
(a)
Interpretation:
Starch should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Starch is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is starch.
Starch consists of many units of monosaccharide as it is a
Thus, starch is classified as polysaccharide.
(b)
Interpretation:
Glucose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glucose.
Glucose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Glucose is obtained by the photosynthesis process and also found in plants.
The structure is:
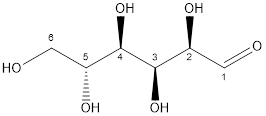
Thus, glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
(c)
Interpretation:
Sucrose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is sucrose.
Sucrose consists of two units of monosaccharide. One fructose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
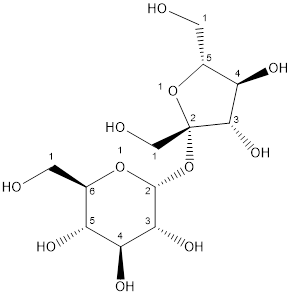
Thus, sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
(d)
Interpretation:
Ribose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is ribose.
Ribose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Ribose consists of an
The structure is:
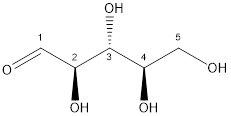
Thus, ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
(e)
Interpretation:
Cellulose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is cellulose.
Cellulose consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
(f)
Interpretation:
Glycogen should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glycogen.
Glycogen consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
(g)
Interpretation:
Fructose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is fructose.
Fructose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule.
The structure is:
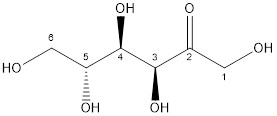
Thus, fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
(h)
Interpretation:
Lactose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is lactose.
Lactose consists of two units of monosaccharide or sugar. One galactose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
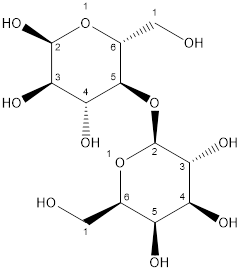
Thus, lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- For the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forwardHow many grams of C are combined with 3.75 ✕ 1023 atoms of H in the compound C5H12?arrow_forwarde. f. CH3O. יון Br NaOCH3 OCH 3 Br H₂Oarrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





