
(a)
Interpretation:
To identify the
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of primary amine is done by using phthalimide and primary alkyl halide in presence of hydroxide base. The important point for this reaction is the phthalimide group has only one hydrogen atom which is attached to nitrogen and can be replaced by alkyl group. Therefore, only one alkyl group can be substitued to the nitrogen atom and so only primary amine will form as the product. The general reaction equation is written as,
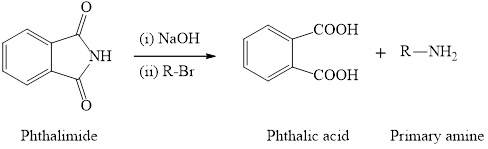
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the alkyl halide used for the preparation of following amines by Gabriel synthesis.
Concept introduction: The synthesis of primary amine is done by using phthalimide and primary alkyl halide in presence of hydroxide base. The important point for this reaction is the phthalimide group has only one hydrogen atom which is attached to nitrogen and can be replaced by alkyl group. Therefore, only one alkyl group can be substitued to the nitrogen atom and so only primary amine will form as the product. The general reaction equation is written as,
(c)
Interpretation:
To identify the alkyl halide used for the preparation of following amines by Gabriel synthesis.
Concept introduction:
The synthesis of primary amine is done by using phthalimide and primary alkyl halide in presence of hydroxide base. The important point for this reaction is the phthalimide group has only one hydrogen atom which is attached to nitrogen and can be replaced by alkyl group. Therefore, only one alkyl group can be substitued to the nitrogen atom and so only primary amine will form as the product. The general reaction equation is written as,
(d)
Interpretation:
To identify the alkyl halide used for the preparation of following amines by Gabriel synthesis.
Concept introduction: The synthesis of primary amine is done by using phthalimide and primary alkyl halide in presence of hydroxide base. The important point for this reaction is the phthalimide group has only one hydrogen atom which is attached to nitrogen and can be replaced by alkyl group. Therefore, only one alkyl group can be substitued to the nitrogen atom and so only primary amine will form as the product. The general reaction equation is written as,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


