
(a)
Interpretation: The
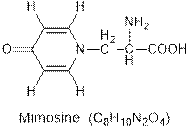
Concept Introduction : Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
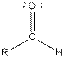
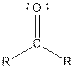
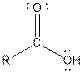
Table given below gives information about some common functional groups:
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Ester | 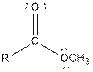 |
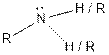 | |
| Alcohol | 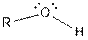 |
(b)
Interpretation: The hybridization of each carbon atom of the given compound mimosine needs to be determined.
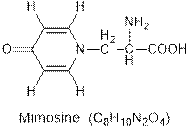
Concept Introduction : Hybridization in chemistry is the mixing of atomic orbitals of the same atom having different energies so that the redistribution of energy takes place and results in the formation of new orbitals of same energy.
(c)
Interpretation: The number of sigma and pi bonds present in the mimosine compound needs to be determined.
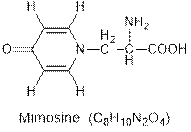
Concept Introduction : Sigma (s) and pi (p) bonds are covalent bonds formed by the overlapping of the atomic orbitals. Sigma (s) bonds are formed from the head to head overlapping of the atomic orbitals while pi (p) bonds are formed from the lateral or sidewise overlapping of the atomic orbitals.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- a. Use bond energies (see Table 3-3) to estimate H for the reaction of two molecules of glycine to form a peptide linkage. b. Would you predict S to favor the formation of peptide linkages between two molecules of glycine? c. Would you predict the formation of proteins to be a spontaneous process?arrow_forward5. Describe the importance of optical isomerism in chiral drugs.arrow_forwardWhich of the following structure(s) is/are non polar? CH3 A. H3C-CH-CH2-CH2 В. НС-СН2-СН, —С—СH C. D. All of the above OA Structure A only OB.Structure B only OC Structure Conly O D.All three structures (A, B. C) are non polararrow_forward
- why are the following molecular formulas impossible? a. CH5 b. C2H7arrow_forwardDescribe the structural differences between DNA and RNA. The monomers in nucleic acids are called nucleotides. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? The compounds adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are called the nucleic acid bases. What structural features in these compounds make them bases? DNA exhibits a double-helical structure. Explain. Describe how the complementary base pairing between the two individual strands of DNA forms the overall double-helical structure. How is complementary base pairing involved in the replication of the DNA molecule during cell division? Describe how protein synthesis occurs. What is a codon, and what is a gene? The deletion of a single base from a DNA molecule can constitute a fatal mutation, whereas substitution of one base for another is often not as serious a mutation. Explain.arrow_forward1. Explain the two ways that methane (CH4) illustrates the need for hybridized molecular bonds. Draw a picture to represent the hybridization of carbon's orbitals and their overlap with hydrogen's. Label each orbital used in bonding with its letters and each bond as sigma or pi.arrow_forward
- 1. Draw three molecules of each compound, i.e. draw the molecules next to one another to visualize IMF.a. Propane, CH 3 CH 2 CH 3b. Heptane, CH 3 (CH 2 ) 5 CH 3c. Propanol, CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OHd. Heptanol, CH 3 (CH 2 ) 6 OH2. For each compound, consider whether or not H-bonding can occur between its molecules. Use a dashed lineto show any H-bonding.3. For each compound, consider whether or not any polar bonds are present.a. Use a different coloured pen to identify any polar bondsb. Which compounds are polar? Which compounds are nonpolar? Explain your reasoning4. Compare your drawings for propanol and heptanol.a. Which compound has stronger dispersion forces? Explain your answer.b. Which compound has a higher boiling point? Explain your answer.5. Compare your drawings of heptane and heptanol.a. Which compound is more polar? Explain your answer.b. Which compound is more soluble in water? Explain your answer Analysis:1. Which compound has higher solubility in water?a. A polar compound or a…arrow_forward4. For the following compound, (1) draw the complete Lewis structure, including any missing hydrogens and nonbonded electron pairs; (2) label all carbons as being sp, sp², or sp' hybridized; (3) identify the functional groups present. carbons, но. CENarrow_forwardIdentify the functional groups in each molecule. . CH₂ CH,CH,CO2 CH;C=H Darvon (analgesic) CH₂N(CH3)2 b. HO CH₂ - တစ CH₂ COOH penicillin G (an antibiotic) ibuprofen (analgesic) .arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements can be used to prove that carbon is tetrahedral? a. CH3Br does not have constitutional isomers. b. CBr4 does not have a dipole moment. c. CH2Br2 does not have constitutional isomers.arrow_forwardAre these chiral centers. Explain why (what are the four different groups attach to it)arrow_forwardHow many chiral centers are present in the molecule below? OH A. 7 B. 5 C. 6 D. 8 O A B C OD Harrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





