 32PPi
Concept introduction:
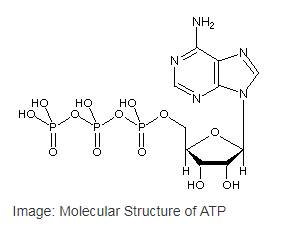
Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is the most common
Translation is the mechanism via which mRNA is decoded and translated into a protein.
(b)
Interpretation:
The formation of isoleucyl-tRNA proceeds through the reversible formation of the enzyme bound Ile AMP intermediate. Prediction of 32P-labelled ATP formation from 32PPi is to be done by ATP and 32PPi
Concept introduction:
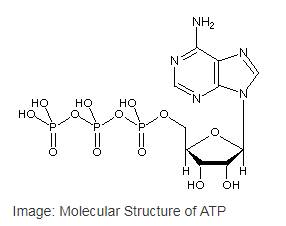
Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is the most common nucleotide in the cell as well as the primary cellular energy currency of in all the life forms. ATP is a type of nucleotide that has a ribose sugar, adenine nitrogenous base and a triphosphate (three-sequential phosphate group). The phosphate groups are attached to each other byphosphoanhydride bonds and the triphosphate is attached to the ribose sugar by a phosphoester bond.
Translation is the mechanism via which mRNA is decoded and translated into a protein.
(c)
Interpretation:
The formation of isoleucyl-tRNA proceeds through the reversible formation of the enzyme bound Ile AMP intermediate. Prediction of 32P-labelled ATP formation from 32PPi is to be done by isoleucine, ATP and32PPi
Concept introduction:
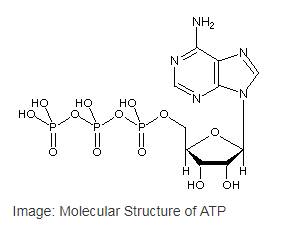
Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is the most common nucleotide in the cell as well as the primary cellular energy currency of in all the life forms. ATP is a type of nucleotide that has a ribose sugar, adenine nitrogenous base and a triphosphate (three-sequential phosphate group). The phosphate groups are attached to each other byphosphoanhydride bonds,and the triphosphate is attached to the ribose sugar by a phosphoester bond.
Translation is the mechanism via which mRNA is decoded and translated into a protein.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 31 Solutions
Biochemistry
- Crohn’s disease. Omega-3 fatty acids have been tested asa means to prevent relapse of Crohn’s disease. Two large,randomized, placebo-controlled studies have shown nosuch benefit from omega-3 fatty acids. Suppose you areasked to design an experiment to further study this claim.Imagine that you have collected data on Crohn’s relapsesin subjects who have used these omega-3 fatty acids and similar subjects who have not used them and that you canmeasure incidences of relapse for these subjects. Statethe null and alternative hypotheses you would use in yourstudy.arrow_forwardBiotransformation. Explain the process of enzyme induction. What are the benefits or down-falls of this process.arrow_forwardI. Active site analysis. Below is a diagram of a putative active site for Monoamine oxidase. As we learned, the purpose of tertiary structure is to form a scaffold so you can orient just a few amino acids in the right orientation to promote binding and/or catalysis. The position where this occurs is the active site. The amino acid architecture of an active site is designed to bind substrates. Amino acid side chains are capable of hydrogen bonding, ionic and hydrophobic interactions. Fill in each amino acid that you think is suitable for interacting with the part of the substrate it is closest to. Assume the pH will be at 7.0 a.a.#1 a.a.#2 a.a.#6 HO Lond NH₂ НО a.a.#5 OH a.a.#3 a.a.#4arrow_forward
- Anabolism & Catabolism of Nitrogenous Bases. a. Differentiate the processes of purine nucleotide biosynthesis & pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis. What are the starting materials for each process? b. Differentiate the processes of purine nucleotide degradation &pyrimidine nucleotide degradation. What are the end products of each process? c. Explain how purine & pyrimidine biosynthesis is regulated to produce balanced levels ofall four nucleotides (ATP, GTP, UTP & CTP)?arrow_forwardInitiation. Bacterial protein synthesis is initiated by: a. S-adenosylmethionyl tRNA b. Methionyl TRNA c. N-formylmethionyl tRNA d. N10-formyltetrahydrofolateN"-formyltetrahydrofolate †RNA „N10arrow_forwardPeptide mass determination. You have isolated a proteinfrom the bacterium E. coli and seek to confirm its identityby trypsin digestion and mass spectrometry. Determinationof the masses of several peptide fragments has enabled youto deduce the identity of the protein. However, there is adiscrepancy with one of the peptide fragments, whichyou believe should have the sequence MLNSFK and an(M 1 H)1 value of 739.38. In your experiments, yourepeat edly obtain an (M 1 H)1 value of 767.38. What isthe cause of this discrepancy and what does it tell youabout the region of the protein from which this peptide isderived?arrow_forward
- Serine protease enzyme mutation To show differences in the effect of the nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl group (C=O) of peptide bond between the catalytic triad of serine, histidine and aspartic acid, and another catalytic triad contains alanine, histidine and aspartic acid Provide/ draw an example of catalytic mechanism with catalytic triad contains alanine, histidine and aspartic Please answer completely will give rating surelyarrow_forward- Keto counterparts. Name the a-ketoacida-ketoacid that is formed by the transamination of each of the following amino acids: Co, a. Alanine b. Leucine c. Aspartate d. Phenylalanine e. Glutamate f. Tyrosinearrow_forwardJust Arrange. The enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) requires pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor. Arrange the steps of the likely mechanism for SHMT‑catalyzed serine degradation (producing glycine and N5,N10‑methylenetetrahydrofolate)arrow_forward
- ATP yield. Each of the following molecules is processed by glycolysis to lactate. How much ATP is generated from each molecule?arrow_forwardThe allosteric site 1). Draw a representation of an allosteric binding site of an enzyme. must bind an allosteric modifier that maintains three hydrophobic regions, a polar charged region and two regions of hydrogen bonding. You choose the order or organization of the characteristics in the allosteric site - label all regions. Details the allosteric site is composed of faces of two separate beta sheets and two separate alpha helices. You might decide that each beta sheet or each alpha helix contributes one amino acid R group to the allosteric site or you may decide that one of the beta sheets or one of the alpha helixes contributes two or more amino acid R groups to the allosteric organization. Your choice but please show R group structure in the allosteric site!arrow_forwardproteins. Which of the following will tell you whether a protein would be found in the lumen of the ER? A. You run a hydropathy plot an look for hydrophobic peaks that span 20-30 amino acids B. You isolate microsomes and see whether the proteins are inserted into the membrane of the microsome C. You run a hydropathy plot an look for a lack of hydrophobic peaks that span 20-30 amino acids O D. You do in vitro translation of each protein in the presence or absence of microsomes and look to see whether there is a size change in the presence of microsomes.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
