
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134604718
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino, Darrell Killian
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 28ESP
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
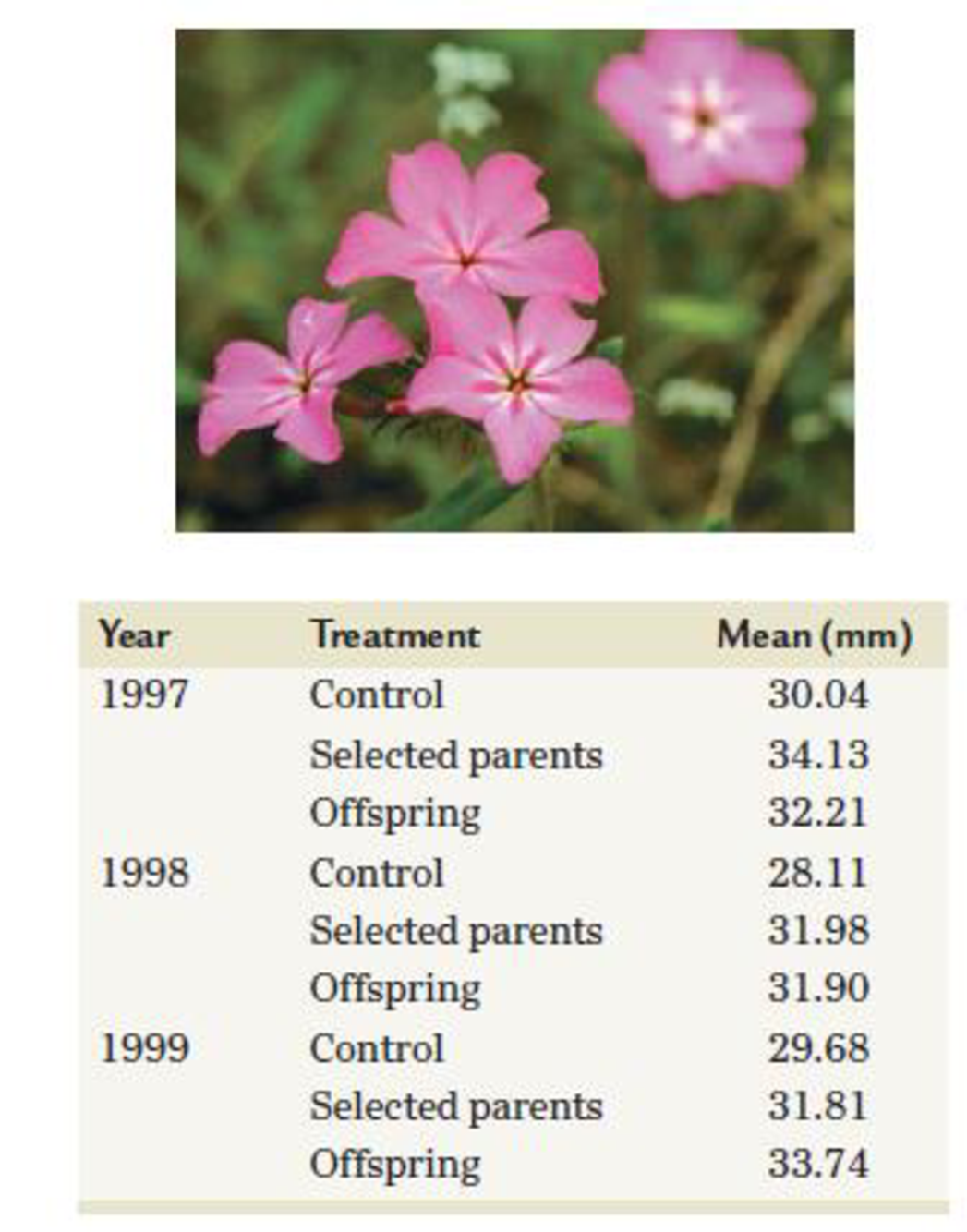
- (a) Considering that differences in control values represent year-to-year differences in greenhouse conditions, calculate (in mm) the average response to selection over the three-year period.
- (b) Calculate the realized heritability for each year and the overall realized heritability.
- (c) Assuming that the realized heritability in phlox is relatively high, what factors might account for such a high response?
- (d) In terms of evolutionary potential, is a population with high heritability likely to be favored compared to one with a low realized heritability?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
One of the effects of climate change on ecological communities is the disruptionof seasonal timing or phenology. A team of biologists is trying to determine the potential forrapid evolutionary responses of plants to changing seasonal conditions. They do alaboratory selection experiment on flowering time in an annual plant to test for the presence ofadditive genetic variance for this trait. They measure the time between germination andflowering for 400 plants under controlled laboratory conditions and then use 25% with theshortest flowering times to find a second generation in the lab (with pollination based onrandom number sampling). The mean flowering time for the overall parental population was 80days. The mean for the selected 25% of individuals was 60 days. In the offspring generation, themean flowering time was 70 days.
6a. What is the narrow-sense heritability for flowering time for these plants under laboratoryconditions?
6b. If you performed another round of selection on the…
A wide-ranging survey of Nicotonia growing in its natural environment recorded a variation in corolla length ranging from 12mm to 47mm with a variance of 36.5. Subsequently, collected seeds were grown in a greenhouse and it was found that the range was now very much lower with most plants having similar corolla lengths and the variance was now only 8.4.
After the plants had grown to maturity and formed seed, seeds were collected from plants with either the shortest and or the longest corollas in the population and planted separately in the greenhouse. When flowers were formed it was found that the variance of the plants with the shortest flowers was now 4.2 while that of the flowers from the longest seeds had become 13.7
Calculate the values for heritability in the different groups of plants and explain why this difference may arise.
In normal plants, the probability that an offspring of a heterozygous parent is heterozygous is 0.5. If the survival of heterozygous offspring differs from that of homozygous offspring, the probability that a surviving offspring is heterozygous may not be equal to 0.5. For the following values of the probability, write a discrete-time dynamical system for the fraction of heterozygous offspring over time, find the solution, and compute the fraction that will be heterozygous after ten generations. How does this compare with the fraction for a normal plant? The probability that an offspring is heterozygous is 0.6.
Chapter 25 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Ch. 25 - A homozygous plant with 20-cm-diameter flowers is...Ch. 25 - The following table shows measurements for fiber...Ch. 25 - The following cable gives the percentage of twin...Ch. 25 - At an interview with a genetic counselor, a couple...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2CSCh. 25 - At an interview with a genetic counselor, a couple...Ch. 25 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on a...Ch. 25 - CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list...Ch. 25 - Define the following: (a) polygenic, (b) additive...Ch. 25 - A dark-red strain and a white strain of wheat are...
Ch. 25 - Height in humans depends on the additive action of...Ch. 25 - An inbred strain of plants has a mean height of 24...Ch. 25 - Erma and Harvey were a compatible barnyard pair,...Ch. 25 - In the following table, average differences of...Ch. 25 - What kind of heritability estimates (broad sense...Ch. 25 - List as many human traits as you can that are...Ch. 25 - Corn plants from a test plot are measured, and the...Ch. 25 - The following variances were calculated for two...Ch. 25 - The mean and variance of plant height of two...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14PDQCh. 25 - Prob. 15PDQCh. 25 - In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies...Ch. 25 - Prob. 17PDQCh. 25 - Prob. 18PDQCh. 25 - In a population of 100 inbred, genotypically...Ch. 25 - Many traits of economic or medical significance...Ch. 25 - A 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant,...Ch. 25 - In a cross between a strain of large guinea pigs...Ch. 25 - Type A1B brachydactyly (short middle phalanges) is...Ch. 25 - In a series of crosses between two true-breeding...Ch. 25 - Students in a genetics laboratory began an...Ch. 25 - Prob. 26ESPCh. 25 - Canine hip dysplasia is a quantitative trait that...Ch. 25 - Floral traits in plants often play key roles in...Ch. 25 - In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are a developmental geneticist and perform a mutagenesis screen in Arabidopsis looking for floral organ mutants. You identify a mutant phenotype that has the following organ arrangement, beginning in whorl 1: Sepal-Sepal-Carpel-Carpel Which class of floral identity genes has been mutated? A-B double mutant O A O SEPALLATA B сarrow_forwardWild type, winter annual accessions of Arabidopsis will flower after 20 days at 23C in long day conditions (critical photoperiod 15 hours) following 30 days at 4C. What is the predicted flowering- time response of each experimental plant's genotype (listed below) relative to a wild-type winter annual accession when both are grown from seed under the following experimental conditions? The possible flowering time responses are: EARLY, LATE, SAME relative to a wild-type winter annual grown under the environmental conditions listed below.arrow_forwardIn general, larger plants have larger organs. So, one option for increased yields is to breed and grow for the largest size possible. However, there are practical reasons to growing smaller plants. What are some drawbacks to breeding and growing increasingly large plants? List and briefly explain two possible reasons.arrow_forward
- The following graph depicts the relationship between the mean flower depth of Zaluzianskya microsiphon plants and the proboscis length of its long-tonged fly Disa nivea pollinator in a specific region. • Zaluzianskya microsiphon 60- O Disa nivea E 50- 물 40- 30- 20- 10- 10 20 30 40 50 Mean fly proboscis length (mm) Based on this correlation, do you think these two species are coevolving? Why or why not? And based on the geographic mosaic theory, would you consider the region were the plants and flies live a cold or a hot spot? Explain your answer. Mean flower depth (mm)arrow_forwardThe crab spider, Thomisus spectabilis, sits on flowers and preys upon visiting honeybees. Do honeybees distinguish between flowers that have crab spiders and flowers that do not? To test this, Heiling et al. (2003) gave 34 bees a choice between 2 flowers: one with, and one without a crab spider. In 24 of the 34 trials, the bees picked the flower that had the spider. In the other trials, the bees chose the spiderless flower. With these data, carry out the appropriate hypothesis test (one- or two-tailed), using the normal approximation to the binomial distribution to determine Z. For a one-tailed test, use the formula =(1-NORM.DIST(Z,0,1,TRUE) in Excel calculate P. For a two-tailed test, use the formula =2(1-NORM.DIST(Z,0,1,TRUE). State your answer for the value of P to three decimal places, and include the leading zero. Do all of the math in Excel DO NOT round the value of Z. Substitute the cell (e.g. B1) for Z in the formula for P.arrow_forwardMonoecious plants such as corn have either staminate or carpelate flowers. Knowing what you do about the molecular mechanisms of floral development, which of the following might explain the development of single-sex flowers? a. Expression of B-type genes in the presumptive carpel whorl will generate staminate flowers. b. Loss of A-type genes in the presumptive petal whorl will allow C-type and B-type genes to produce stamens instead of petals in that whorl. c. Restricting B-type gene expression to the presumptive petal whorl will generate carpelate flowers. d. All of the choices are correct.arrow_forward
- What is a feasible explanation why there is lesser percentage of germination and growth rate in monggo seeds when sprinkled with water added with 3/4 teaspoon as compared to monggo seed set-ups sprinkled with water?arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothetical gene a plant g&T produces a protein that impacts the stem length. There are two alleles for GT which produces long stem and tea little tea which results in short stint. Which of the following genome types above would have a different pheno type? And what would the phenotype be for the genotype?arrow_forwardIn the experiment conducted to test why individuals in the tree species Fuschsia excorticata retain flowers after they turn red even though the trees pollinate and offer a nectar reward only when flowers are green (Figure attached 10.28 first tested the 'pollinator-attraction' hypothesis that red flowers attract pollinators: once drawn to a tree, pollinators could forage on the green flowers still present, increasing overall pollination efficiency. Please assess the lowercase-Roman-numeral-labelled statements that appear immediately below and click the uppercase-letter-labelled response that appears below and conveys the most accurate information. i. If the pollinator-attraction hypothesis were correct, then green flowers surrounded by red flowers should receive more pollen than should green flowers surrounded by only green flowers. ii. The prediction in statement i could be tested by removing red flowers from some trees, forming one experimental group, and leaving red flowers on…arrow_forward
- What specific RIM is being described by each of the following statements?Explain your answer in each letter _______E) Offspring of hybrid cotton (genus Gossypium) plants either die during early development or grow into unhealthy plants.arrow_forwardThe drooping, bell-like flower Aquilegia canadensis is adapted for cross-pollination. However, if the plant has not been pollinated previously, self-pollination can occur. However, if cross pollination occurs after self-pollination takes place, the pollen from cross pollination reaches the style before the pollen from self-pollination. Using course concepts and vocabulary 1) Provide a reasoning for this phenomenon. 2) Would this adaptation for reproduction be beneficial for the plant?arrow_forwardFigure 19-16 shows the results of a QTL fine-mapping experiment. Which gene would be implicated as controlling fruit weight if the mean fruit weight for each linewas as follows?Line Fruit weight (g)1 181.42 169.33 170.74 171.25 171.46 182.27 180.68 180.79 181.810 169.3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
How to solve genetics probability problems; Author: Shomu's Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Beyond Mendelian Genetics: Complex Patterns of Inheritance; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EmvmBuK-B8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY