
(a)
Interpretation:
Thecomposition of the soap formed by basic hydrolysis of given triacylglycerol needs to be determined.

Concept Introduction:
Lipids are
Triacylglycerol are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
Saponification reaction of triacylglycerol is an alkaline hydrolysis of these triesters that forms sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids (soap) and glycerol as the product. The hydrolysis of triacylglycerol can be done in the presence of aqueous solution of base like
(b)
Interpretation:
The composition of the soap formed by basic hydrolysis of given triacylglycerol needs to be determined.
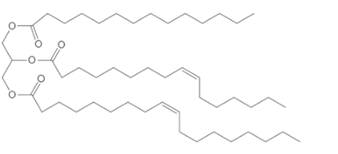
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules which are involved in different biochemical reactions.They are special types of organic molecules which can only identify with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group.
Triacylglycerol are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
Saponification reaction of triacylglycerol is an alkaline hydrolysis of these triesters that forms sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids (soap) and glycerol as the product. The hydrolysis of triacylglycerol can be done in the presence of aqueous solution of base like
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardThe vibrational contribution isa) temperature independent for internal energy and heat capacityb) temperature dependent for internal energy and heat capacityc) temperature independent for heat capacityd) temperature independent for internal energyarrow_forward
- Quantum mechanics. Explain the basis of approximating the summation to an integral in translational motion.arrow_forwardQuantum mechanics. In translational motion, the summation is replaced by an integral when evaluating the partition function. This is correct becausea) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very small compared to the product kTb) the spacing of the translational energy levels is comparable to the product kTc) the spacing of the translational energy levels is very large compared to the product kTarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raiting don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIf the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forwardIf the viscosity of hydrogen gas (at 0oC and 1 atm) is 8.83x10-5 P. If we assume that the molecular sizes are equal, calculate the viscosity of a gas composed of deuterium.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





