
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 28.5, Problem 14P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
It should explained that why was a deuterated compound used in the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
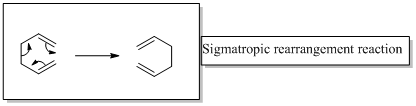
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't used Ai solution
What is the absorption spectrum of a solution of naphthalene in benzene , and the vibronic transitions responsible for the vibrational fine structure ?
3. Titanium(III) chloride can be used to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene. It is prepared by hydrogen reduction of
Titanium(IV) chloride. Reaction of hydrogen gas with titanium(IV) chloride gas produces solid titanium(III) chloride and
hydrogen chloride gas.
(a) Write a BALANCED chemical reaction for the preparation of titanium(III) chloride
(b) A 250 L reaction vessel at 325°C is filled with hydrogen gas to a pressure of 1.3 atm. Titanium(IV) chloride is then added
to bring the total pressure to 3.00 atm. How many grams of titanium(III) chloride will be produced after completion of the
reaction?
(c) What will be the pressure of the resulting hydrogen chloride gas that is also produced?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 28.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 28.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 28.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 28.2 - Give a molecular orbital description for each of...Ch. 28.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 28.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 28.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 28.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 28.4 - Prob. 10PCh. 28.4 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 28.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 28.5 - a. Draw the product of the following reaction: b....Ch. 28.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 28.5 - Prob. 15PCh. 28.5 - Prob. 17PCh. 28.5 - Prob. 18PCh. 28.6 - Prob. 19PCh. 28.6 - Explain why the hydrogen and the methyl...Ch. 28.6 - Chorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a...Ch. 28.7 - Convince yourself that the TE-AC method for...Ch. 28 - Draw the product of each of the following...Ch. 28 - Draw the product of each of the following...Ch. 28 - Prob. 25PCh. 28 - Show how norbornance can be prepared from...Ch. 28 - Prob. 27PCh. 28 - Prob. 28PCh. 28 - Draw the product of each of the following...Ch. 28 - Prob. 30PCh. 28 - Prob. 31PCh. 28 - Prob. 32PCh. 28 - Prob. 33PCh. 28 - When the following compound is heated, a product...Ch. 28 - Prob. 35PCh. 28 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 28 - Prob. 37PCh. 28 - Prob. 38PCh. 28 - Prob. 39PCh. 28 - Prob. 40PCh. 28 - If isomer A is heated to about 100 C, a mixture of...Ch. 28 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 28 - Prob. 43PCh. 28 - A student found that heating any one of the...Ch. 28 - Prob. 45PCh. 28 - Prob. 46PCh. 28 - Prob. 47P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Sodium azide (NaN3) is the primary chemical substance used in automobile air bags. Upon impact, the decomposition of sodium azide is initiated to produce sodium metal and nitrogen gas which then inflates the bag. How many liters of nitrogen gas are produced at 1.15 atm and 30.0°C when 145.0 grams of sodium azide decomposes? 2. Calcium carbonate (such as that in limestone) reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide, aqueous calcium chloride and water. How many liters of carbon dioxide are produced at 20°C and 745 torr when 3.583 grams of calcium carbonate is dissolved in solution containing 1.550 grams of hydrochloric acid?arrow_forwardShow all work (where appropriate) for full credit. 1. Describe (steps, equipment and quantities) how to accurately prepare 250.0 mL of a 0.0075 M solution of NaCl (aq) from a 500 mL, 0.0500 M stock solution. 2. Describe (steps, equipment and quantities) how to accurately prepare 250.0 mL of a 0.0075 M solution of NaCl (aq) from 100 g of solid NaCl.arrow_forward5. An unlabeled gas cylinder was recently found in the laboratory. A sample of the gas was removed and analyzed. A 500.0 mL sample of the gas at 15°C and a pressure of 736 mmHg was found to weigh 2.688 g. Determine the molar mass of the gas. What element is the gas?arrow_forward
- 4. Nitrogen gas is commonly sold in 49.0 L steal cylinders at a pressure of 150 atm. (a) How many moles of nitrogen are in the container if the temperature of the cylinder is 21°C. (b) How many moles of nitrogen will there be if the container above is heated to 100°C? (careful here) (c) What is the mass of nitrogen gas in the cylinder in part (a)? (d) What volume would the nitrogen occupy at 21°C, if the pressure was reduced to 1.02 atm? (e) What would be the pressure of the nitrogen gas in the cylinder when the temperature is raised to 39°C?arrow_forward6. A 0.4550 g sample of an unknown organic compound with the empirical formula CH2O was placed into a 150.0 ml vessel and was vaporized into a gas. At 175.0°C, the pressure of the vaporized compound was measured at 941.1 torr. (a) Determine the molar mass of the compound (b) Determine the molecular formula of the compound.arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 3. A particular reaction calls for 2.40 g of chloride ion. The only source of chloride ion available is a 0.00300 M stock solution of strontium chloride. How much (in L) of this solution is needed for this reaction?arrow_forwardAbsorption Spectrum of NaphthaleneTitle: Understanding the Absorption Spectrum of NaphthaleneGraph: Show a graph with labeled peaks indicating the absorption spectrum of naphthalene in a suitable solventarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning