
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of MOs in the given compound
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
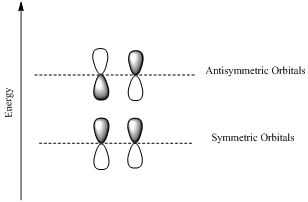
(b)
Interpretation: The designation of HOMO for the given molecule’s molecular orbital has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
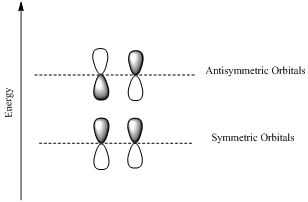
(c)
Interpretation: Number of nodes in the given molecule has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Molecular orbital theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combines to create molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbitals can be constructed from linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Bonding orbotals are formed by the additive combination of atomic orbitals and the antibonding orbitals are formed by the substractive combination of atomic orbitals.
Antibonding orbital is a molecular orbital that results when two parallel atomic orbitals with opposite phases interact.
Antibonding orbitals have higher energy than the bonding molecular orbitals.
Ground state and and exited states are the positions with lower and higher energy respectively.
HOMO is a molecular orbital which is the abbrevation of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
LUMO is also a molecular orbital which is the short form of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
If the lobes at the ends of the MO are in phase, then the MO is symmetric.
If the two lobes are out phase then the MO is antisymmetric.
Node is the site with zero electron density.
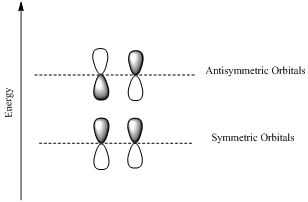
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Answer the following questions for the MOs of 1,3-butadiene: a. Which are pie bonding MOs, and which are p* antibonding MOs? b. Which MOs are symmetric, and which are antisymmetric? c. Which MO is the HOMO and which is the LUMO in the ground state? d. Which MO is the HOMO and which is the LUMO in the excited state? e. What is the relationship between the HOMO and the LUMO and symmetric and antisymmetric orbitals?arrow_forward2. Provide the following answer using the following compound below. a. Assign the hybridization for each atom, except hydrogen. b. Determine the number of atomic orbitals and Molecular orbitals (AO, MO). c. Draw the atomic orbitals for each atom and their MO d. Draw the energy diagram. e. Assign the HOMO and LUMO in the energy diagram. H H-C-C=C-H FO: Harrow_forward29. Recalling that the orthonitrate anion (NO43) is best described as acyclic, how many non-bonded (lone) electron pairs are there (in total) in this ion in its most important resonance structure? A. 3 non-bonded (lone) electron pairs in total. B. 9 non-bonded (lone) electron pairs in total C. 11 non-bonded (lone) electron pairs in total D. 12 non-bonded (lone) electron pairs in total E. None of the above 30. Given that the orthonitrate anion (NO43) is best described as acyclic, how many resonance structures contribute to its resonance hybrid when using the Octet Rule? A. There is only one (1) important resonance structure B. There are two (2) important resonance structures C. There are three (3) important resonance structures D. There are four (4) important resonance structures E. None of these are correctarrow_forward
- 3. Which of the following compounds exhibit pi electron delocalization? |- Allene Il- 1,3-butadiene I- Benzene IV- Toluene A. Tonly B. I and II C. I, Il and IIarrow_forward4. What is the configuration of all double bonds in the following molecule? Forma 1 2 3 4 5 retinol A. 1: Z; 2: Z; 3: Z; 4: Z; 5: Z B. 1: E; 2: Z; 3: Z; 4: Z; 5: Z C. 1: Z; 2: E; 3: E; 4: E; 5: E D. 1: E; 2: E; 3: E; 4: E; 5: E OHarrow_forwardWhat are the configurations of the double bond and at the carbons marked C2 and C3 respectively? OH H3C Select one: O a. (E), (S), (S) O b. (E), (S), (R) O C. CH3 d. O e. O f. (E), (R), (S) (E), (R), (R) (Z), (S), (S) (Z), (R), (S) g. (Z), (S), (R) Oh. (Z), (R), (R) H3C 3 CH3 CH3 CH3arrow_forward
- How many atoms of each hybridization state are there (sp,sp2, sp3)?What would be the result after the shown molecule is carried through the 4 step sequence? Show each intermediate and stereochemistry 1. 1eq. MeLi, then H2O workup 2.TsCl/pyr 3.NaOtBu/BuOH 4.OsO4/NaHSO3 And What is the relationship between the isomeric end products from them?arrow_forwardWhat are the bond-line formulas for the following compounds? a. 6-butyl-4,7-diethylundecaneb. 1-bromo-3-ethyl-5-methylcyclohexanec. trans-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane d. 1-bromopropane (the most stable Newman projection)e. trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane (the most stable chair conformation)arrow_forwardDraw the molecular orbital diagram of a linear C-H (i.e. one carbon atom bonded to one hydrogen atom). Draw out the MOs for orbitals containing electrons. 1. Would you expect C-H to behave as a carbocation, carbanion, or radical? 2. Would removal of one electron from C-H to generate C-H+ increase or decrease the bond length between carbon and hydrogen?arrow_forward
- Let us construct the molecular orbital diagram of ethylene (in pieces). a. First, construct the MO diagram of linear carbene (CH2). Draw pictures of all 6 orbitals b. Now bend the carbene to a bond angle of about 120°. How does this change your MO diagram? Draw pictures of all 6 orbitals. c. Now bring two of these carbene molecules together to make ethylene. Draw pictures of all 12 orbitals.arrow_forwardRank the following diatomic species of carbon in order of bond length and bond strength. В. С A. C2 C. C, Longest Next Shortest Bond Length Strongest Next Weakest Bond Strength Use this template to help answer the question: 2p 2P E O2sarrow_forward1. Which MO of ethylene will it use to accept the metal d-electrons through backbonding? a.σ b.π* c.σ* d.πarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
