
Interpretation:
The structure of benzene and its unusual stability needs to explained.
Concept introduction:
Benzene is an
Explanation of Solution
The benzene compound looks like a ring of six carbon atoms with three alternate double bonds. The molecular formula of benzene is
Structure of benzene is as follows:
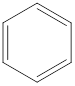
Benzene due to its planar structure and alternate double and single bond in it undergoes resonance (delocalization of electrons) which attributes to its high stability. All the bond lengths are equal and lie in between single and double bond in strength and magnitude unlike to
Resonance in benzene occurs as follows:
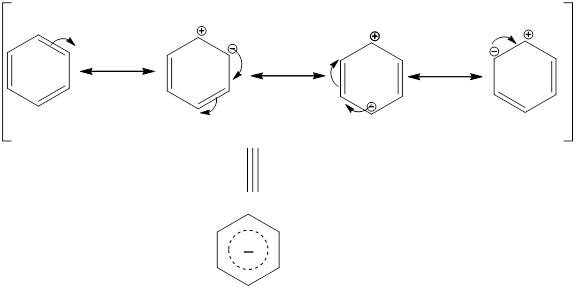
The delocalization of electron or resonance, it does not undergo addition reactions and inert to most of the reactions that an unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon undergo, hence is more stable than it.
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
CHEMISTRY-TEXT
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
Inorganic Chemistry
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





